Mapping Africa: A Visual Journey Through Time And Space
Mapping Africa: A Visual Journey Through Time and Space
Related Articles: Mapping Africa: A Visual Journey Through Time and Space
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Mapping Africa: A Visual Journey Through Time and Space. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Mapping Africa: A Visual Journey Through Time and Space

The African continent, a vast tapestry of diverse landscapes, cultures, and histories, has long been a subject of fascination and exploration. Maps, as visual representations of the world, have played a crucial role in understanding and navigating this intricate continent. From ancient cartographic depictions to modern satellite imagery, maps of Africa offer a powerful lens through which to analyze its evolution, complexities, and potential.
A Historical Perspective:
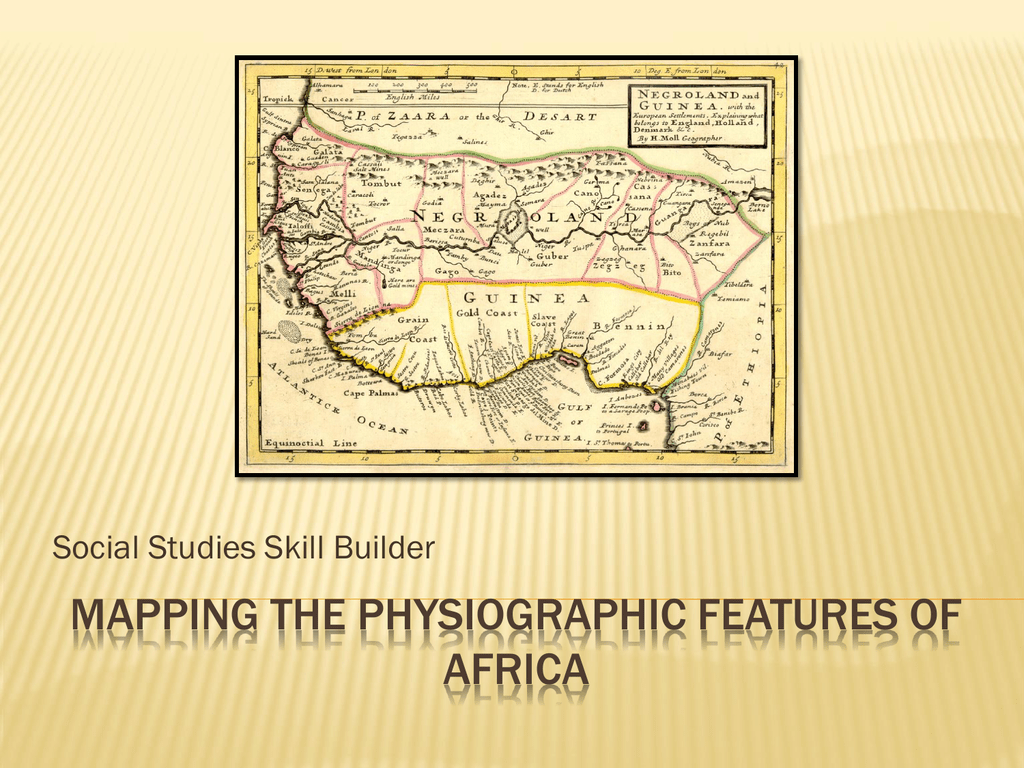
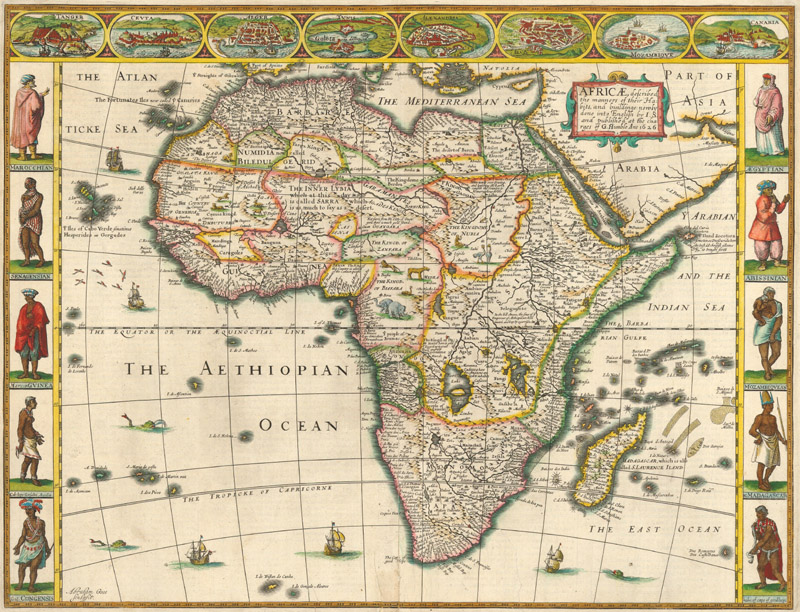
The earliest known maps of Africa, dating back to ancient Egypt and Greece, were primarily focused on coastal regions and trade routes. These maps, often inscribed on papyrus or clay tablets, served practical purposes, guiding traders and explorers through unfamiliar territories. With the rise of the Roman Empire, more detailed maps emerged, capturing the expanding knowledge of the continent’s interior. However, these early depictions were often riddled with inaccuracies and mythical creatures, reflecting the limitations of exploration and knowledge at the time.
