Japan’s Position On The World Map: A Nation Of Islands And Global Significance
Japan’s Position on the World Map: A Nation of Islands and Global Significance
Related Articles: Japan’s Position on the World Map: A Nation of Islands and Global Significance
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Japan’s Position on the World Map: A Nation of Islands and Global Significance. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Japan’s Position on the World Map: A Nation of Islands and Global Significance

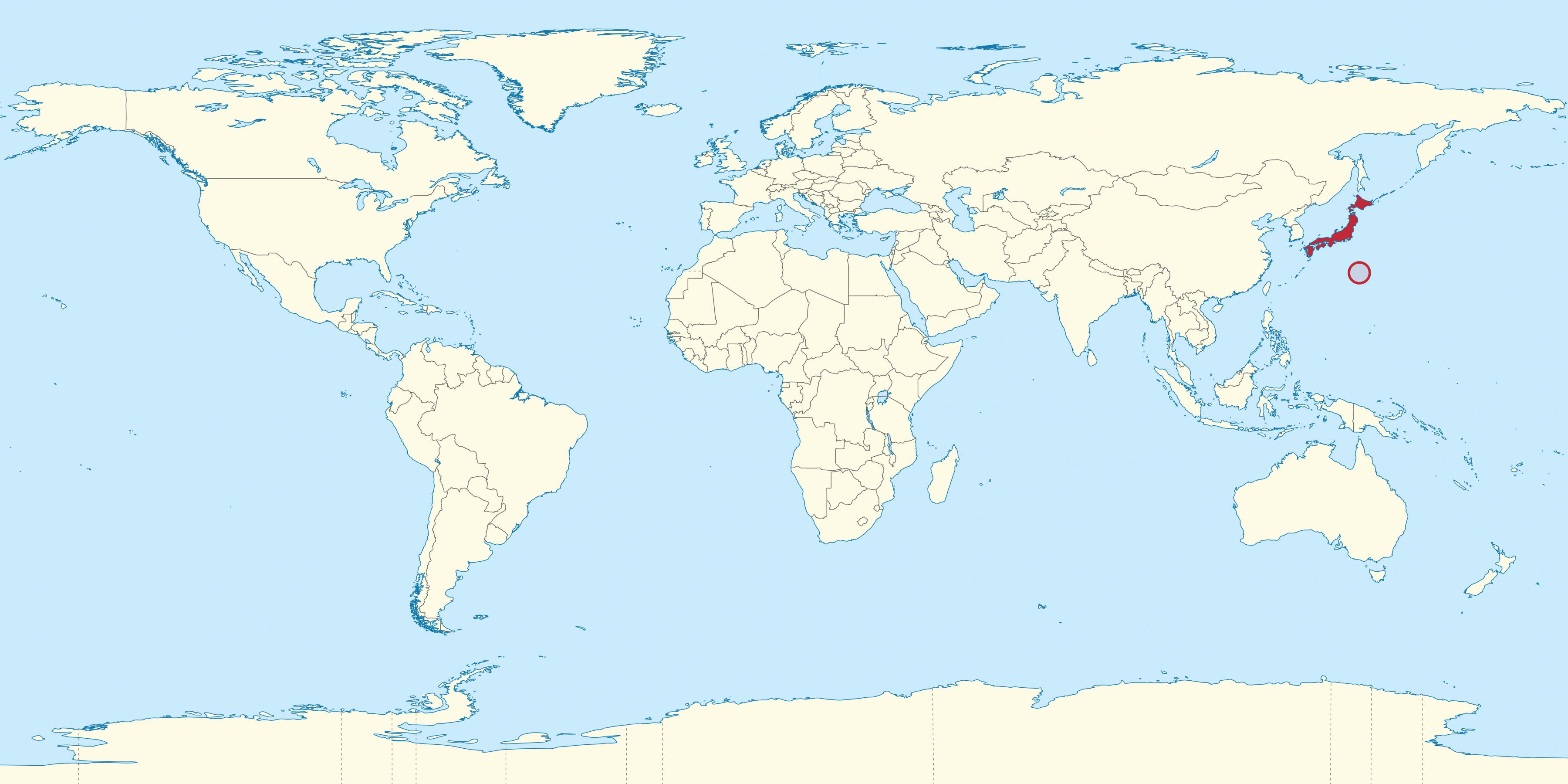
Japan, a nation of over 6,800 islands, occupies a unique and strategically important position in the northeastern region of Asia. Situated in the northwest Pacific Ocean, Japan’s archipelago stretches across a considerable distance, extending from the Sea of Okhotsk in the north to the East China Sea in the south. This geographical location has significantly influenced Japan’s history, culture, and its role in the global landscape.
A Nation of Islands:
Japan’s main islands, Hokkaido, Honshu, Shikoku, and Kyushu, along with numerous smaller islands, form a distinct geographical entity. These islands are separated from the Asian mainland by the Sea of Japan, a marginal sea bordered by Japan, the Korean Peninsula, and Russia. This maritime setting has played a vital role in shaping Japan’s cultural identity, its economic prosperity, and its interactions with other nations.
Location and Proximity:
Japan’s location in East Asia places it in close proximity to some of the world’s most populous and economically dynamic countries. It shares maritime borders with South Korea, China, and Russia, and its proximity to these nations has fostered significant trade and cultural exchange.
- China: Japan’s closest neighbor, China, is separated by the East China Sea. This close proximity has resulted in a complex and multifaceted relationship, marked by both cooperation and competition.
- South Korea: Separated by the Korea Strait, South Korea shares a close geographical and cultural connection with Japan. The two nations have historically experienced periods of both conflict and collaboration.
- Russia: Japan’s northernmost neighbor, Russia, is separated by the Sea of Okhotsk and the Sea of Japan. The two countries have a long-standing territorial dispute over the Kuril Islands, which continues to affect their bilateral relations.
Strategic Significance:
Japan’s location within the northwest Pacific Ocean makes it a strategically important nation. The region is a major shipping route, and Japan’s control over key straits and waterways is essential for maintaining global trade and security.
- The Tsugaru Strait: This narrow strait separates Hokkaido from Honshu and is a vital waterway for shipping between the Pacific Ocean and the Sea of Japan.
- The Sōya Strait: Located between Hokkaido and Sakhalin Island, this strait is another important shipping route connecting the Sea of Okhotsk to the Pacific Ocean.
Natural Resources and Economic Importance:
Despite its mountainous terrain and limited land area, Japan possesses significant natural resources, including abundant marine resources, forests, and mineral deposits. These resources have contributed significantly to Japan’s economic prosperity.
