Japan’s Position On The World Map: A Nation Shaped By Geography
Japan’s Position on the World Map: A Nation Shaped by Geography
Related Articles: Japan’s Position on the World Map: A Nation Shaped by Geography
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Japan’s Position on the World Map: A Nation Shaped by Geography. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Japan’s Position on the World Map: A Nation Shaped by Geography

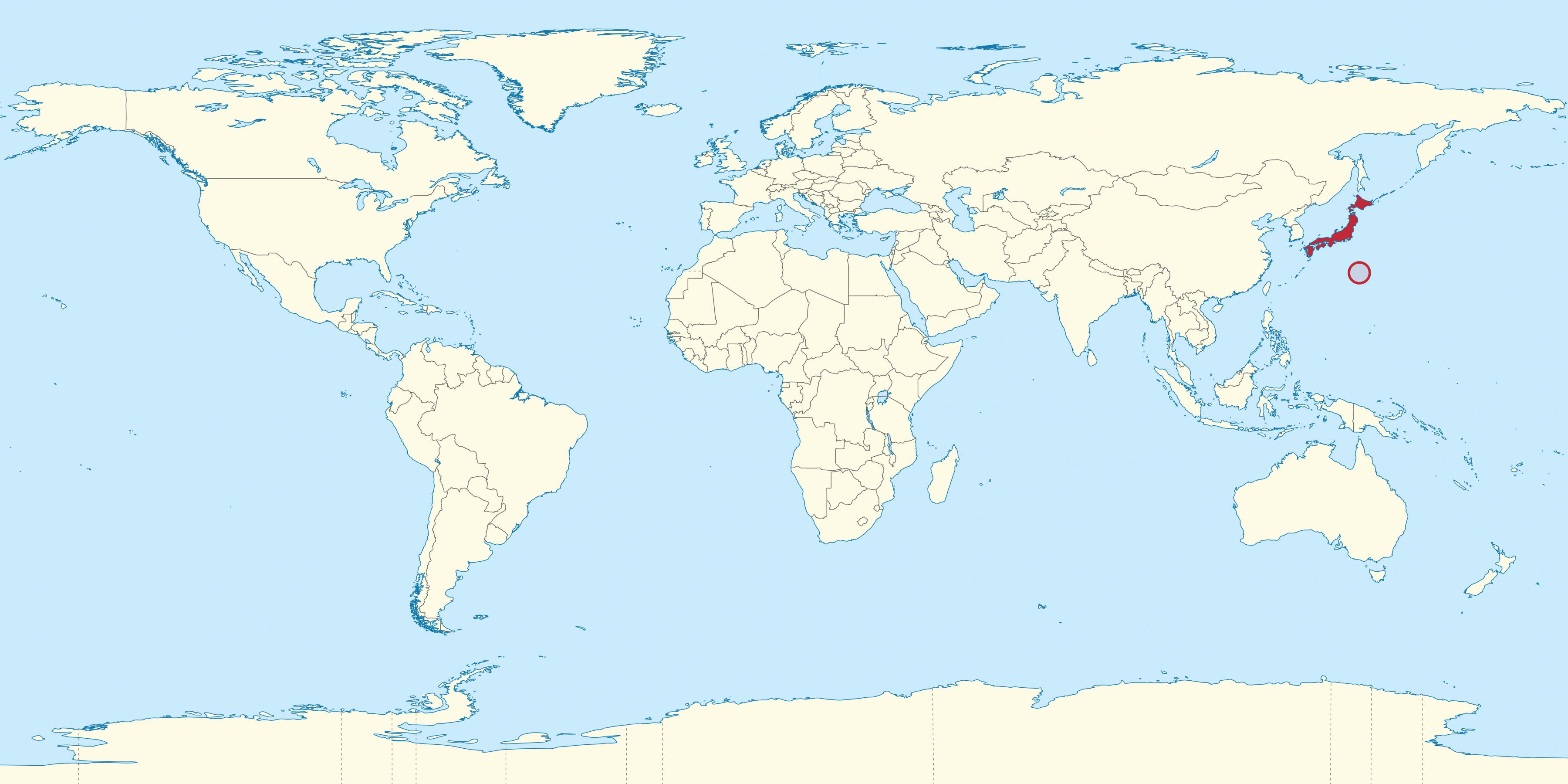
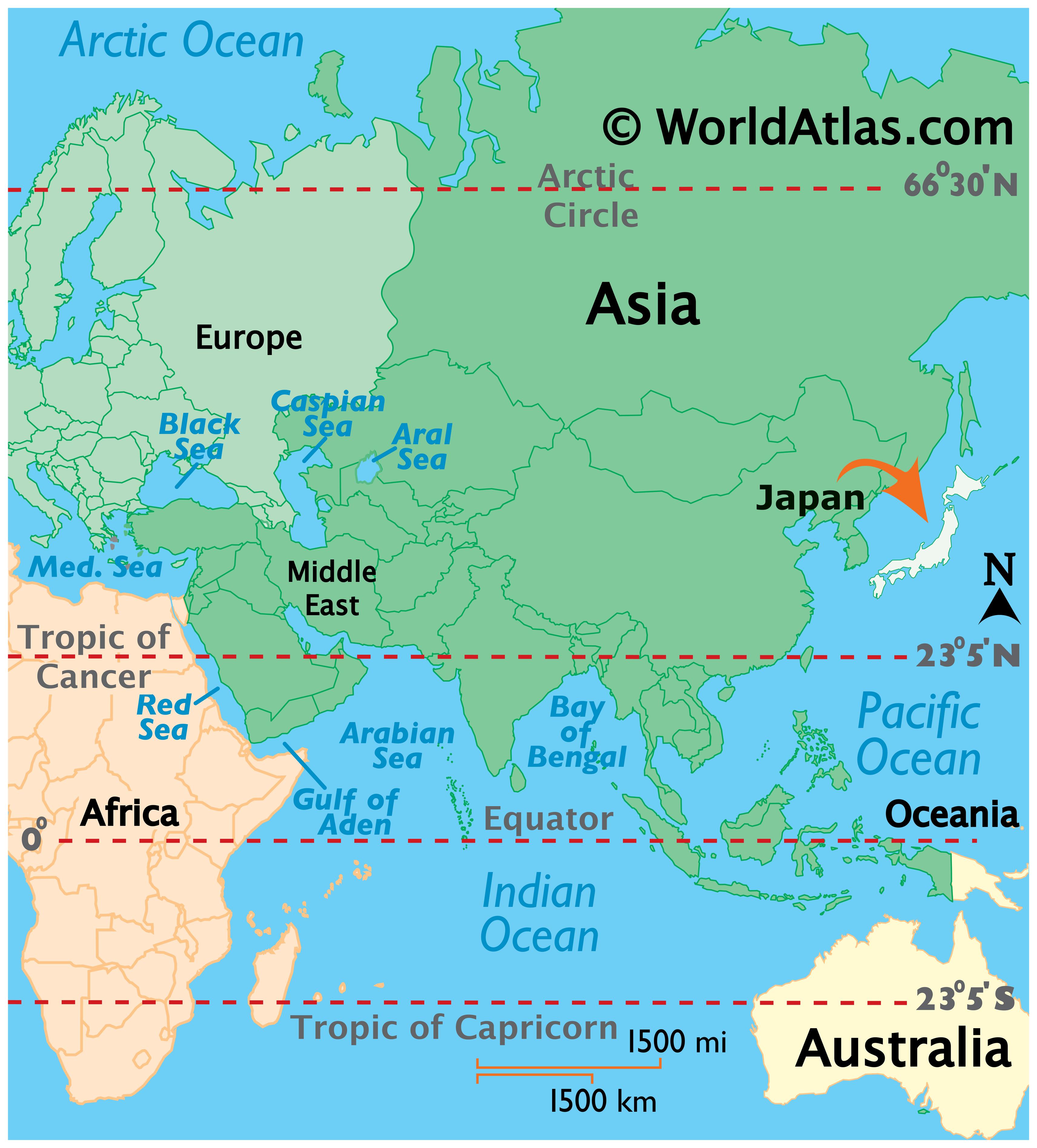
Japan, an archipelago nation in East Asia, holds a unique position on the world map. Its geographic location, characterized by a string of islands stretching across the northwest Pacific Ocean, has profoundly shaped its history, culture, and development. Understanding Japan’s position on the world map unlocks insights into its cultural distinctiveness, economic prowess, and geopolitical significance.
A Chain of Islands in the Pacific:
Japan’s location, a chain of four main islands – Hokkaido, Honshu, Shikoku, and Kyushu – and over 6,800 smaller islands, places it at the crossroads of the Asian continent and the vast Pacific Ocean. This insular position has fostered a sense of isolation and cultural uniqueness, while simultaneously facilitating connections with neighboring countries through maritime trade and cultural exchange.
