Mapping The Land Of Ancient Israel: A Journey Through Time And Place
Mapping the Land of Ancient Israel: A Journey Through Time and Place
Related Articles: Mapping the Land of Ancient Israel: A Journey Through Time and Place
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Mapping the Land of Ancient Israel: A Journey Through Time and Place. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Mapping the Land of Ancient Israel: A Journey Through Time and Place

The land of ancient Israel, nestled between the Mediterranean Sea and the Jordan River, holds a history as rich and complex as its geography. Understanding the map of this region is crucial for comprehending the biblical narratives, the development of Jewish and Christian faiths, and the historical evolution of the Middle East. This article delves into the complexities of ancient Israel’s geography, exploring its physical features, political boundaries, and the significance of its various locations.
The Physical Landscape: A Tapestry of Diversity
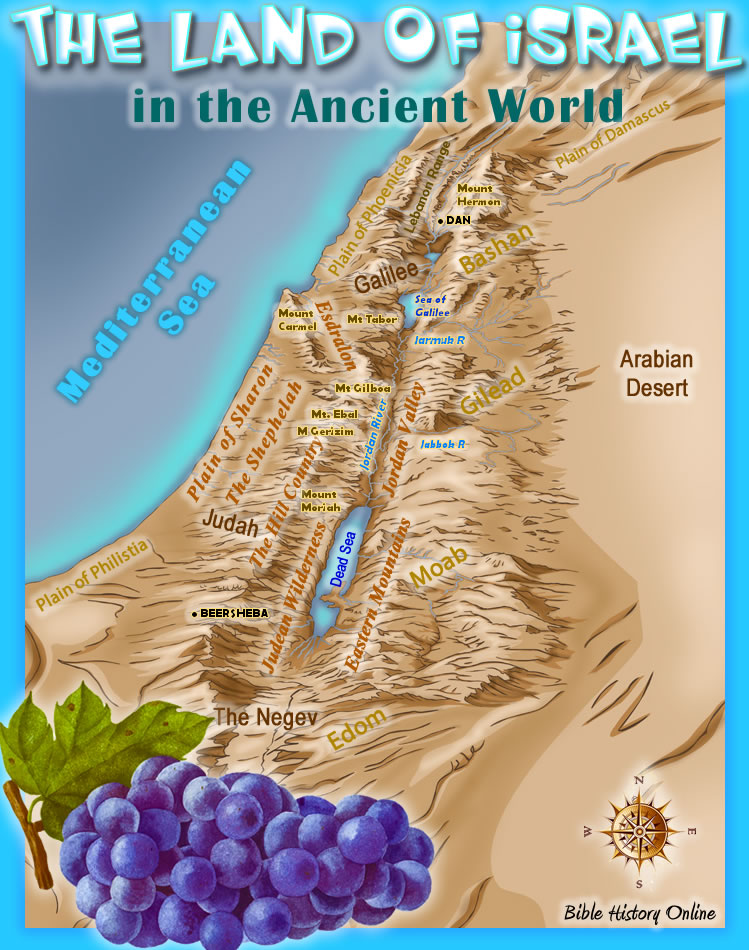
Ancient Israel, encompassing the modern-day territories of Israel, Palestine, Lebanon, and parts of Jordan, is a land of striking contrasts. Its physical landscape, a mosaic of diverse terrains, has played a significant role in shaping its history and culture.
- The Coastal Plain: This fertile strip along the Mediterranean Sea provided access to trade routes and a rich agricultural resource. Cities like Ashkelon, Jaffa, and Tyre flourished on this plain, serving as centers of commerce and cultural exchange.
- The Central Highlands: This mountainous region, dominated by the Judean Hills and the Samaria Mountains, offered natural defenses and fertile valleys, making it ideal for agriculture and settlement. Jerusalem, strategically located on a ridge, became the political and religious heart of the region.
