Mapping Africa Today: Navigating A Continent In Flux
Mapping Africa Today: Navigating a Continent in Flux
Related Articles: Mapping Africa Today: Navigating a Continent in Flux
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Mapping Africa Today: Navigating a Continent in Flux. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Mapping Africa Today: Navigating a Continent in Flux
Africa, a continent of immense diversity, is undergoing a period of rapid transformation. From burgeoning economies to technological advancements, the landscape is evolving at an unprecedented pace. Understanding this dynamism requires a comprehensive and nuanced approach, one that goes beyond simplistic generalizations and embraces the complexities of a continent on the move. This exploration delves into the key aspects shaping contemporary Africa, highlighting its challenges and opportunities, and emphasizing the crucial role of mapping in navigating this dynamic landscape.
The Shifting Landscape: A Continent in Transition
Africa is no longer viewed as a monolithic entity defined by its past. Instead, it is a continent of diverse nations, each with its unique history, culture, and aspirations. This dynamism is reflected in the continent’s economic landscape, where a new breed of entrepreneurs and innovators are driving growth and transforming industries.
Economic Growth and Diversification:
Gone are the days when Africa’s economy was solely dependent on primary commodities. While natural resources remain significant, the continent is experiencing a surge in economic diversification. Countries like Rwanda, Ethiopia, and Ghana are experiencing impressive growth rates fueled by investments in technology, infrastructure, and services. The rise of digital economies, driven by mobile technology and internet access, is further reshaping the landscape, creating new opportunities for entrepreneurs and boosting economic activity.
Technological Advancements:
The digital revolution is sweeping across Africa, connecting people and businesses in ways previously unimaginable. Mobile money platforms, for instance, are revolutionizing financial inclusion, allowing individuals without access to traditional banking services to participate in the formal economy. The expansion of internet access and the growth of e-commerce platforms are further empowering entrepreneurs and fostering innovation.
Political Transitions:
Africa is experiencing a wave of democratic transitions, with many countries embracing multi-party systems and holding regular elections. While challenges remain, the continent is witnessing a growing commitment to good governance, human rights, and the rule of law. These transitions, however, are often fraught with complexities, requiring careful navigation and a commitment to inclusivity and dialogue.
The Power of Mapping: Navigating Complexity
Mapping plays a crucial role in understanding and navigating this complex and evolving landscape. It provides a framework for:
1. Visualizing and Analyzing Data:
Maps serve as powerful tools for visualizing and analyzing diverse data sets, from population density and economic activity to infrastructure development and environmental change. By layering data onto maps, researchers, policymakers, and businesses can gain a deeper understanding of spatial patterns and trends, informing decision-making and resource allocation.
2. Identifying Opportunities and Challenges:
Mapping allows for the identification of areas with high potential for growth, investment, and development. Conversely, it can highlight areas facing specific challenges, such as poverty, conflict, or environmental degradation. This information is crucial for targeted interventions, ensuring that resources are allocated effectively and efficiently.
3. Planning and Implementing Development Strategies:
Mapping plays a vital role in planning and implementing development strategies. It enables the identification of key infrastructure projects, the allocation of resources for education and healthcare, and the monitoring of progress towards achieving sustainable development goals.
4. Facilitating Collaboration and Partnerships:
Mapping fosters collaboration and partnerships by providing a common platform for information sharing and knowledge exchange. By bringing together diverse stakeholders, from government agencies to civil society organizations and businesses, mapping can facilitate joint efforts to address critical challenges and unlock opportunities.
The Importance of Geographic Information Systems (GIS)
Geographic Information Systems (GIS) are powerful tools that utilize mapping techniques to analyze and manage spatial data. GIS enables the creation of interactive maps that can be used for a wide range of applications, including:
1. Environmental Monitoring and Management:
GIS can be used to monitor deforestation, track wildlife populations, assess the impact of climate change, and manage natural resources. This information is crucial for developing effective conservation strategies and mitigating environmental risks.
2. Urban Planning and Development:
GIS helps in planning sustainable cities by analyzing population growth, identifying infrastructure needs, optimizing transportation networks, and managing urban sprawl. This data-driven approach ensures efficient resource allocation and promotes inclusive urban development.
3. Disaster Management and Response:
GIS plays a vital role in disaster management by providing real-time information on the location and severity of natural disasters, facilitating rapid response efforts and optimizing resource allocation.
4. Public Health and Disease Surveillance:
GIS can be used to track the spread of diseases, identify high-risk areas, and develop targeted public health interventions. This data-driven approach is crucial for preventing and controlling outbreaks, promoting public health, and ensuring the well-being of communities.
FAQs on Mapping Africa Today:
1. What are the key challenges facing mapping efforts in Africa?
- Data Availability and Quality: Access to reliable and comprehensive data is often limited in Africa, hindering the development of accurate and detailed maps.
- Technical Capacity: Building local capacity in GIS and mapping technologies is crucial for ensuring sustainable mapping initiatives.
- Funding and Resources: Securing sufficient funding and resources is essential for supporting mapping projects and ensuring their long-term sustainability.
- Collaboration and Coordination: Effective collaboration between governments, research institutions, and private sector organizations is vital for developing comprehensive and coordinated mapping initiatives.