Geographic Features and Their Impact:
Japan’s geography is marked by a complex interplay of mountains, volcanoes, and coastlines. The Japanese Alps, a mountain range traversing Honshu, dominate the landscape, influencing climate patterns and shaping the distribution of population. Active volcanoes, a consequence of Japan’s location on the Pacific Ring of Fire, have both threatened and enriched the nation, providing fertile volcanic soil for agriculture and geothermal energy resources.
The extensive coastline, with its numerous inlets and harbors, has been instrumental in the development of Japan’s maritime culture and its thriving fishing industry. The country’s strategic location also allowed for the establishment of major ports like Yokohama and Kobe, facilitating trade and cultural exchange with other nations.
Geopolitical Significance:
Japan’s position on the world map has significant geopolitical implications. Its proximity to major powers like China, Russia, and South Korea, coupled with its economic strength and technological advancements, makes it a crucial player in regional and global affairs.
The country’s strategic location in the Pacific Ocean has also made it a key factor in maintaining regional stability and security. The United States, a long-standing ally, maintains a significant military presence in Japan, contributing to the overall security of the region.
Cultural and Economic Impacts:
Japan’s geographic isolation and its unique natural environment have fostered a distinct cultural identity. The country’s rich artistic traditions, from calligraphy and ceramics to anime and manga, are deeply rooted in its history and landscape. The mountainous terrain and limited arable land have influenced agricultural practices, leading to a focus on rice cultivation and a strong emphasis on seafood in the Japanese diet.
Japan’s geographic location has also been a key factor in its economic success. The country’s strategic position in East Asia, combined with its skilled workforce and innovative spirit, has enabled it to become a leading global economic powerhouse. Its manufacturing prowess, technological advancements, and robust export sector have cemented its place as a significant player in the global economy.
Challenges and Opportunities:
While Japan’s geographic location offers numerous advantages, it also presents challenges. The country is prone to natural disasters, including earthquakes, tsunamis, and volcanic eruptions, which have historically caused significant damage and loss of life. The limited landmass and mountainous terrain also pose challenges for infrastructure development and resource management.
However, Japan’s geographic location also presents significant opportunities. The country’s strategic location in the Pacific Ocean positions it as a key player in regional trade and maritime security. The country’s advanced technological capabilities and its focus on sustainability offer potential solutions for global challenges like climate change and resource scarcity.
Conclusion:
Japan’s position on the world map is a testament to the profound impact of geography on a nation’s history, culture, and development. The country’s insular location has fostered cultural uniqueness and economic resilience, while its strategic position in the Pacific Ocean has made it a key player in regional and global affairs. As Japan continues to navigate the complexities of the 21st century, its geographic location will continue to shape its future, presenting both challenges and opportunities for this dynamic nation.
FAQs:
Q: What are the main islands of Japan?
A: The four main islands of Japan are Hokkaido, Honshu, Shikoku, and Kyushu.
Q: What is the Pacific Ring of Fire?
A: The Pacific Ring of Fire is a zone of intense seismic and volcanic activity surrounding the Pacific Ocean. Japan’s location on this ring makes it prone to earthquakes and volcanic eruptions.
Q: What are some of the major ports in Japan?
A: Major ports in Japan include Yokohama, Kobe, Nagoya, and Osaka.
Q: How has Japan’s geography influenced its culture?
A: Japan’s mountainous terrain, limited arable land, and extensive coastline have shaped its agricultural practices, artistic traditions, and culinary habits.
Q: What are some of the challenges Japan faces due to its geography?
A: Japan faces challenges related to natural disasters, limited landmass, and resource management.
Q: What are some of the opportunities Japan has due to its geography?
A: Japan has opportunities related to regional trade, maritime security, and global leadership in technology and sustainability.
Tips:
- Use a world map to visualize Japan’s location and its surrounding countries.
- Research the history of Japan’s geographic influence on its culture and development.
- Explore the impact of Japan’s location on its economic growth and technological advancements.
- Learn about the challenges and opportunities Japan faces due to its unique geographic position.
- Consider the role of Japan in regional and global affairs, considering its strategic location in the Pacific Ocean.
Conclusion:
Japan’s position on the world map is a defining characteristic of this nation, shaping its history, culture, and development. From its unique island geography to its strategic location in the Pacific Ocean, Japan’s place on the world map continues to influence its present and future. Understanding Japan’s location provides valuable insights into its cultural distinctiveness, economic prowess, and geopolitical significance.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Japan’s Position on the World Map: A Nation Shaped by Geography. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!