Mapping Indonesia’s Place In The World: A Geographic And Strategic Perspective
Mapping Indonesia’s Place in the World: A Geographic and Strategic Perspective
Related Articles: Mapping Indonesia’s Place in the World: A Geographic and Strategic Perspective
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Mapping Indonesia’s Place in the World: A Geographic and Strategic Perspective. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Mapping Indonesia’s Place in the World: A Geographic and Strategic Perspective
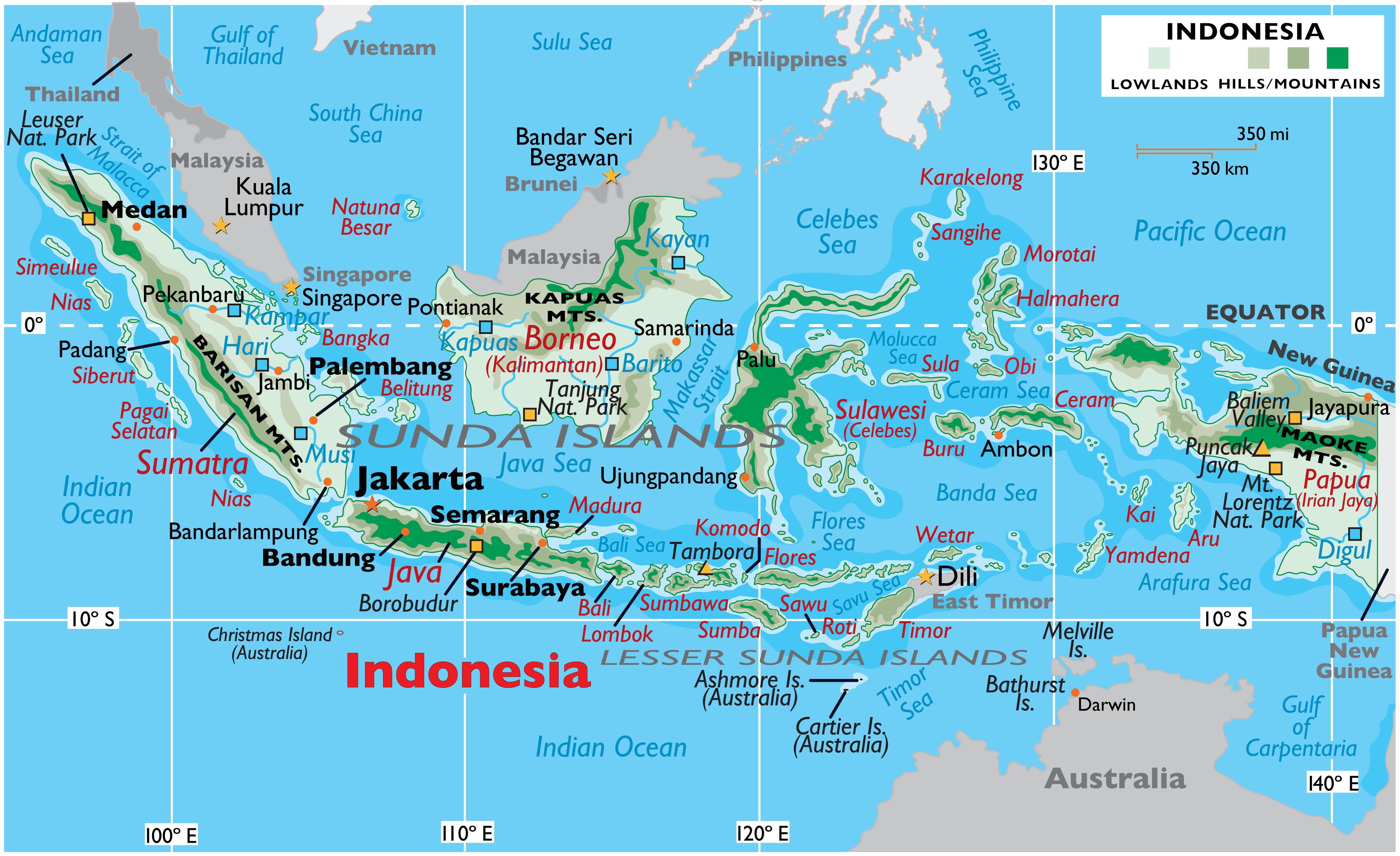
