Japan’s Archipelago: A Tapestry Of Land And Sea
Japan’s Archipelago: A Tapestry of Land and Sea
Related Articles: Japan’s Archipelago: A Tapestry of Land and Sea
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Japan’s Archipelago: A Tapestry of Land and Sea. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Japan’s Archipelago: A Tapestry of Land and Sea
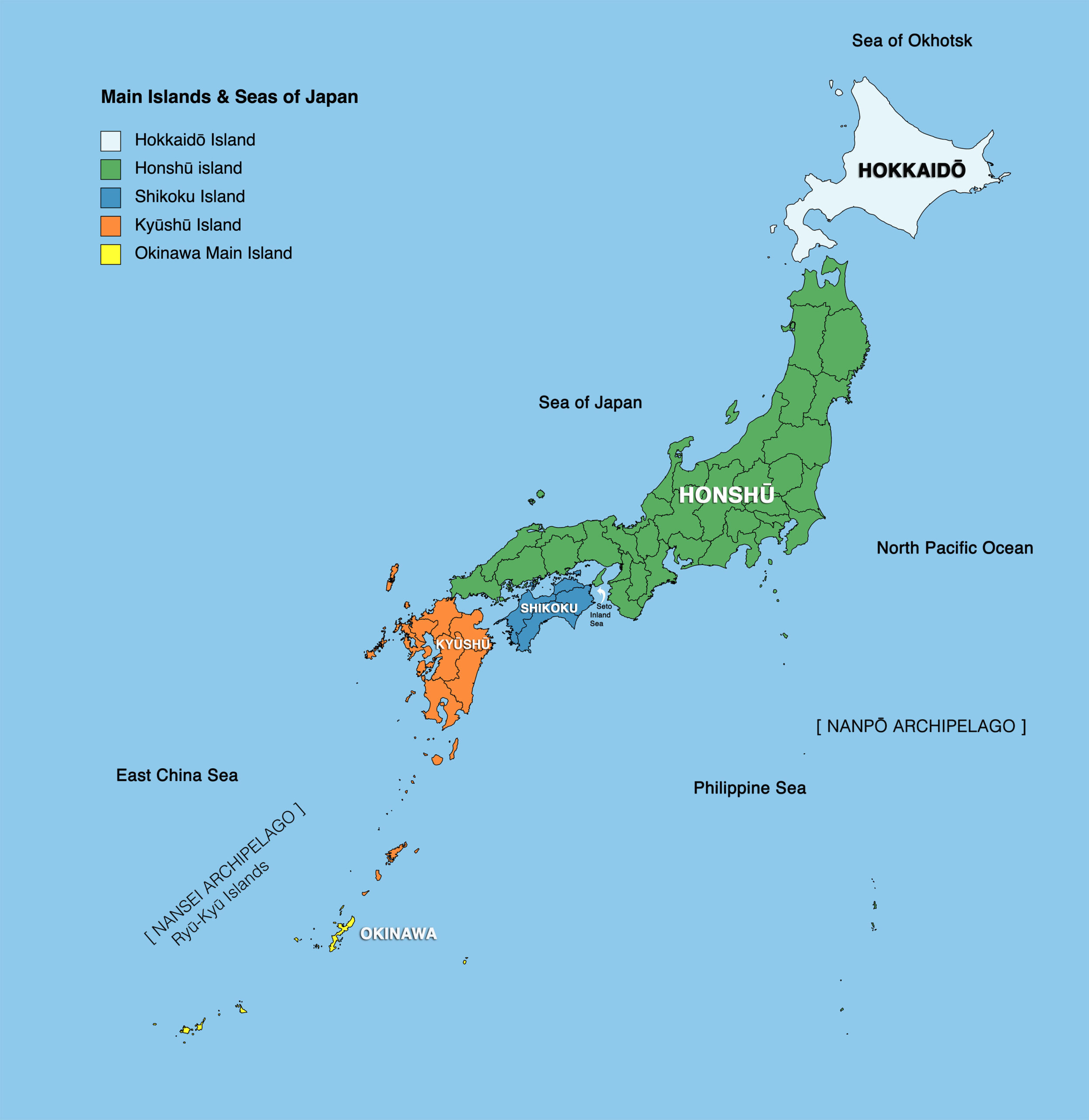
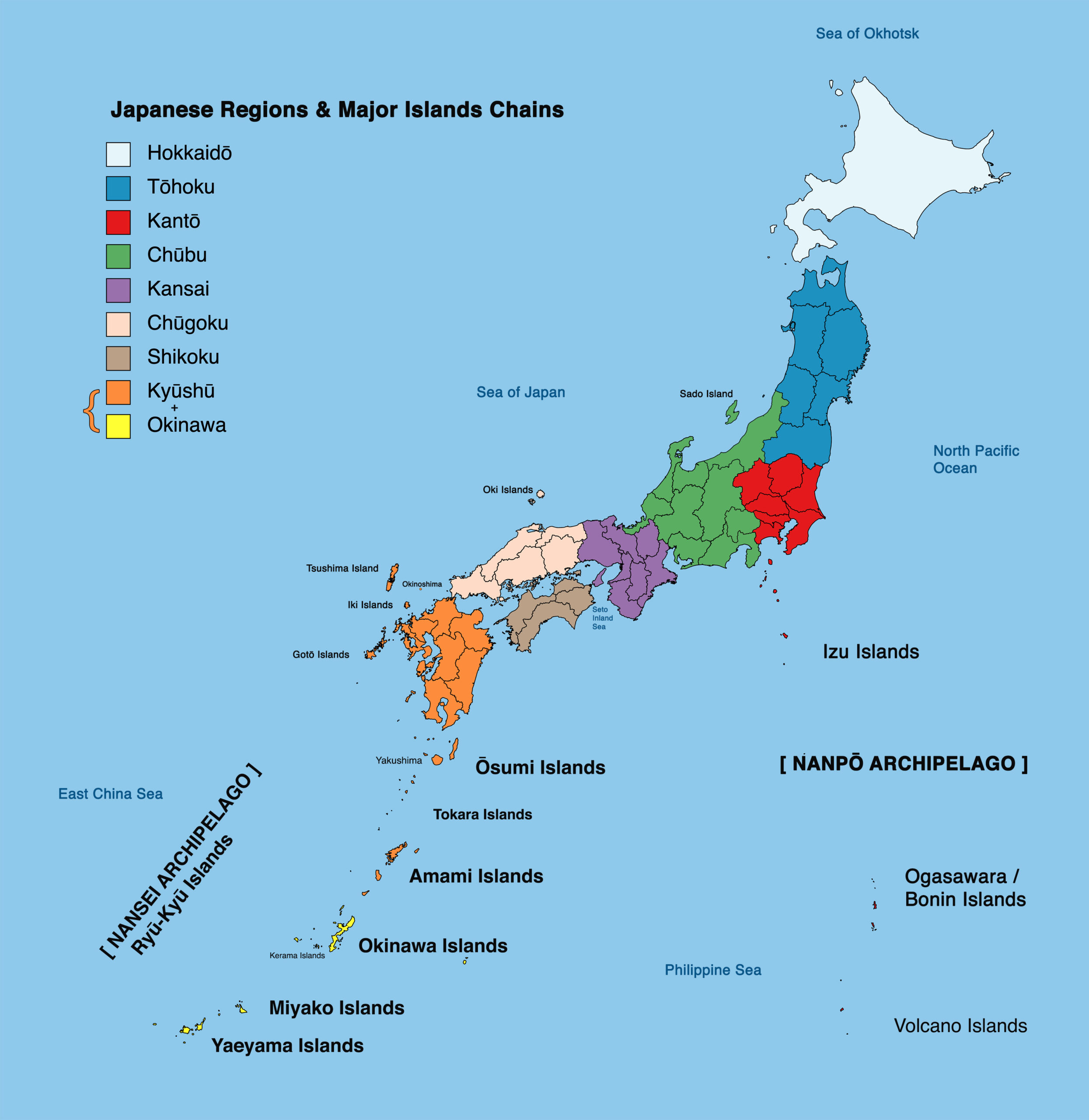
Japan, an island nation in East Asia, is geographically defined by its unique archipelago structure. Comprising four main islands – Hokkaido, Honshu, Shikoku, and Kyushu – and over 6,800 smaller islands, Japan’s map reveals a complex tapestry of land and sea. This intricate geography has profoundly shaped the nation’s history, culture, and identity.
The Four Main Islands:
- Hokkaido, the northernmost island, is known for its rugged mountains, volcanic landscapes, and abundant natural resources. It is a popular destination for outdoor enthusiasts, offering skiing, hiking, and wildlife viewing.
