Mapping India: A Journey Through Time, Terrain, And Transformation
Mapping India: A Journey Through Time, Terrain, and Transformation
Related Articles: Mapping India: A Journey Through Time, Terrain, and Transformation
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Mapping India: A Journey Through Time, Terrain, and Transformation. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Mapping India: A Journey Through Time, Terrain, and Transformation

The Indian map, a vibrant tapestry of diverse landscapes, cultural nuances, and historical narratives, is far more than a mere geographical representation. It is a living document, constantly evolving with the pulse of a nation, reflecting its triumphs and challenges, and serving as a crucial tool for understanding its past, present, and future.
A Historical Perspective: Tracing the Evolution of India’s Map
The mapping of India has a long and fascinating history, intertwined with the country’s political and cultural evolution. Early maps, crafted by ancient civilizations, often reflected a blend of geographical accuracy and mythological narratives. The Indus Valley Civilization, known for its sophisticated urban planning, left behind evidence of rudimentary maps etched on seals. Later, ancient Indian texts like the Puranas and the Mahabharata contained detailed descriptions of geographical features, including rivers, mountains, and kingdoms.
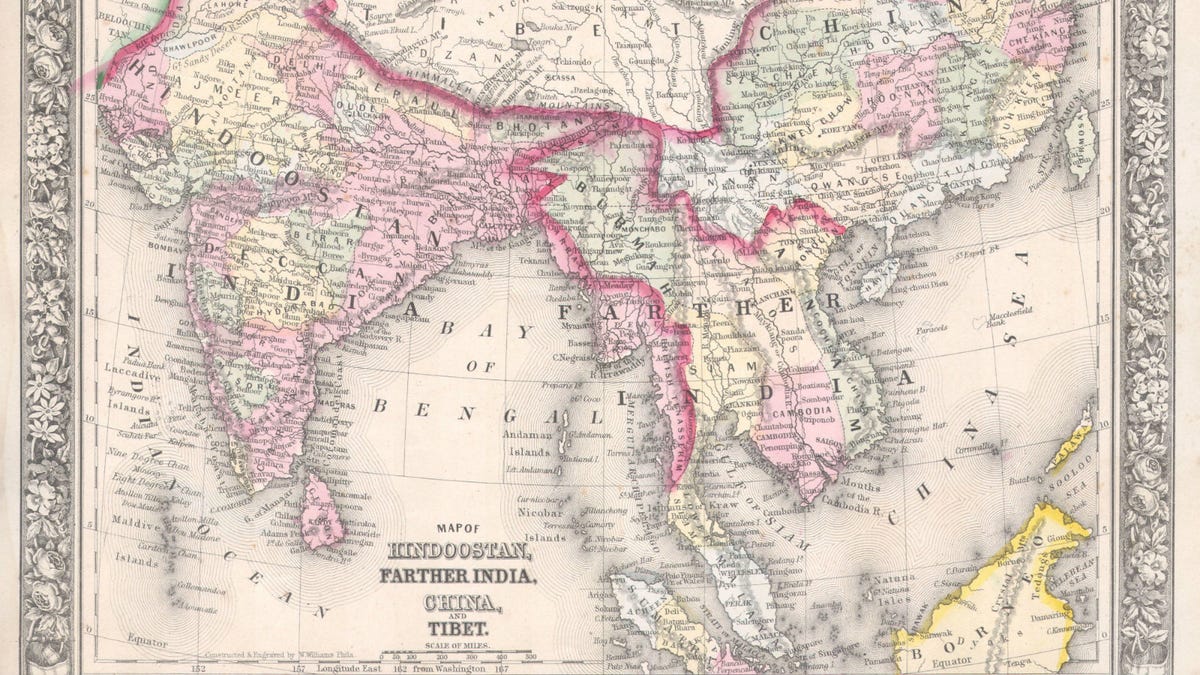
The arrival of foreign powers, particularly the Greeks and Romans, brought about a new era of mapmaking. Ptolemy, a renowned Greek cartographer, produced a map of India in the 2nd century AD, incorporating information gleaned from travelers and traders. During the medieval period, Islamic scholars and travelers like Al-Biruni made significant contributions to cartography, providing valuable insights into the geography and culture of the subcontinent.
The arrival of European powers, particularly the British, ushered in a period of systematic mapping. The British East India Company, seeking to consolidate its control over the region, commissioned detailed surveys and maps. The Great Trigonometrical Survey of India, launched in 1802, was a monumental undertaking that spanned over a century, resulting in the creation of highly accurate maps that laid the foundation for modern cartography in India.