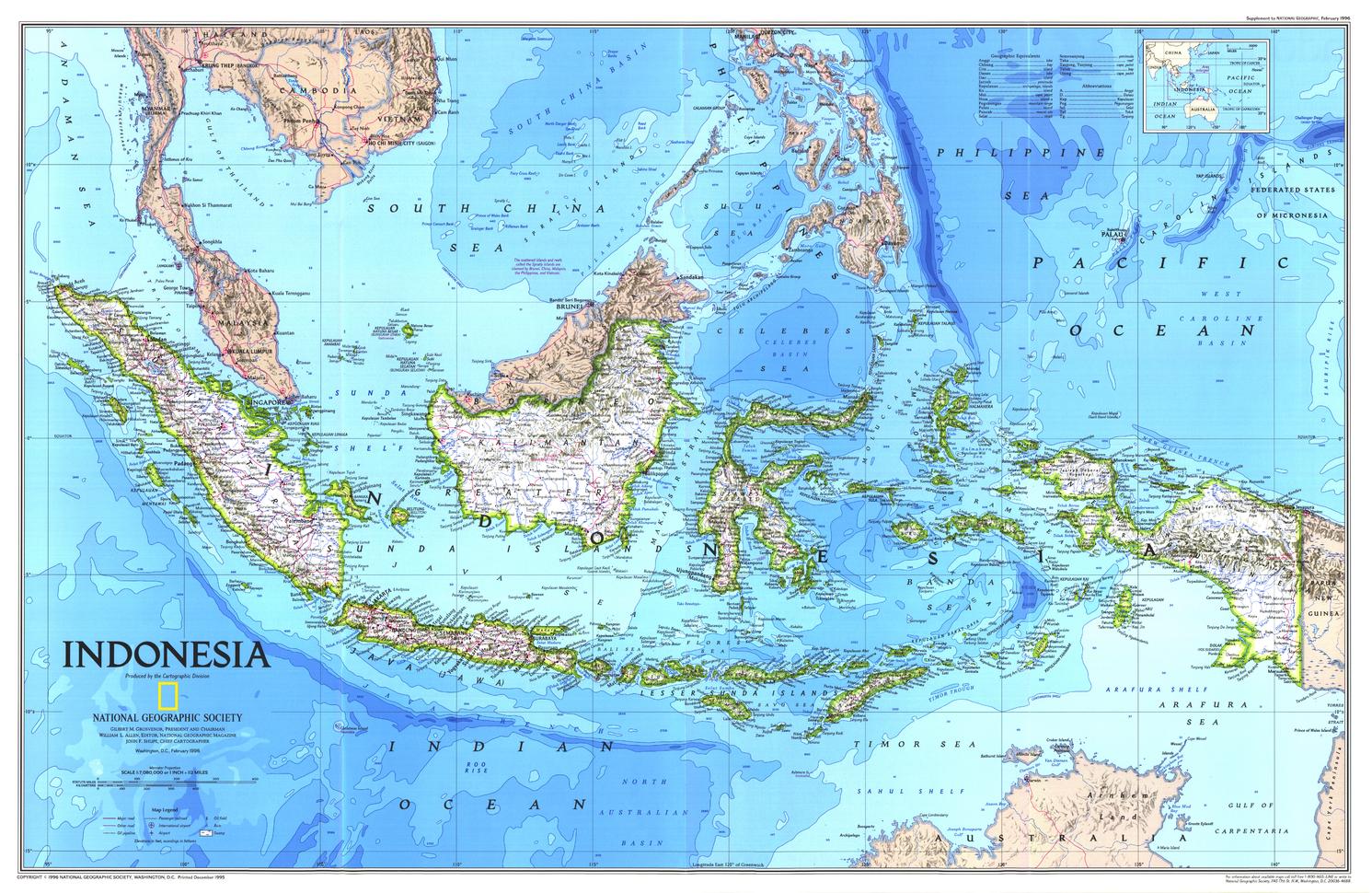
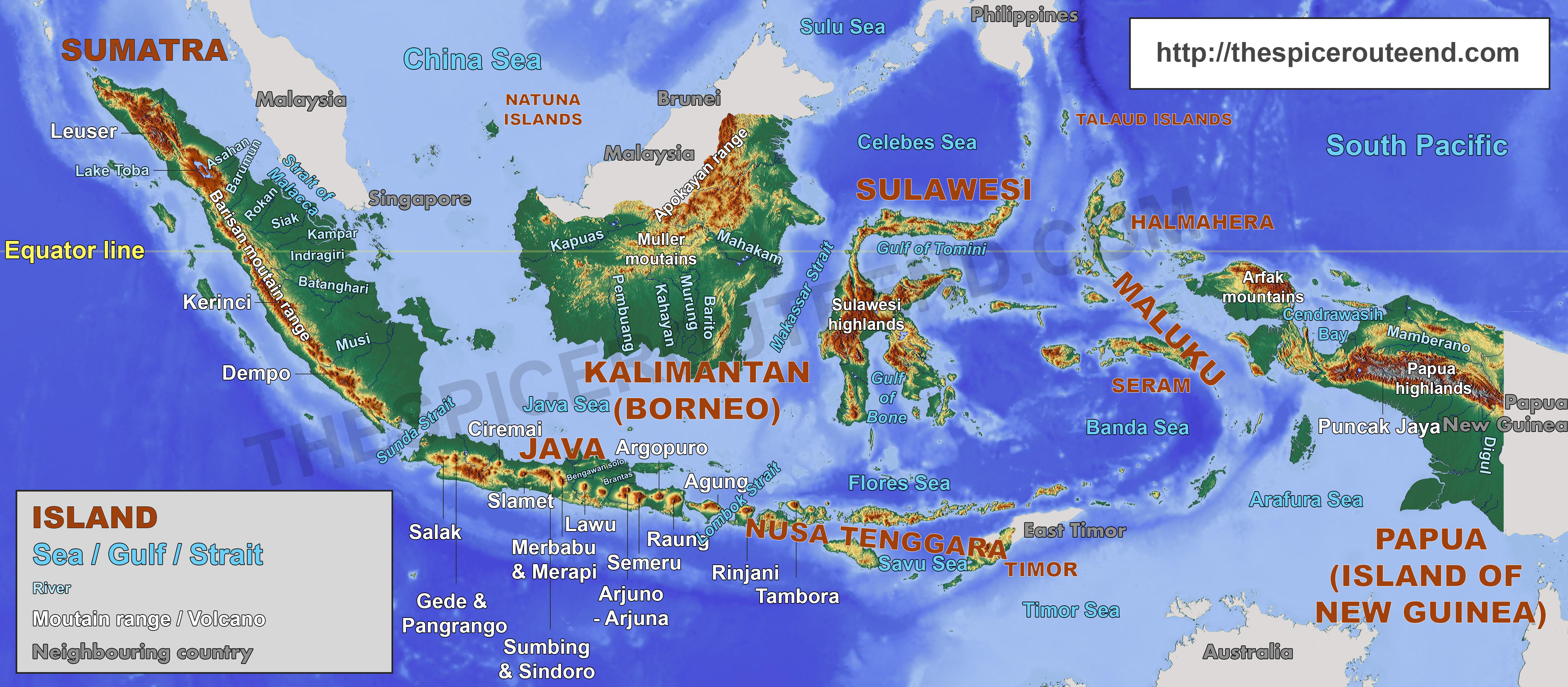
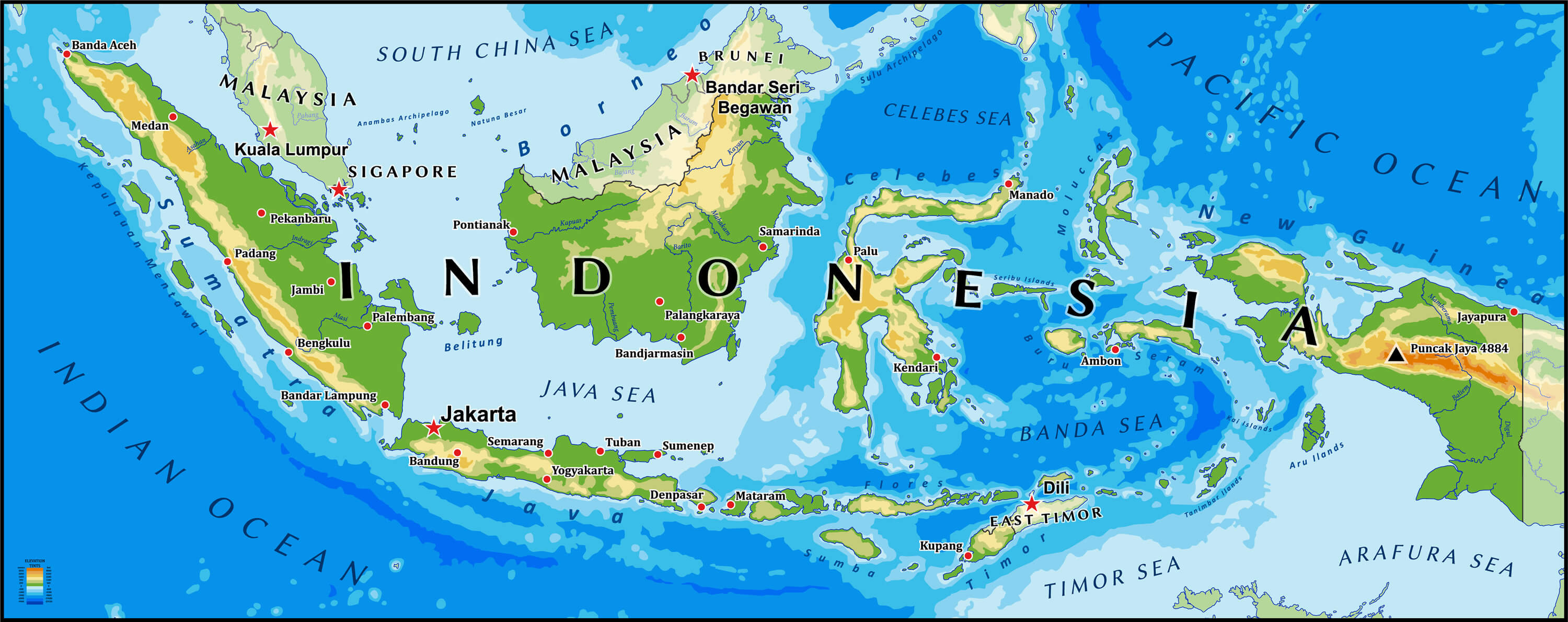
Indonesia, the world’s largest archipelago nation, is a tapestry of diverse cultures, landscapes, and economies. Its geographic position, encompassing over 17,000 islands stretching across the equator, has profoundly shaped its history, development, and role in the global arena. Understanding Indonesia’s place in the world requires a multi-dimensional approach, exploring its physical geography, economic significance, geopolitical influence, and cultural richness.
