Mapping The Kingdom: Israel Under King David
Mapping the Kingdom: Israel Under King David
Related Articles: Mapping the Kingdom: Israel Under King David
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Mapping the Kingdom: Israel Under King David. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Mapping the Kingdom: Israel Under King David
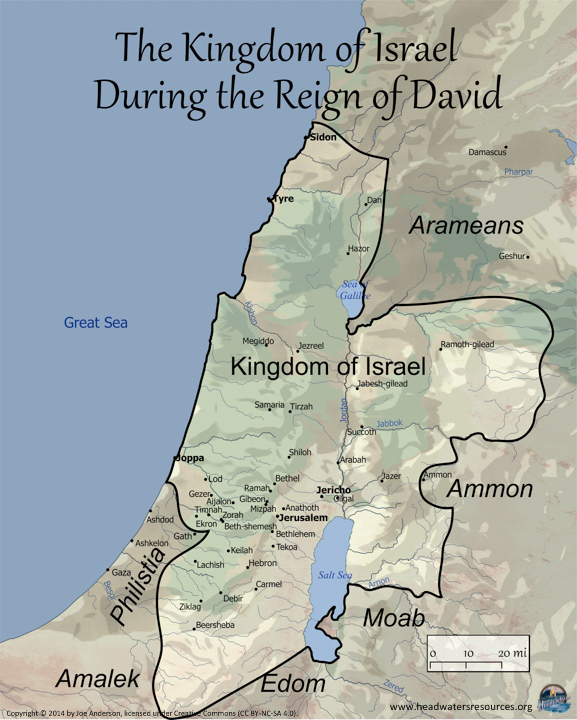
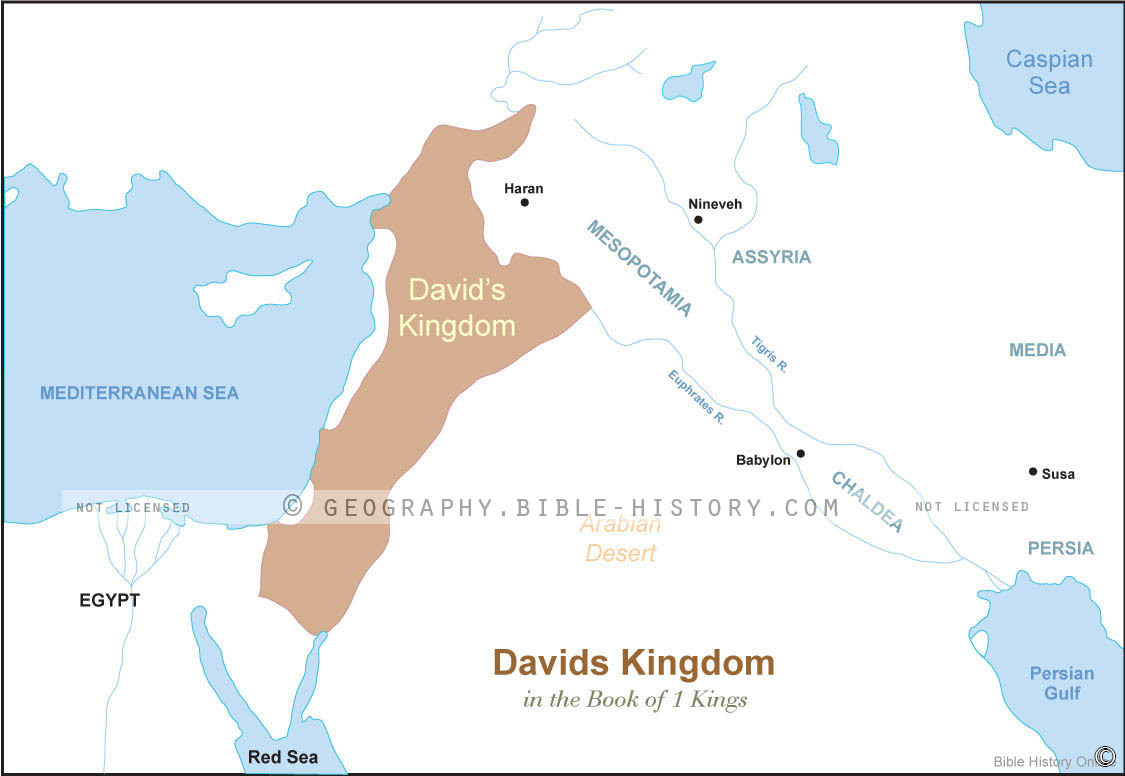
The reign of King David, a pivotal period in Israelite history, witnessed the transformation of a fledgling nation into a formidable regional power. This transformation is inextricably linked to the expansion of David’s kingdom, which stretched far beyond the boundaries of the earlier tribal confederation. Understanding the geography of David’s realm, therefore, offers crucial insights into the political, social, and religious landscape of ancient Israel.