Beyond Borders: Understanding the Complexities of the Indian Map
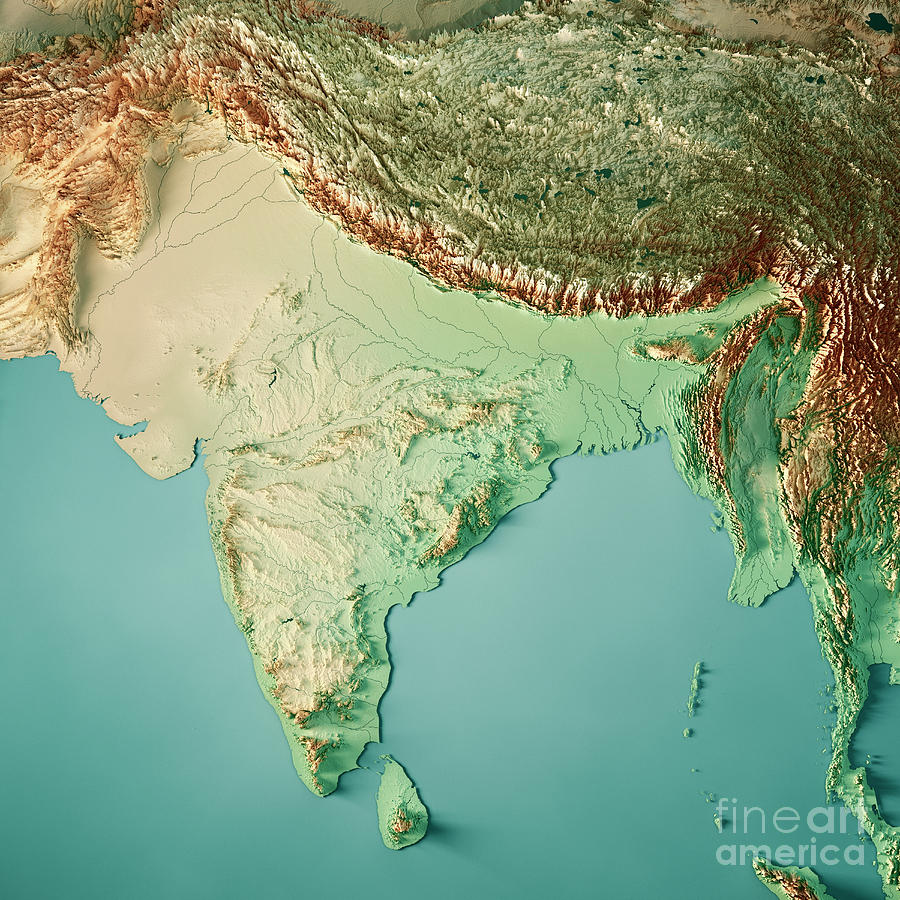
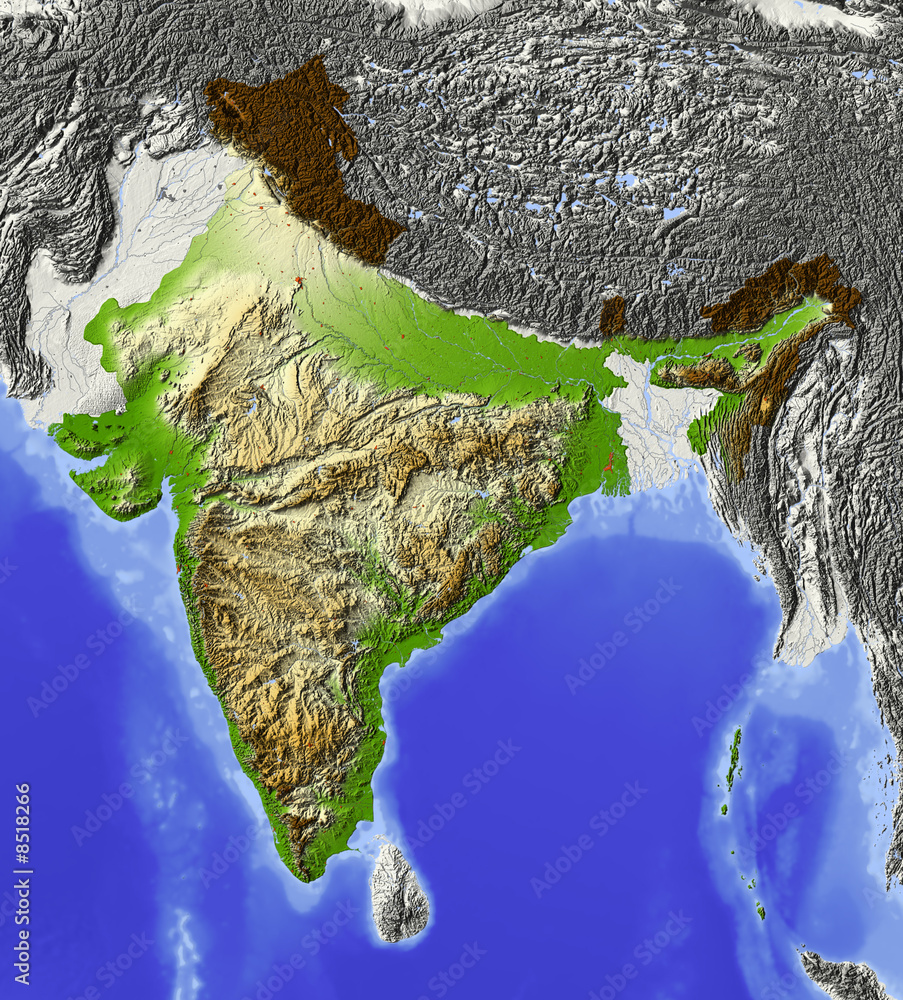
The Indian map is not simply a static representation of borders; it is a dynamic portrayal of a country grappling with a multitude of complexities. From the snow-capped peaks of the Himalayas to the vast expanse of the Indian Ocean, the country’s topography is as diverse as its people. The map reveals the intricate network of rivers, including the mighty Ganges and Brahmaputra, which sustain life and connect communities. It highlights the fertile plains of the Indo-Gangetic basin, a cradle of civilization, and the rugged terrain of the Deccan Plateau, a land of ancient kingdoms and rich cultural heritage.
