Japan’s Position: A Nation At The Crossroads Of East Asia
Japan’s Position: A Nation at the Crossroads of East Asia
Related Articles: Japan’s Position: A Nation at the Crossroads of East Asia
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Japan’s Position: A Nation at the Crossroads of East Asia. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Japan’s Position: A Nation at the Crossroads of East Asia

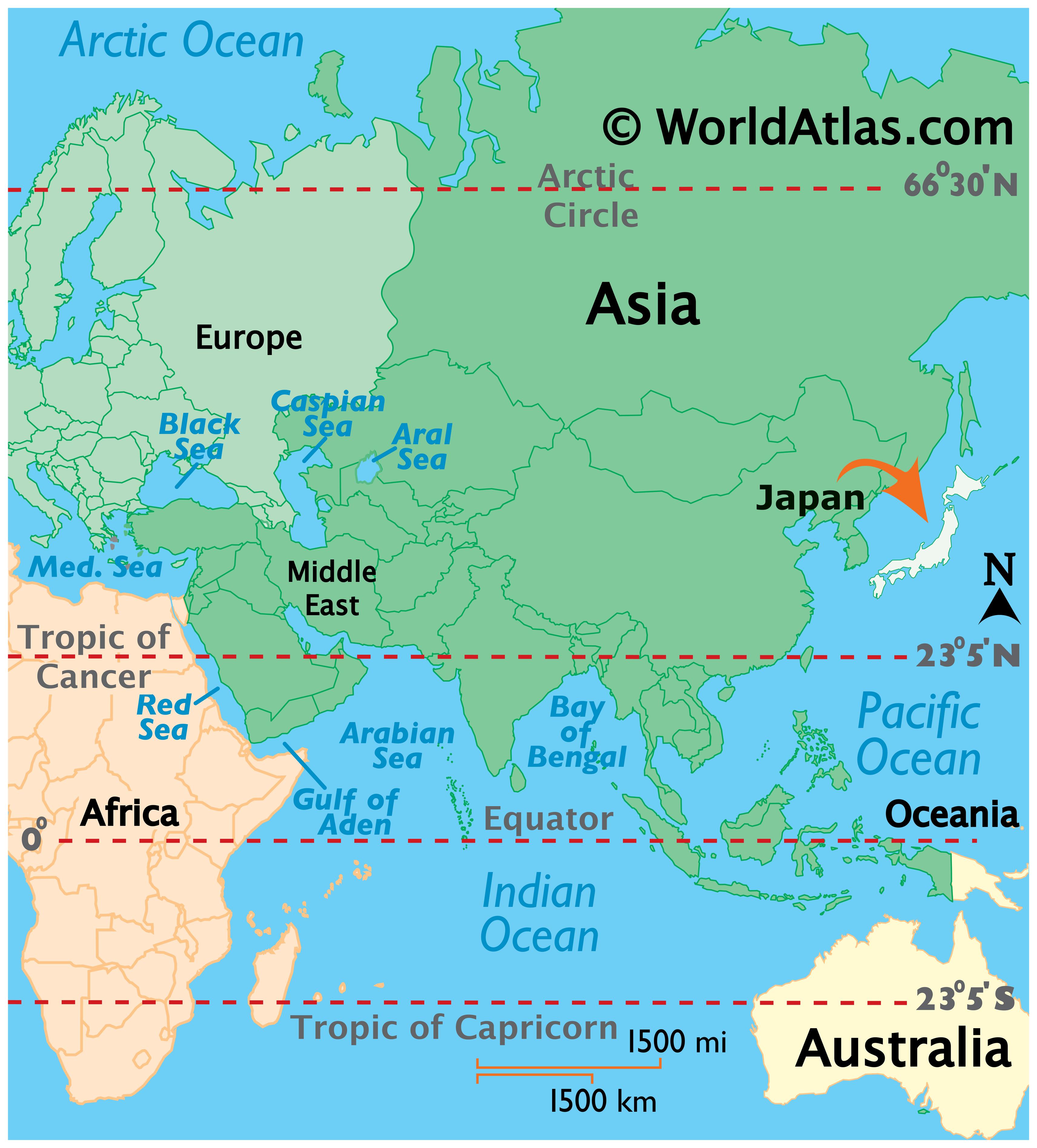