Defining the Boundaries:
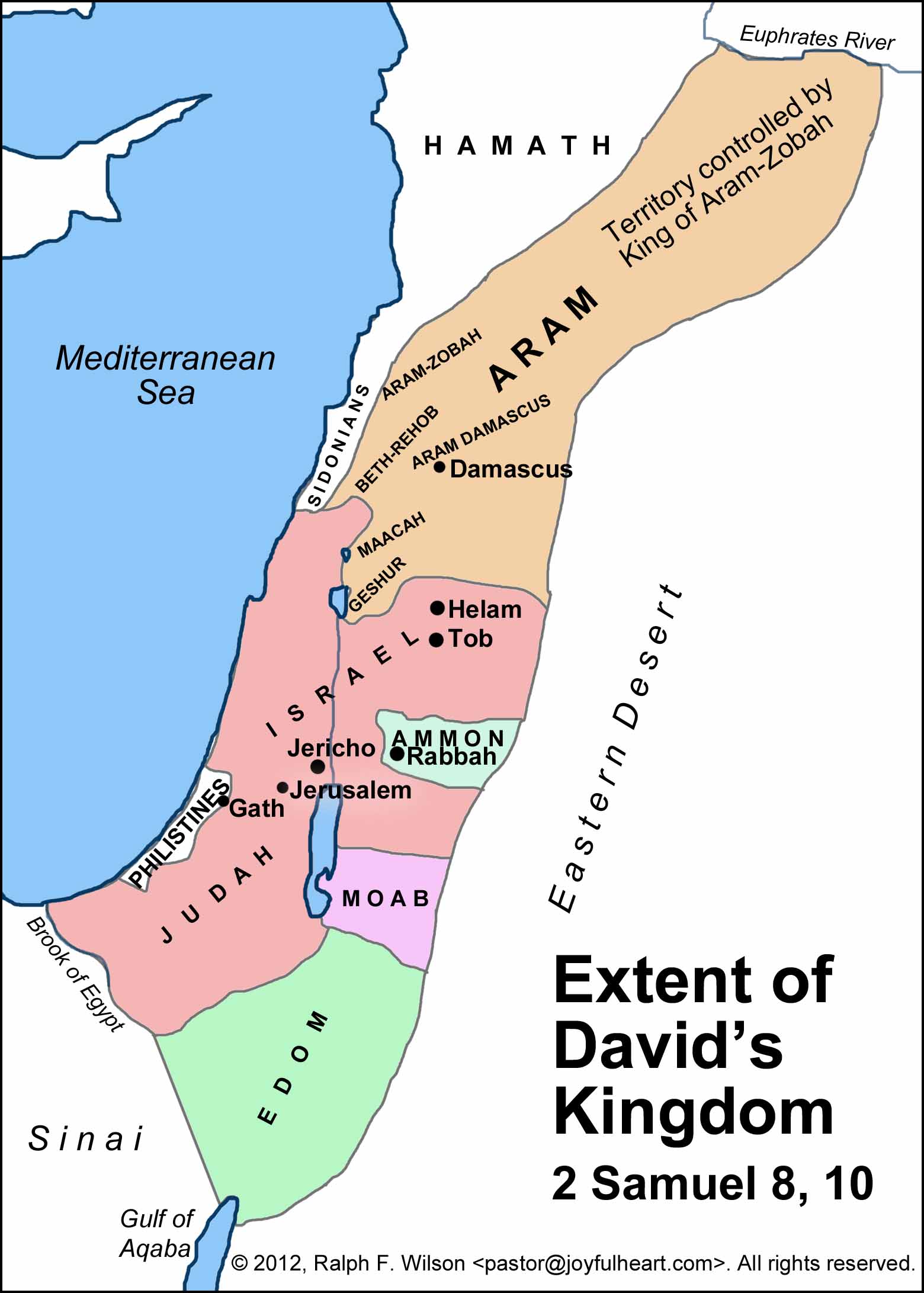
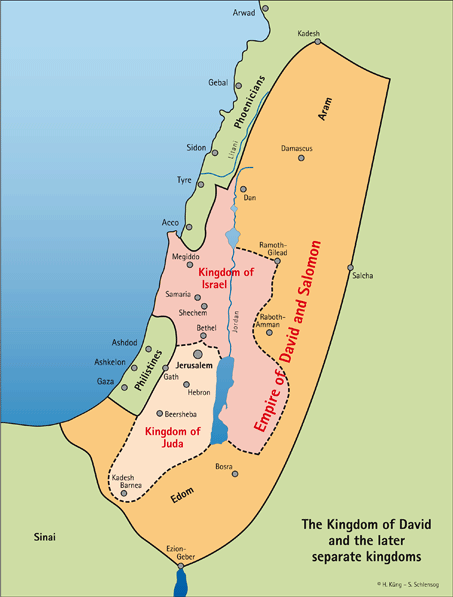
Reconstructing the precise map of David’s kingdom presents a challenging task, as historical records are often fragmented and subject to interpretation. However, by combining textual evidence from the Bible, archaeological findings, and insights from related historical sources, scholars have pieced together a general picture of the kingdom’s extent.