A Nation of Islands:
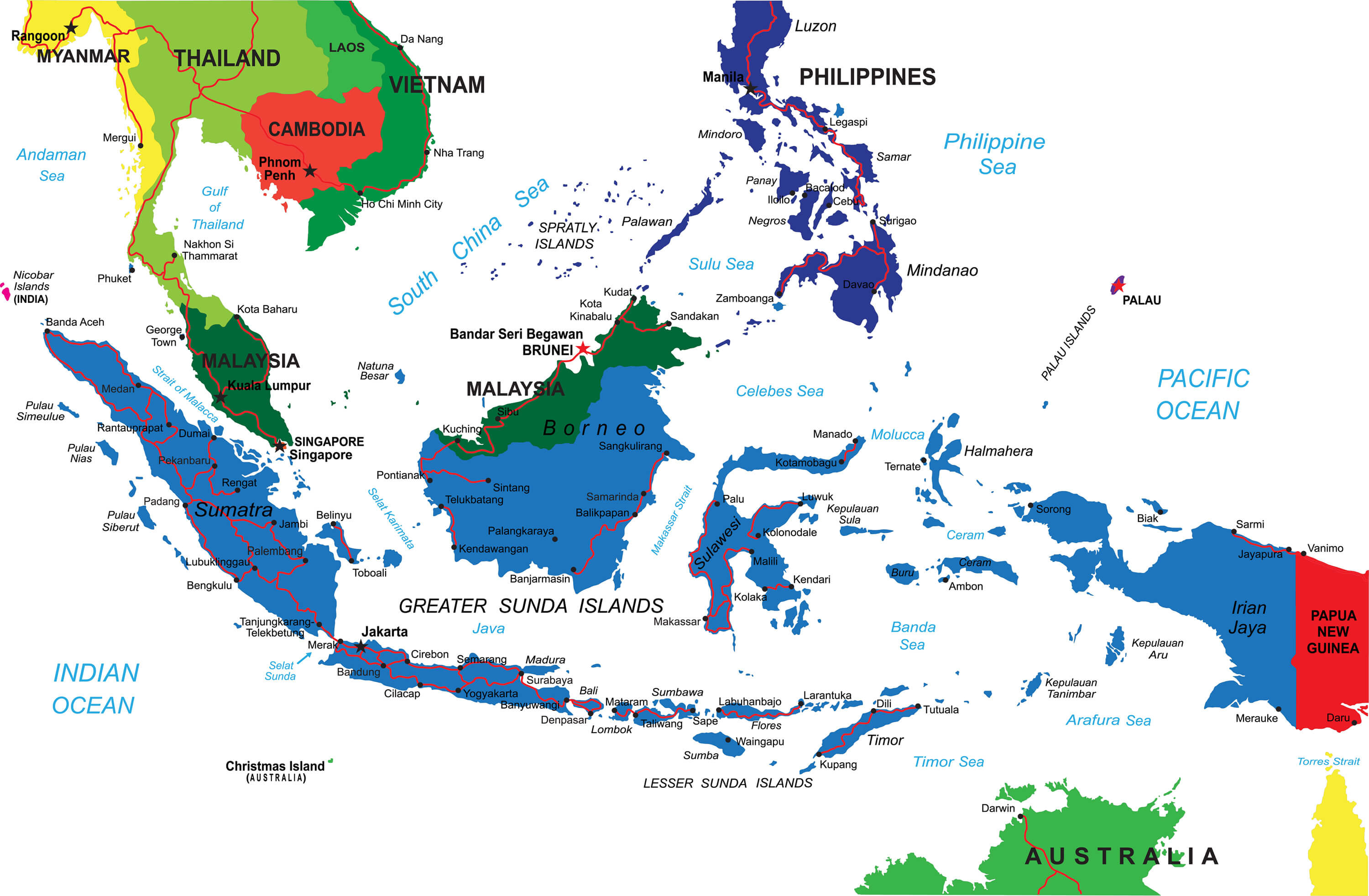
Indonesia’s geography is its defining characteristic. Located in Southeast Asia, it sits astride the crossroads of major maritime trade routes, connecting the Indian and Pacific Oceans. This strategic location has historically fostered trade and cultural exchange, making Indonesia a melting pot of diverse ethnicities and religions.