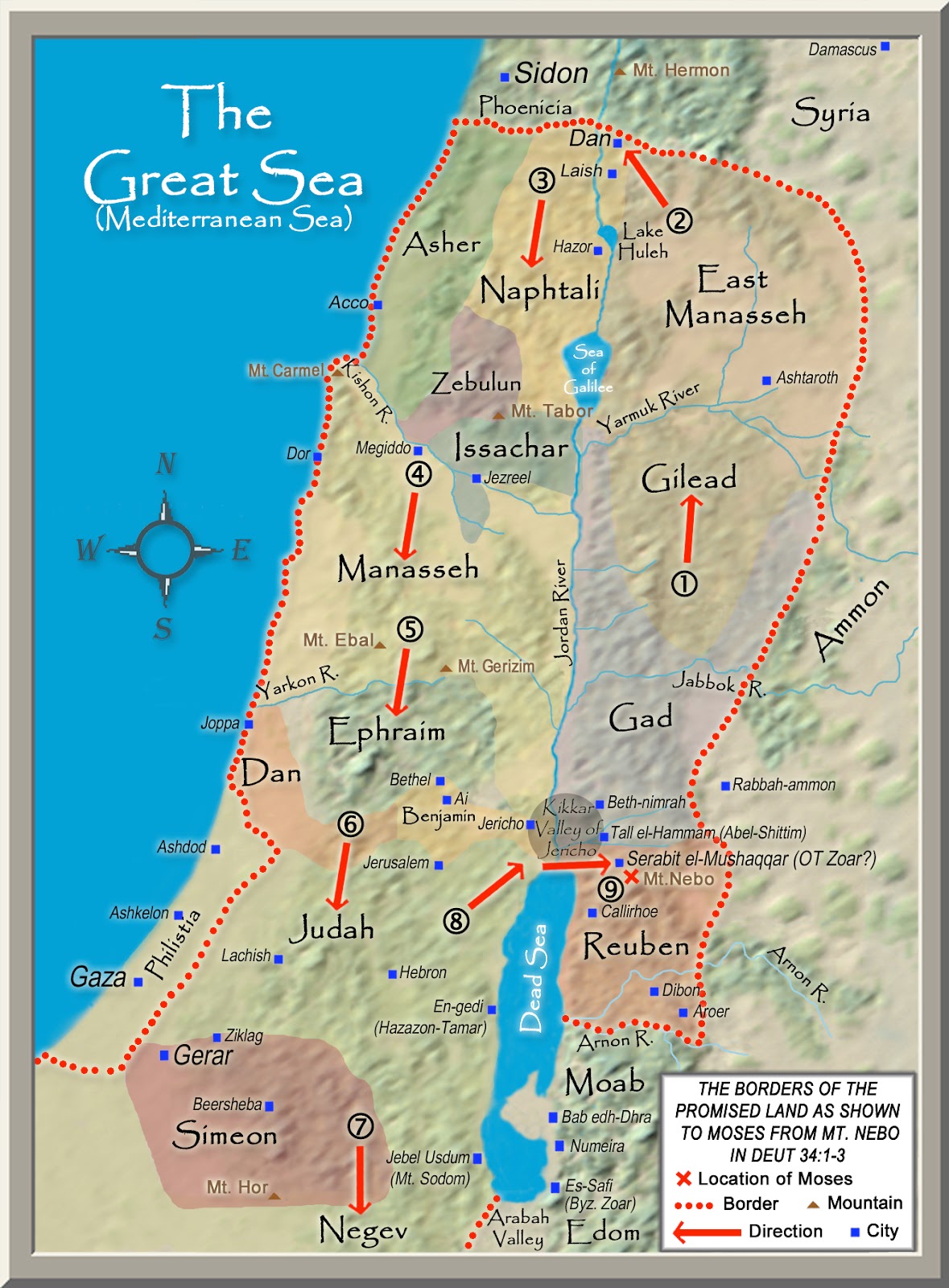
- The Jordan Rift Valley: This dramatic geological depression, stretching from the Sea of Galilee to the Dead Sea, offered a unique ecological environment. The Jordan River, its lifeblood, provided a vital water source and transportation route. The Dead Sea, with its high salt content, provided a valuable resource for salt production.
- The Negev Desert: This arid region, encompassing the southern portion of ancient Israel, presented challenges for settlement. However, its strategic location along trade routes and its rich mineral deposits made it an important area for nomadic tribes and later, for the development of mining and agriculture.
Political Boundaries: A Shifting Mosaic
The political boundaries of ancient Israel were fluid, reflecting the ebb and flow of power throughout its history. Various empires, kingdoms, and tribes held sway over the land, each leaving their mark on its cultural and political landscape.