The Core Territories:
The heart of David’s kingdom encompassed the land traditionally associated with the tribes of Judah and Benjamin. This region, known as Judea, stretched from the southern Negev desert in the south to the northern borders of Samaria, encompassing the cities of Hebron, Jerusalem, Bethlehem, and Jericho.
Expansion into the North:
David’s military successes led to the incorporation of territories previously held by the Philistines and other Canaanite city-states. This expansion extended northwards, incorporating the coastal plain, the Shephelah region, and the fertile valleys of the Jezreel and Sharon. Key cities acquired during this period include Gath, Ashdod, Ekron, and Megiddo.
Beyond the Jordan:
David’s influence extended beyond the Jordan River, incorporating the Transjordan region, known as Gilead. This region, strategically important for its pasturelands and access to trade routes, included the cities of Rabbah (modern Amman), Mahanaim, and Edrei.
The Significance of David’s Kingdom:
The geographical expanse of David’s kingdom had profound implications for the development of Israelite society and culture:
- Political Unity: The consolidation of disparate tribes under David’s rule fostered a sense of national unity and identity, laying the foundation for the future monarchy.
- Economic Prosperity: The control of key trade routes and agricultural regions facilitated economic growth and prosperity, allowing for the development of infrastructure and social institutions.
- Military Strength: The expansion of David’s kingdom established Israel as a significant military force in the region, capable of defending its interests and challenging regional powers.
- Religious Impact: The establishment of Jerusalem as the capital city and the centralization of religious practices at the Temple Mount contributed to the development of a unified religious identity and the rise of the Jerusalem cult.
Challenges and Limitations:
Despite its impressive territorial gains, David’s kingdom faced challenges and limitations:
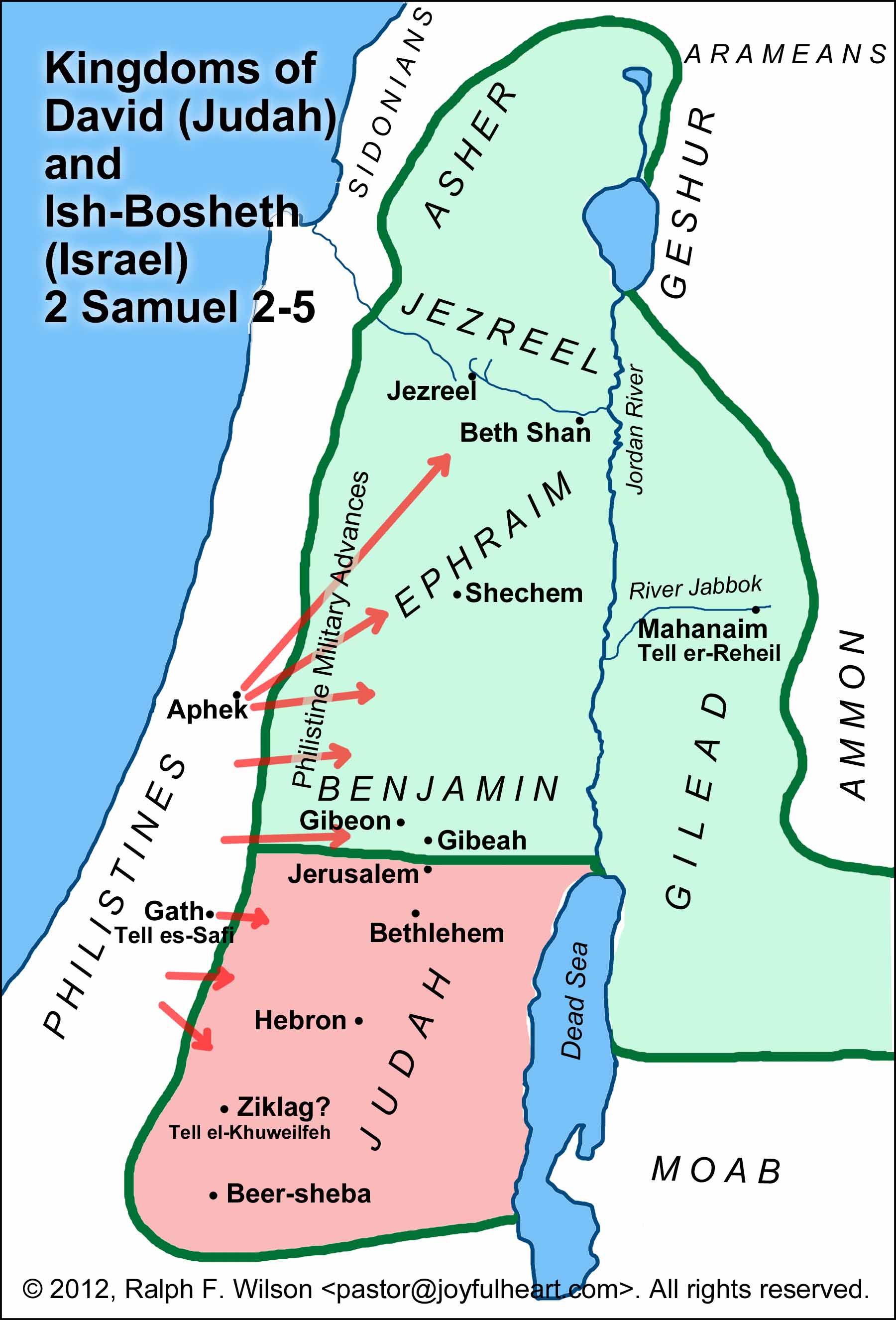
- Internal Divisions: The kingdom’s vast size and diverse population presented challenges in maintaining internal cohesion and stability. The threat of rebellions and internal conflicts remained a constant concern.
- Regional Rivalries: David’s expansionist policies inevitably led to conflicts with neighboring kingdoms, particularly the Philistines and the Arameans, creating a constant state of tension and warfare.
- Succession Crisis: The question of David’s successor remained unresolved, setting the stage for a power struggle between his sons, which ultimately led to the division of the kingdom.
FAQs on the Map of Israel During King David’s Reign:
Q: What is the evidence for the geographical extent of David’s kingdom?
A: Evidence comes from various sources, including:
- Biblical Texts: The Books of Samuel, Kings, and Chronicles provide accounts of David’s conquests and the boundaries of his kingdom.