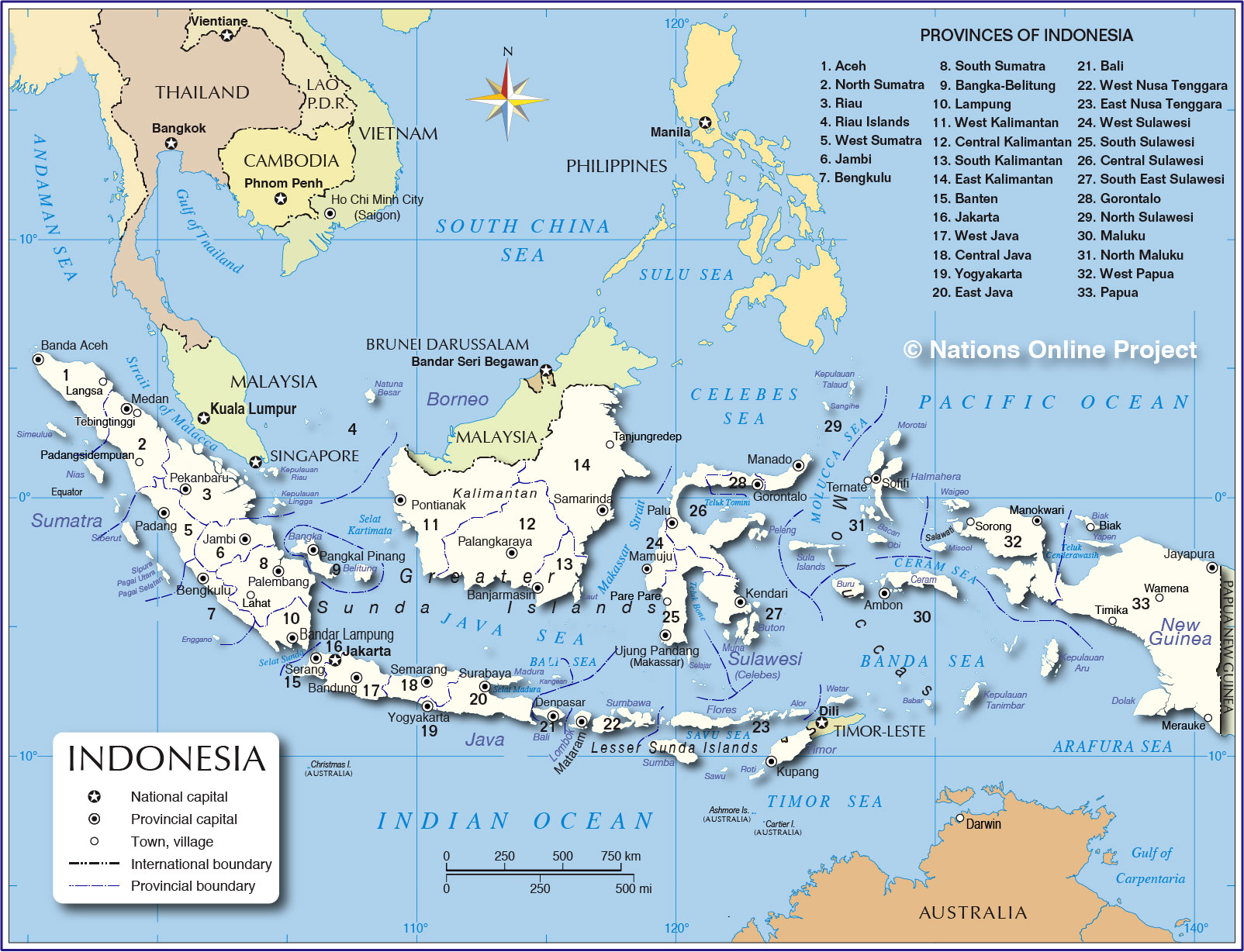
The archipelago is divided into five major islands: Sumatra, Java, Kalimantan (Borneo), Sulawesi, and Papua. Each island boasts unique ecosystems, from the lush rainforests of Borneo to the volcanic landscapes of Java, contributing to Indonesia’s immense biodiversity. The vast expanse of the archipelago, coupled with its mountainous terrain and numerous rivers, presents both opportunities and challenges for transportation, infrastructure development, and resource management.
Economic Powerhouse in the Making:
Indonesia’s vast natural resources, including oil, gas, coal, tin, and timber, have fueled its economic growth. The country is a major producer of palm oil, rubber, and coffee, contributing significantly to global agricultural markets. Its growing manufacturing sector, particularly in automotive, electronics, and textiles, is attracting foreign investment and driving industrialization.
Despite significant progress, Indonesia faces challenges in addressing economic disparities, improving infrastructure, and fostering sustainable development. The country is actively pursuing economic diversification, promoting innovation, and investing in education and human capital to enhance its global competitiveness.
Geopolitical Significance and Regional Leadership:
Indonesia’s strategic location and growing economic power have made it a pivotal player in the Asia-Pacific region. It is a member of the Association of Southeast Asian Nations (ASEAN), playing a key role in promoting regional integration and cooperation.