- Fisheries: Japan is a major fishing nation, with a vast and productive fishing industry. Its coastal waters are rich in diverse marine life, supporting a wide range of fisheries.
- Forestry: Japan’s forests cover over 68% of its land area and are an important source of timber, paper, and other forest products.
- Mineral Resources: While Japan’s mineral resources are limited, it possesses significant deposits of coal, copper, and other minerals.
Cultural and Historical Significance:
Japan’s location at the crossroads of East Asia has made it a melting pot of diverse cultures and traditions. Its history has been shaped by interactions with China, Korea, and other neighboring countries, resulting in a rich and multifaceted cultural heritage.
- Buddhism: Introduced from China in the 6th century, Buddhism has deeply influenced Japanese culture, art, and philosophy.
- Shintoism: Japan’s indigenous religion, Shintoism, emphasizes reverence for nature and ancestral spirits.
- Traditional Arts: Japan is renowned for its traditional arts, including calligraphy, ceramics, and martial arts, which have evolved over centuries.
FAQs about Japan’s Location:
1. What is the closest country to Japan?
South Korea is the closest country to Japan, separated by the Korea Strait.
2. What is the largest island in Japan?
Honshu is the largest island in Japan, followed by Hokkaido, Kyushu, and Shikoku.
3. Is Japan a part of Asia?
Yes, Japan is located in East Asia, specifically in the northwest Pacific Ocean.
4. What are the major cities in Japan?
Major cities in Japan include Tokyo, Osaka, Nagoya, Sapporo, and Fukuoka.
5. What is the climate like in Japan?
Japan experiences a diverse range of climates due to its geographical location. The northern regions have a cold, snowy climate, while the southern regions enjoy a subtropical climate.
Tips for Understanding Japan’s Location:
- Use a world map: Familiarize yourself with the location of Japan on a world map.
- Research its neighboring countries: Understand the countries surrounding Japan and their geographical relationships.
- Explore online resources: Utilize online maps and resources to visualize Japan’s location and its surrounding waters.
Conclusion:
Japan’s position on the world map is a testament to its unique geographical characteristics and its profound cultural and historical significance. Its island nation status, its strategic location in East Asia, and its abundant natural resources have shaped its destiny and its role in the global community. Understanding Japan’s location is essential for comprehending its history, culture, and its continued importance in the 21st century.


![Where is and What’s What Japan: [ So where is Japan?] Location of the Japan island in the world map.](https://2.bp.blogspot.com/-tqz6n1cYsRg/UR9qvfTHUxI/AAAAAAAAAJk/dBYINEk5AdY/s1600/whereisjapan_locationofjapanintheworldmap_1024.jpg)




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Japan’s Position on the World Map: A Nation of Islands and Global Significance. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!