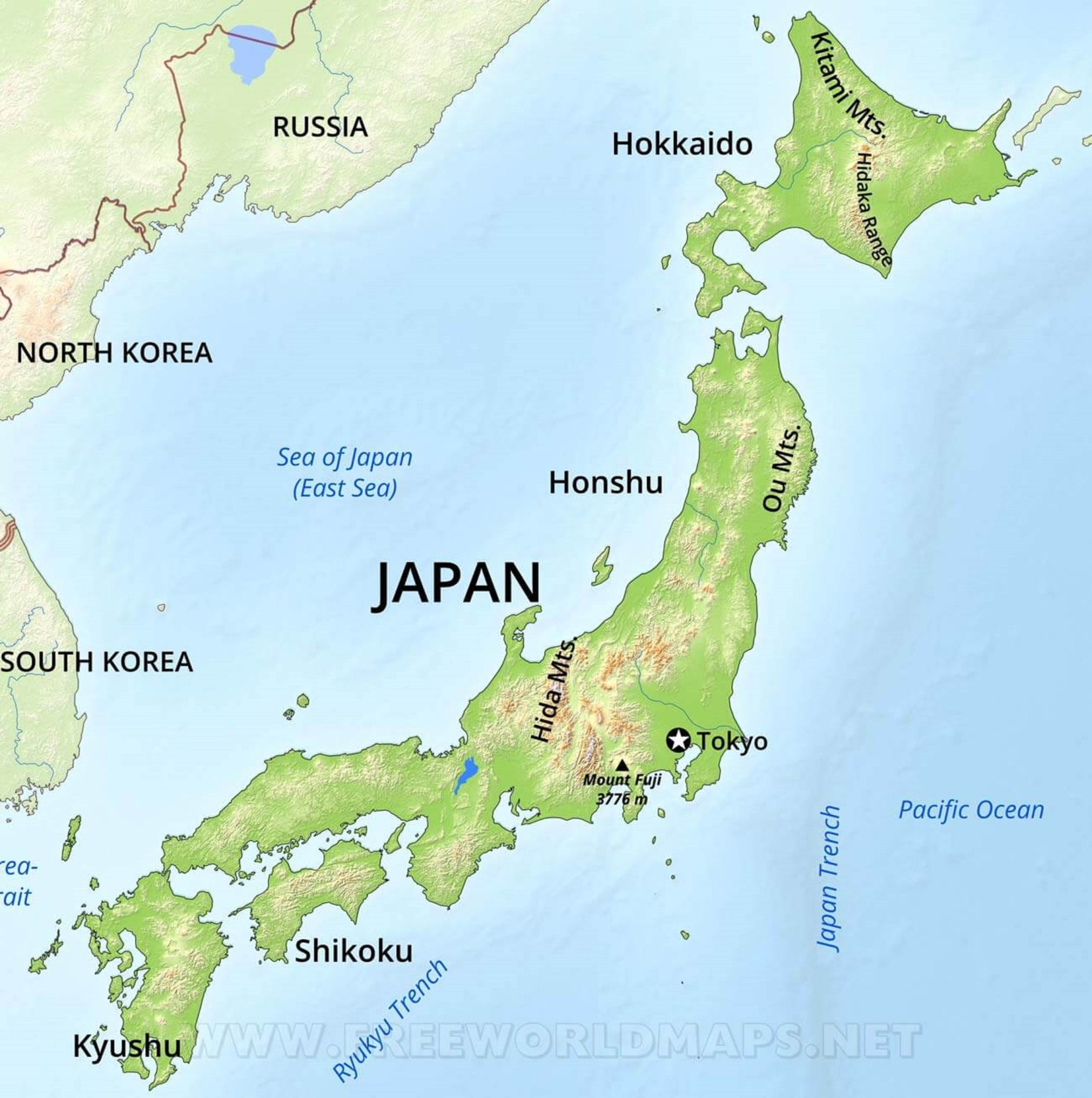
Japan, a nation renowned for its technological prowess, rich cultural heritage, and captivating landscapes, occupies a unique position on the world map. Situated in the northwestern Pacific Ocean, Japan is an archipelago comprising four main islands – Hokkaido, Honshu, Shikoku, and Kyushu – and over 6,800 smaller islands. This island nation’s geographical location has profoundly shaped its history, culture, and economy.