Indonesia actively engages in international forums, advocating for peace, stability, and sustainable development. Its diplomatic efforts focus on promoting multilateralism, fostering dialogue, and addressing global challenges like climate change and terrorism.
Cultural Tapestry and Global Influence:
Indonesia’s rich cultural heritage is a testament to its diverse history and interactions with the world. The country is home to numerous indigenous languages, traditions, and artistic expressions. Its vibrant music, dance, and culinary arts have captivated audiences worldwide.
Indonesia’s cultural influence is felt globally through its popular music, movies, and television shows. Its cuisine, with its unique blend of flavors and spices, has gained international recognition, attracting food enthusiasts from around the world.
Challenges and Opportunities:
While Indonesia enjoys considerable advantages, it also faces numerous challenges. These include:
- Natural Disasters: Indonesia is prone to earthquakes, volcanic eruptions, tsunamis, and floods, posing significant risks to its infrastructure and population.
- Environmental Degradation: Deforestation, pollution, and unsustainable resource extraction pose threats to the country’s biodiversity and natural resources.
- Social Inequality: Despite economic growth, income disparities persist, leading to social tensions and challenges in providing equitable access to education, healthcare, and other essential services.
- Political Stability: Indonesia has made significant strides in consolidating democracy, but political polarization and corruption remain concerns.
Navigating the Future:
Indonesia is at a critical juncture in its development. It has the potential to become a major economic and political power in the 21st century. However, realizing this potential requires addressing its challenges effectively and strategically.
The Indonesian government is actively pursuing policies to promote sustainable development, reduce poverty, improve infrastructure, and enhance its global competitiveness. It is also strengthening its regional and international partnerships to address shared challenges and seize opportunities.
FAQs about Indonesia’s Place in the World:
1. What are the key factors that contribute to Indonesia’s strategic location?
Indonesia’s location at the crossroads of major maritime trade routes connecting the Indian and Pacific Oceans, as well as its proximity to major economies like China, Japan, and India, make it a strategically important location.
2. How does Indonesia’s geography impact its development?
Indonesia’s archipelago nature presents challenges in terms of transportation, infrastructure development, and resource management. However, its diverse ecosystems and natural resources offer significant opportunities for economic growth and sustainable development.
3. What are the main economic sectors driving Indonesia’s growth?
Indonesia’s economy is fueled by its natural resources, agriculture, manufacturing, and tourism. The country is a major producer of palm oil, rubber, and coffee, and is attracting foreign investment in automotive, electronics, and textiles.
4. How does Indonesia contribute to regional stability and cooperation?
Indonesia plays a crucial role in the Association of Southeast Asian Nations (ASEAN), promoting regional integration and cooperation. It actively engages in international forums, advocating for peace, stability, and sustainable development.
5. What are the key challenges facing Indonesia’s future development?
Indonesia faces challenges in addressing natural disasters, environmental degradation, social inequality, and political stability. It must navigate these challenges strategically to realize its full potential.
Tips for Understanding Indonesia’s Place in the World:
- Explore Indonesia’s diverse cultures: Learn about the country’s indigenous languages, traditions, and artistic expressions.
- Engage with Indonesian media: Follow Indonesian news outlets and social media to gain insights into current events and perspectives.
- Travel to Indonesia: Experience the country’s diverse landscapes, cultures, and cuisine firsthand.
- Support Indonesian businesses and organizations: Contribute to the country’s economic and social development.
- Advocate for sustainable practices: Promote environmental conservation and responsible tourism.
Conclusion:
Indonesia’s place in the world is multifaceted and dynamic. Its strategic location, rich cultural heritage, and growing economic power make it a significant player in the global arena. The country faces challenges, but with its commitment to sustainable development, regional cooperation, and global engagement, Indonesia is poised to play an even greater role in shaping the future. Understanding Indonesia’s unique position in the world is crucial for fostering international collaboration and achieving a more peaceful, prosperous, and sustainable future for all.


Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Mapping Indonesia’s Place in the World: A Geographic and Strategic Perspective. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!