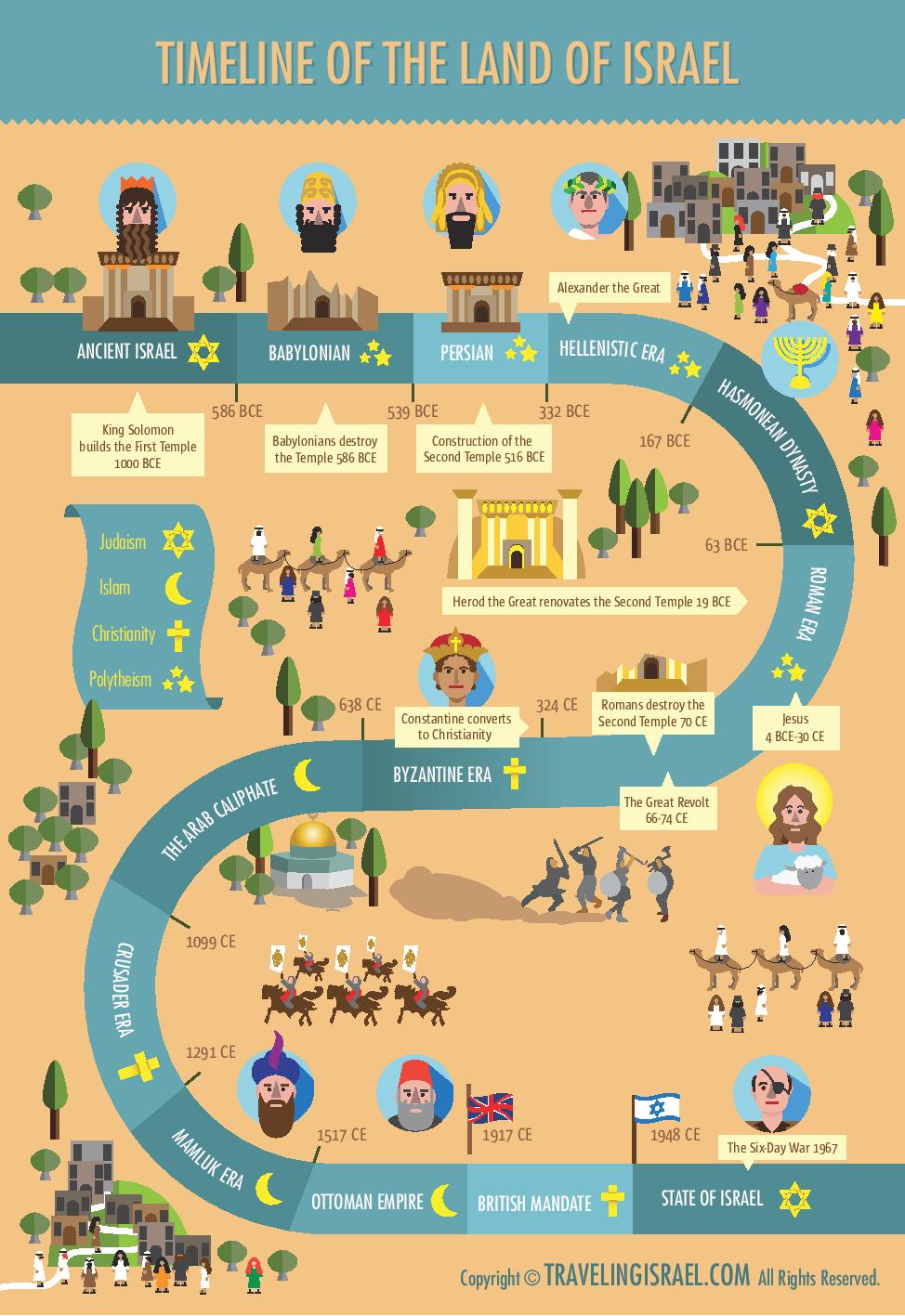
- The Early Kingdoms: The period of the early kingdoms, characterized by the reigns of Saul, David, and Solomon, witnessed the unification of the Israelites under a single rule. The Kingdom of Israel, encompassing the northern region, and the Kingdom of Judah, encompassing the southern region, emerged as distinct entities.
- The Divided Kingdom: Following Solomon’s death, the kingdom split into two, with the northern kingdom falling under the rule of the Israelites and the southern kingdom under the rule of the Judeans. This division had profound implications for the development of the Jewish faith and the cultural identity of the two groups.