- Archaeological Discoveries: Excavations at sites like Megiddo, Gath, and Rabbah have revealed evidence of Israelite presence and influence during David’s reign.
- Ancient Inscriptions: Inscriptions from neighboring kingdoms, such as the Mesha Stele, provide insights into the political landscape and the interactions between Israel and its neighbors.
Q: How did David’s kingdom differ from the earlier tribal confederation?
A: David’s kingdom was characterized by a centralized authority and a more unified political structure compared to the earlier tribal confederation. This central authority allowed for greater military coordination, economic development, and cultural integration.
Q: What was the significance of Jerusalem as the capital of David’s kingdom?
A: Jerusalem’s strategic location, its relative neutrality among the tribes, and its religious significance made it an ideal choice for the capital. The city became a symbol of national unity, a center of religious worship, and a base for the king’s administration.
Q: What were the long-term consequences of David’s kingdom for the history of Israel?
A: David’s reign laid the foundation for the future monarchy and the development of a unified Israelite identity. His conquests and territorial expansion established Israel as a major regional power, while his cultural and religious initiatives contributed to the formation of a distinct Israelite culture.
Tips for Understanding the Map of Israel During King David’s Reign:
- Visualize the Geographical Context: Use maps and historical atlases to visualize the terrain, key cities, and trade routes within David’s kingdom.
- Consider the Historical Context: Understand the political and military circumstances that shaped the boundaries of David’s kingdom.
- Examine the Archaeological Evidence: Explore the archaeological findings that support or challenge the historical accounts of David’s reign.
- Compare Different Sources: Analyze the different historical sources, including biblical texts, inscriptions, and archaeological evidence, to gain a comprehensive understanding of the map.
Conclusion:
The map of Israel during King David’s reign provides a tangible illustration of a pivotal period in Israelite history. The expansion of David’s kingdom, driven by military prowess and political acumen, transformed a loose tribal confederation into a powerful and unified nation. This territorial expansion had profound implications for the development of Israelite culture, religion, and society, shaping the course of the nation’s history for centuries to come. While the precise boundaries of David’s kingdom remain subject to scholarly debate, the evidence suggests a significant expansion beyond the earlier tribal territories, laying the foundation for the future kingdoms of Israel and Judah.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Mapping the Kingdom: Israel Under King David. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!