2. What are the potential benefits of utilizing mapping technologies in Africa?
- Improved Infrastructure Development: Mapping can guide the development of efficient and sustainable infrastructure, including roads, railways, and communication networks, fostering economic growth and connectivity.
- Enhanced Resource Management: Mapping can facilitate the sustainable management of natural resources, ensuring their long-term availability for future generations.
- Improved Disaster Response: Mapping can enhance disaster preparedness and response by providing real-time information on the location and severity of events, facilitating efficient rescue and relief efforts.
- Sustainable Development: Mapping can support the achievement of Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) by providing data and insights for informed decision-making across various sectors.
3. How can mapping contribute to peacebuilding and conflict resolution in Africa?
- Conflict Mapping and Analysis: Mapping can be used to analyze conflict dynamics, identifying key actors, areas of tension, and potential triggers. This information can inform peacebuilding efforts and conflict prevention strategies.
- Resource Management and Sharing: Mapping can help in managing and sharing resources equitably, reducing tensions over scarce resources and promoting peaceful coexistence.
- Monitoring and Evaluation: Mapping can be used to monitor the implementation of peace agreements and evaluate the effectiveness of peacebuilding interventions.
Tips for Effective Mapping in Africa:
- Prioritize Data Quality: Ensure the accuracy and reliability of data used in mapping projects.
- Foster Local Ownership: Involve local communities and stakeholders in mapping initiatives to ensure relevance and sustainability.
- Promote Capacity Building: Invest in training and education programs to develop local expertise in GIS and mapping technologies.
- Embrace Open Data Principles: Promote open data sharing and collaboration to maximize the impact of mapping initiatives.
- Promote Innovation and Technology: Explore new technologies and approaches to enhance the effectiveness of mapping efforts.
Conclusion:
Mapping Africa today is not just about creating static representations of the continent. It is about utilizing data and technology to understand the continent’s dynamic complexities, identify opportunities, and address challenges. By embracing the power of mapping, Africa can harness its potential, navigate its complexities, and build a brighter future for its people. The future of Africa is one where mapping plays a crucial role in empowering communities, driving sustainable development, and ensuring a brighter future for the continent.


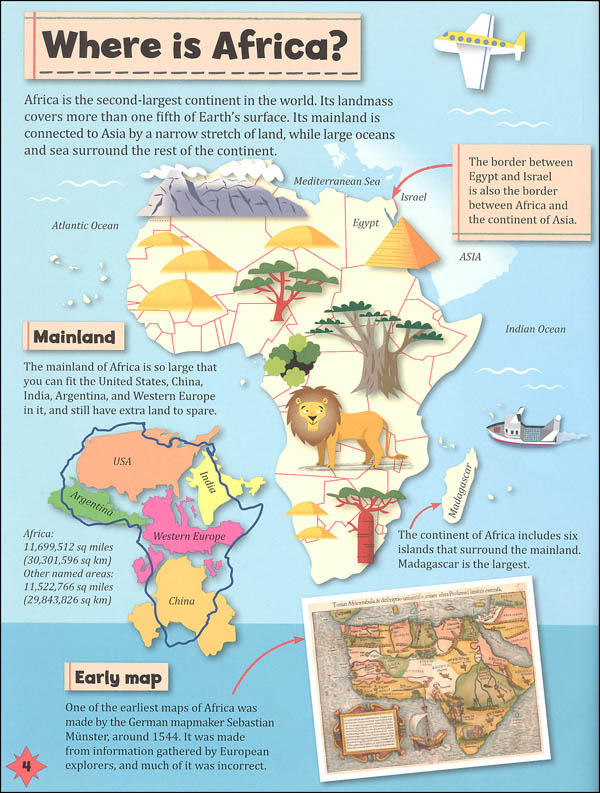
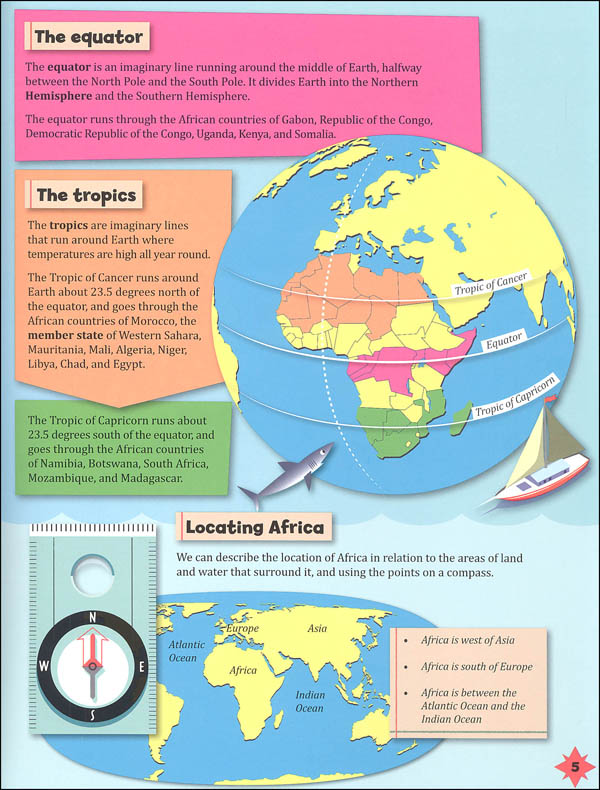

Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Mapping Africa Today: Navigating a Continent in Flux. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!