The Indian map also reflects the country’s political and administrative divisions. It showcases the 28 states and 8 union territories, each with its own unique identity, language, and cultural traditions. The map illuminates the intricate tapestry of religious and linguistic diversity, highlighting the presence of numerous religions, including Hinduism, Islam, Sikhism, Christianity, and Buddhism, and a multitude of languages and dialects.
A Tool for Development and Progress: The Significance of Mapping in Modern India
The Indian map is not merely a historical relic; it is a vital tool for development and progress. It plays a crucial role in planning and executing infrastructure projects, including roads, railways, and communication networks. Mapping is essential for resource management, identifying areas with potential for agriculture, mining, and other economic activities. It also helps in disaster management, enabling authorities to assess the impact of natural calamities and deploy resources effectively.
In the digital age, mapping has taken on new dimensions. Geographic Information Systems (GIS) and remote sensing technologies are revolutionizing the way we understand and interact with the world. These tools provide real-time data, enabling us to monitor environmental changes, track urban growth, and manage resources more efficiently.
Navigating the Future: The Role of Mapping in Shaping India’s Destiny
As India continues its journey towards becoming a global power, the role of mapping becomes even more critical. It will be instrumental in achieving sustainable development goals, promoting inclusive growth, and addressing the challenges posed by climate change. Accurate and up-to-date maps are crucial for planning smart cities, managing water resources, and ensuring food security.
Mapping will also play a vital role in fostering regional integration and connectivity. By understanding the geographical and cultural landscape, India can strengthen its ties with its neighbors and contribute to the development of the entire South Asian region.
FAQs about Mapping India:
1. What are the main geographical features of India?
India is a land of diverse geographical features, including the Himalayas, the Indo-Gangetic Plain, the Deccan Plateau, and the Indian Ocean coastline. The country is also home to numerous rivers, including the Ganges, Brahmaputra, and Indus.
2. How has the Indian map evolved over time?
The map of India has evolved significantly over time, reflecting changes in political boundaries, administrative divisions, and the understanding of the country’s geography. Early maps were often inaccurate and based on limited information, while modern maps are highly detailed and accurate.
3. What are the benefits of mapping in India?
Mapping plays a crucial role in development, resource management, disaster management, and planning infrastructure projects. It also helps in understanding the country’s cultural diversity and promoting regional integration.
4. What are some of the challenges faced in mapping India?
Challenges in mapping India include the vast size and diverse terrain of the country, the need for accurate and up-to-date data, and the complexities of managing a rapidly changing landscape.
5. How can mapping contribute to India’s future?
Mapping will play a crucial role in achieving sustainable development goals, promoting inclusive growth, managing climate change, and fostering regional integration.
Tips for Understanding the Indian Map:
- Study the physical features: Pay attention to the mountains, rivers, plains, and coastlines to understand the country’s geography.
- Explore the political divisions: Learn about the states and union territories, their capitals, and their unique characteristics.
- Examine the cultural diversity: Explore the various religions, languages, and cultural traditions that make up the Indian tapestry.
- Use online resources: Utilize interactive maps, GIS platforms, and satellite imagery to gain a deeper understanding of the country.
- Travel and experience: The best way to understand India is to travel and experience its diverse landscape and rich culture firsthand.
Conclusion:
The Indian map is a testament to the country’s rich history, vibrant culture, and immense potential. It is a powerful tool for understanding the past, navigating the present, and shaping the future. By embracing the power of mapping, India can unlock its full potential, fostering sustainable development, promoting inclusive growth, and securing a brighter future for all its citizens.



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Mapping India: A Journey Through Time, Terrain, and Transformation. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!