The Age of Exploration and Colonialism:
The European Age of Exploration, beginning in the 15th century, brought about a surge in cartographic activity. European explorers, driven by a thirst for wealth and new trade routes, embarked on voyages to Africa, meticulously charting coastlines and mapping previously unknown territories. These maps, often created by skilled cartographers, provided valuable information for navigation, trade, and colonization. However, they also reflected the prevailing Eurocentric perspective, often distorting or omitting indigenous knowledge and perspectives.
The Rise of Modern Cartography:
With the advent of scientific methods and advanced technologies in the 19th and 20th centuries, cartography underwent a profound transformation. The invention of the printing press enabled the mass production of maps, making them accessible to a wider audience. The development of aerial photography and satellite imagery revolutionized mapmaking, providing unprecedented detail and accuracy. Modern maps of Africa, incorporating sophisticated data analysis and Geographic Information Systems (GIS), offer a comprehensive and nuanced understanding of the continent’s geography, demographics, and socio-economic conditions.
The Importance of Visualizing Africa:
Maps of Africa serve multiple purposes, offering valuable insights into the continent’s past, present, and future. They provide a visual representation of:
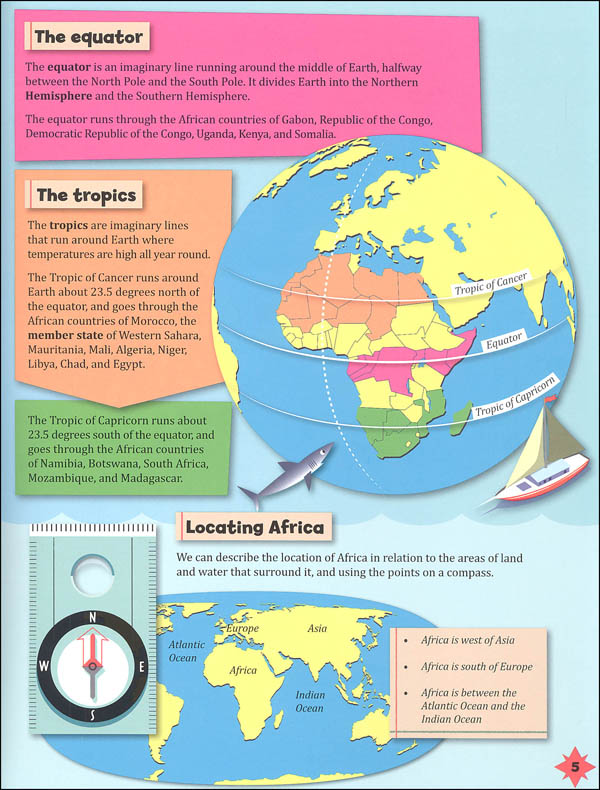
- Geography: Maps showcase the diverse landscapes of Africa, from towering mountains and vast deserts to fertile plains and lush rainforests. They highlight the distribution of natural resources, including water bodies, mineral deposits, and agricultural land.