- Foreign Rule: The ancient Israelites faced numerous foreign powers throughout their history. The Assyrians, Babylonians, Persians, Greeks, and Romans, among others, conquered and ruled the land, leaving behind their cultural influences and administrative structures.
Key Locations: A Tapestry of History
Each location in ancient Israel holds a story, a testament to the rich and complex history of the land. Understanding these locations is crucial for comprehending the events and narratives that shaped the region.
- Jerusalem: The city’s strategic location, atop a ridge overlooking the Judean Hills, made it a natural choice for a capital city. Its religious significance, as the site of the Temple Mount and the Western Wall, solidified its importance as a focal point for Judaism and later, Christianity.
- Bethlehem: This small town, located south of Jerusalem, holds immense religious significance as the birthplace of Jesus Christ.
- Nazareth: This Galilean town, situated in the fertile Jezreel Valley, is believed to be the place where Jesus spent his childhood and youth.
- Masada: This fortress, perched atop a plateau in the Judean Desert, became a symbol of Jewish resistance against Roman rule. The story of the Masada rebellion, where Jewish zealots held out against Roman forces, has resonated throughout history.
- Caesarea Maritima: This port city, built by Herod the Great, served as an important center of commerce and administration during Roman rule. It played a crucial role in the development of the region and its connection to the Roman world.
Understanding the Map: A Key to Unlocking the Past
The map of ancient Israel serves as a powerful tool for understanding the history, culture, and religion of this fascinating region. It allows us to visualize the physical landscape, trace the paths of ancient trade routes, and locate the sites of important historical events.
- Visualizing the Terrain: The map helps us understand the significance of the physical landscape, its impact on settlement patterns, and its influence on the development of agriculture and trade.
- Tracing the Flow of History: The map allows us to trace the changing political boundaries, the rise and fall of empires, and the migration patterns of various groups.
- Locating Key Sites: The map provides a visual reference for understanding the locations of key religious sites, historical monuments, and archaeological finds.
Benefits of Studying the Map of Ancient Israel:
- Enriching Historical Understanding: The map provides a visual context for understanding the events and narratives of ancient Israel, offering a deeper understanding of the complexities of its history.
- Expanding Religious Knowledge: The map helps us understand the geographical context of religious texts, providing insights into the locations of key events and the development of religious practices.
- Appreciating Cultural Diversity: The map reveals the cultural diversity of the region, highlighting the influence of various civilizations and the interplay of different cultures.
Frequently Asked Questions:
-
What are the major geographical features of ancient Israel?
- Ancient Israel encompasses a diverse landscape, including the Coastal Plain, the Central Highlands, the Jordan Rift Valley, and the Negev Desert.
-
What are the key political divisions of ancient Israel?
- The region was ruled by various empires, kingdoms, and tribes, including the early kingdoms of Israel and Judah, the divided kingdoms, and foreign powers like the Assyrians, Babylonians, and Romans.
-
What are the most important locations in ancient Israel?
- Key locations include Jerusalem, Bethlehem, Nazareth, Masada, and Caesarea Maritima, each holding historical and religious significance.
-
How can studying the map of ancient Israel be beneficial?
- The map provides a visual context for understanding the history, culture, and religion of the region, enriching our knowledge and appreciation of its complexities.
Tips for Studying the Map of Ancient Israel:
- Use a detailed map: Choose a map that includes various geographic features, political boundaries, and key locations.
- Focus on key regions: Pay attention to the Coastal Plain, the Central Highlands, the Jordan Rift Valley, and the Negev Desert, understanding their importance in shaping the region.
- Trace the flow of history: Study the changing political boundaries, the rise and fall of empires, and the impact of foreign rule on the land.
- Locate key sites: Identify the locations of important religious sites, historical monuments, and archaeological finds.
- Connect the map to historical narratives: Use the map to visualize the events and stories described in biblical texts and historical accounts.
Conclusion:
The map of ancient Israel is a powerful tool for understanding the rich tapestry of history, culture, and religion that has shaped this region. It offers a visual framework for comprehending the complexities of the land, the ebb and flow of power, and the significance of its various locations. By studying the map, we can gain a deeper appreciation for the events and narratives that have shaped the land of ancient Israel, providing a window into a world that continues to resonate with us today.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Mapping the Land of Ancient Israel: A Journey Through Time and Place. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!