An Island Nation at the Crossroads:
Japan’s location at the eastern edge of the Eurasian continent places it at a strategic crossroads. The Sea of Japan separates it from the Korean Peninsula to the west, while the East China Sea lies between Japan and mainland China. To the east, the Pacific Ocean stretches vast and deep, connecting Japan to North America and other Pacific Rim nations.
This strategic position has been both a blessing and a challenge for Japan throughout its history. It has facilitated trade and cultural exchange with neighboring countries while also making it vulnerable to invasion.
The Ring of Fire and Seismic Activity:
Japan’s location along the Pacific Ring of Fire, a zone of intense seismic activity, has significantly impacted the country’s landscape and daily life. The Ring of Fire is a horseshoe-shaped area in the Pacific Ocean where tectonic plates collide, causing frequent earthquakes, volcanic eruptions, and tsunamis.
These natural hazards pose a constant threat to Japan, but they also contribute to the country’s unique geological features, such as the iconic Mount Fuji, a dormant volcano that stands as a symbol of Japan.
Climate and Topography:
Japan’s climate is diverse, ranging from subarctic conditions in Hokkaido to subtropical climates in the southern islands. The country experiences four distinct seasons, with warm, humid summers and cold, snowy winters. The mountainous terrain, covering over 73% of the country, creates varied microclimates and contributes to the beauty of Japan’s natural landscapes.
Navigating the Waters:
The surrounding seas have played a vital role in shaping Japan’s history and culture. The Japanese archipelago has been a hub of maritime activity for centuries, with its people developing advanced shipbuilding and navigation techniques. Fishing remains a significant industry, and the country’s coastal waters are teeming with diverse marine life.
Strategic Importance in the Modern World:
Today, Japan’s location continues to be of immense strategic importance. The country is a major economic power, with its industries playing a critical role in global supply chains. Its location in the Pacific region makes it a key player in regional security and diplomacy.
FAQs on Japan’s Location:
Q: Is Japan part of Asia?
A: Yes, Japan is located in East Asia, bordering the Sea of Japan, the East China Sea, and the Pacific Ocean.
Q: How far is Japan from the mainland?
A: The distance between Japan and the mainland varies depending on the specific location. The closest point between Japan and mainland Asia is the Korean Peninsula, which is about 200 kilometers away.
Q: What are the major islands of Japan?
A: The four main islands of Japan are Hokkaido, Honshu, Shikoku, and Kyushu.
Q: What is the climate like in Japan?
A: Japan experiences a diverse range of climates, from subarctic in the north to subtropical in the south. The country has four distinct seasons: spring, summer, autumn, and winter.
Q: What are the major cities in Japan?
A: Some of the major cities in Japan include Tokyo (the capital), Osaka, Nagoya, Kyoto, and Fukuoka.
Tips for Understanding Japan’s Location:
- Use a world map or atlas: This will help you visualize Japan’s location in relation to other countries and continents.
- Explore online maps: Websites like Google Maps offer interactive maps with detailed information about Japan’s geography, cities, and landmarks.
- Read about Japan’s history and culture: Understanding the historical context of Japan’s location can provide valuable insights into its present-day significance.
- Consider visiting Japan: Experiencing the country firsthand will provide a deeper understanding of its unique geographical features and cultural identity.
Conclusion:
Japan’s location at the crossroads of East Asia has shaped its history, culture, and economy. Its strategic position, diverse climate, and unique geological features have made it a nation of contrasts and captivating beauty. Understanding Japan’s location is crucial to appreciating its role in the world today and its enduring cultural significance.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Japan’s Position: A Nation at the Crossroads of East Asia. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!