- Honshu, the largest and most populous island, is the heart of Japan. It houses the capital city, Tokyo, and major urban centers like Osaka, Kyoto, and Nagoya. Honshu’s diverse terrain encompasses towering mountains, fertile plains, and sprawling coastal areas.
- Shikoku, the smallest of the four main islands, is renowned for its scenic beauty, including the Shikoku Pilgrimage route, a 1,200-kilometer journey connecting 88 temples. It is also a center for agriculture and fishing.
- Kyushu, the southernmost island, is known for its volcanic activity, hot springs, and vibrant culture. It boasts the city of Fukuoka, a major economic hub, and the island of Okinawa, famous for its unique culture and pristine beaches.
The Importance of Japan’s Archipelago:
The archipelago structure of Japan has played a pivotal role in its history and development. Its island nature has provided natural barriers, protecting the nation from invasion and fostering a distinct cultural identity. The surrounding seas have been a source of sustenance, facilitating trade and communication with neighboring countries.
The Influence of Topography:
Japan’s mountainous terrain, with over 73% of its land area covered by mountains, has shaped its settlement patterns, agriculture, and transportation infrastructure. While the mountains have posed challenges for development, they have also offered stunning natural beauty and opportunities for recreation.
The Impact of Climate:
Japan’s location within the temperate zone, combined with its mountainous terrain, creates a diverse range of microclimates. The country experiences distinct seasons, with warm and humid summers and cold, snowy winters. This climate variability influences agriculture, tourism, and the nation’s lifestyle.
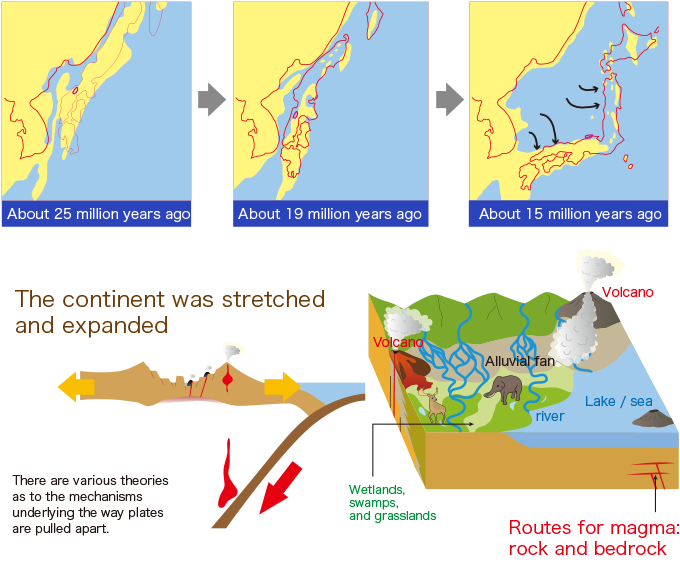
Geological Activity:
Japan sits on the Ring of Fire, a region of intense seismic and volcanic activity. This geological instability presents both challenges and opportunities. While earthquakes and volcanic eruptions pose risks, they also provide geothermal energy resources and create unique landscapes.
The Importance of the Sea:
The sea has been an integral part of Japan’s history and culture. Fishing has been a vital industry, providing food and livelihood for generations. The surrounding waters have also facilitated trade and transportation, connecting Japan to the rest of the world.