- Demographics: Maps can illustrate population density, distribution, and migration patterns, revealing the demographic dynamics of different regions. They can also depict ethnic and linguistic diversity, contributing to a deeper understanding of cultural landscapes.
- Socio-Economic Conditions: Maps can visualize economic activities, infrastructure development, and access to essential services such as healthcare and education. They can highlight areas of poverty, inequality, and conflict, providing valuable data for development planning and intervention.
- Historical Events: Maps can depict the impact of historical events, such as colonial boundaries, migration routes, and the spread of diseases. They can also visualize the evolution of political borders and the rise of new nation-states.
- Environmental Change: Maps play a crucial role in monitoring and understanding environmental change, such as deforestation, desertification, and climate change. They can visualize the impact of these changes on ecosystems, biodiversity, and human populations.
Engaging with Maps of Africa:
Beyond their practical applications, maps of Africa can also serve as powerful tools for education, awareness, and advocacy. They can challenge stereotypes, promote cultural understanding, and foster empathy for the diverse people and communities that call Africa home. By visualizing the continent’s complexities and interconnectedness, maps can inspire action and encourage sustainable development initiatives.
FAQs Regarding Maps of Africa:
1. What are the different types of maps used to represent Africa?
There are various types of maps used to represent Africa, each with its specific purpose and focus:
- Political Maps: These maps focus on administrative boundaries, showing countries, regions, and major cities.
- Physical Maps: These maps emphasize the continent’s landforms, including mountains, rivers, lakes, and deserts.
- Thematic Maps: These maps highlight specific data or themes, such as population density, economic activity, or disease prevalence.
- Historical Maps: These maps depict historical events, such as colonial boundaries, migration routes, or the spread of empires.
- Satellite Imagery: These images provide a detailed and up-to-date view of the continent’s surface, capturing changes in land cover and urban development.
2. What are the challenges associated with mapping Africa?
Mapping Africa presents unique challenges, including:
- Data Availability: Access to accurate and comprehensive data is crucial for creating reliable maps. However, data collection in many parts of Africa can be difficult due to logistical constraints, political instability, and lack of resources.
- Cultural Sensitivity: Maps should be created with cultural sensitivity, avoiding generalizations and stereotypes that can perpetuate harmful narratives.
- Technological Infrastructure: Access to advanced technologies, such as GIS software and satellite imagery, is essential for creating high-quality maps. However, technological infrastructure in some parts of Africa remains underdeveloped.
- Funding and Resources: Mapping initiatives require significant funding and resources, which can be limited in developing countries.
3. How can maps of Africa be used to promote sustainable development?
Maps can play a vital role in promoting sustainable development in Africa by:
- Identifying Areas of Need: Maps can pinpoint areas with high poverty rates, limited access to essential services, or environmental degradation, guiding development interventions.
- Monitoring Progress: Maps can track the progress of development projects, helping to assess their effectiveness and identify areas for improvement.
- Raising Awareness: Maps can raise awareness about the challenges facing Africa, encouraging public support for development initiatives.
- Facilitating Collaboration: Maps can facilitate collaboration between governments, NGOs, and local communities, promoting a shared understanding of development priorities.
Tips for Using Maps of Africa:
- Consider the Source: Always evaluate the source of a map, ensuring it is reliable and unbiased.
- Read the Legend: Pay close attention to the legend or key to understand the symbols and colors used on the map.
- Analyze the Scale: The scale of the map determines the level of detail it provides. Consider the purpose of the map and choose an appropriate scale.
- Look for Patterns: Identify patterns and trends within the data presented on the map, drawing connections and insights.
- Use Maps in Conjunction with Other Data: Integrate maps with other data sources, such as demographic statistics, economic indicators, and environmental data, for a more comprehensive understanding.
Conclusion:
Maps of Africa offer a powerful visual language, providing insights into the continent’s geography, history, culture, and development. They serve as tools for navigation, exploration, and understanding, helping to bridge the gap between knowledge and action. By engaging with maps of Africa, we can gain a deeper appreciation for the continent’s complexities and potential, contributing to a more informed and equitable future.



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Mapping Africa: A Visual Journey Through Time and Space. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!