Understanding Japan’s Map: FAQs
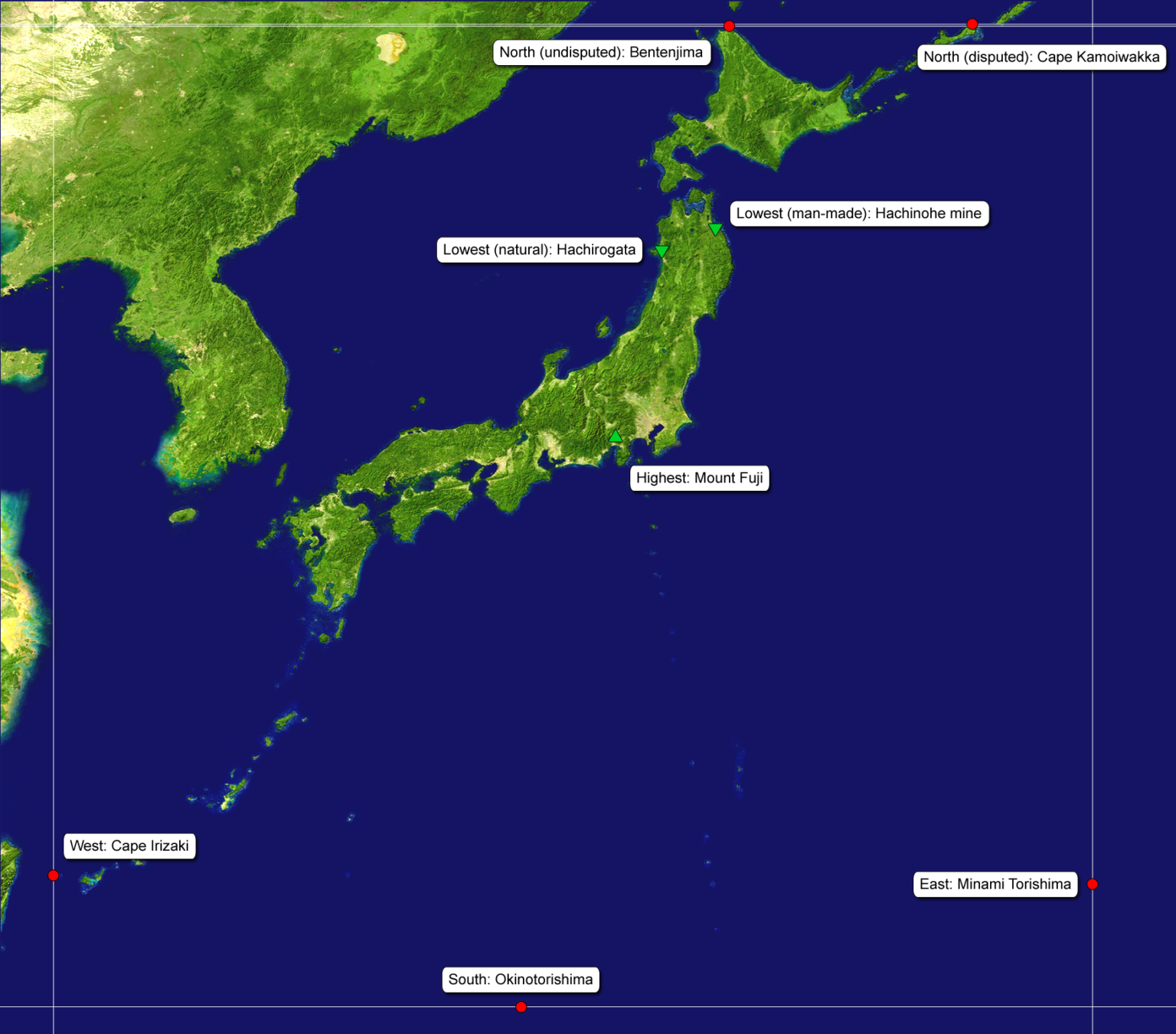
Q: What is the highest mountain in Japan?
A: Mount Fuji, a dormant volcano, is the highest mountain in Japan, standing at 3,776 meters (12,388 feet).
Q: What is the largest city in Japan?
A: Tokyo is the largest city in Japan, with a population of over 13 million.
Q: What are the major rivers in Japan?
A: The major rivers in Japan include the Shinano River, Tone River, and Ishikari River.
Q: What are the major islands in Japan?
A: The four main islands of Japan are Hokkaido, Honshu, Shikoku, and Kyushu.
Q: How many prefectures are there in Japan?
A: Japan is divided into 47 prefectures, each with its own unique characteristics and governance.
Tips for Understanding Japan’s Map:
- Study the major islands and their relative sizes and positions.
- Identify the major cities and urban centers.
- Locate the major rivers, mountains, and other geographical features.
- Explore the different regions of Japan and their unique characteristics.
- Use online maps and resources to enhance your understanding.
Conclusion:
Japan’s map is a fascinating reflection of its unique geographical features and their profound influence on the nation’s history, culture, and identity. From its volcanic peaks to its pristine beaches, Japan’s archipelago offers a diverse and captivating landscape. Understanding the intricate tapestry of land and sea that constitutes Japan’s map provides valuable insight into the nation’s rich history, vibrant culture, and resilient spirit.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Japan’s Archipelago: A Tapestry of Land and Sea. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!