Japan On The Map: A Nation Of Contrasts And Enduring Influence
Japan on the Map: A Nation of Contrasts and Enduring Influence
Related Articles: Japan on the Map: A Nation of Contrasts and Enduring Influence
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Japan on the Map: A Nation of Contrasts and Enduring Influence. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Japan on the Map: A Nation of Contrasts and Enduring Influence
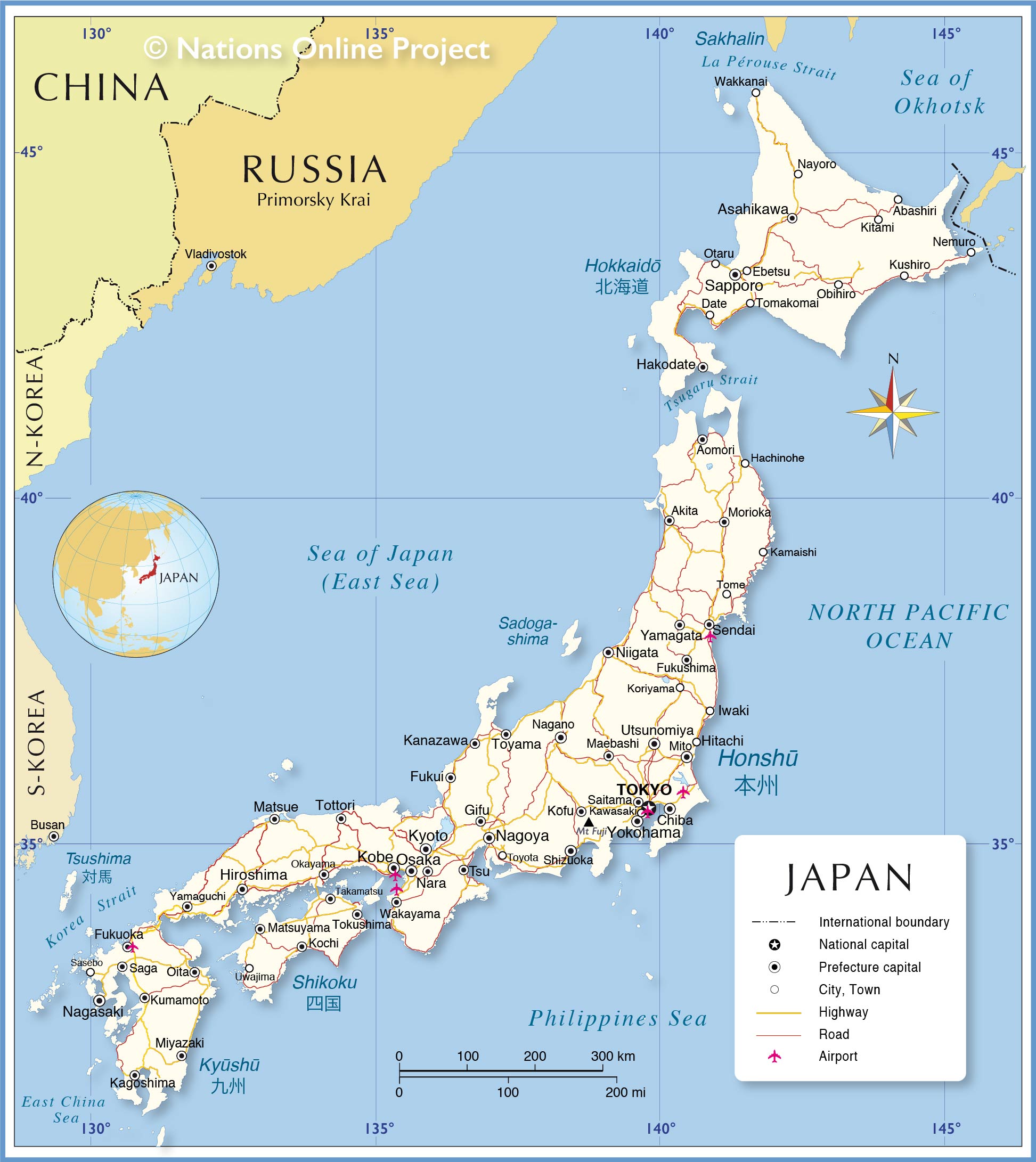
Japan, an archipelago nation nestled in the northwest Pacific Ocean, holds a unique position on the world map. Its geographical isolation, coupled with its rich cultural heritage and technological prowess, has shaped a nation of fascinating contradictions. From the towering peaks of Mount Fuji to the neon-lit streets of Tokyo, Japan presents a tapestry of ancient traditions and modern innovation, captivating the imagination of the world.
A Land of Islands and Mountains:
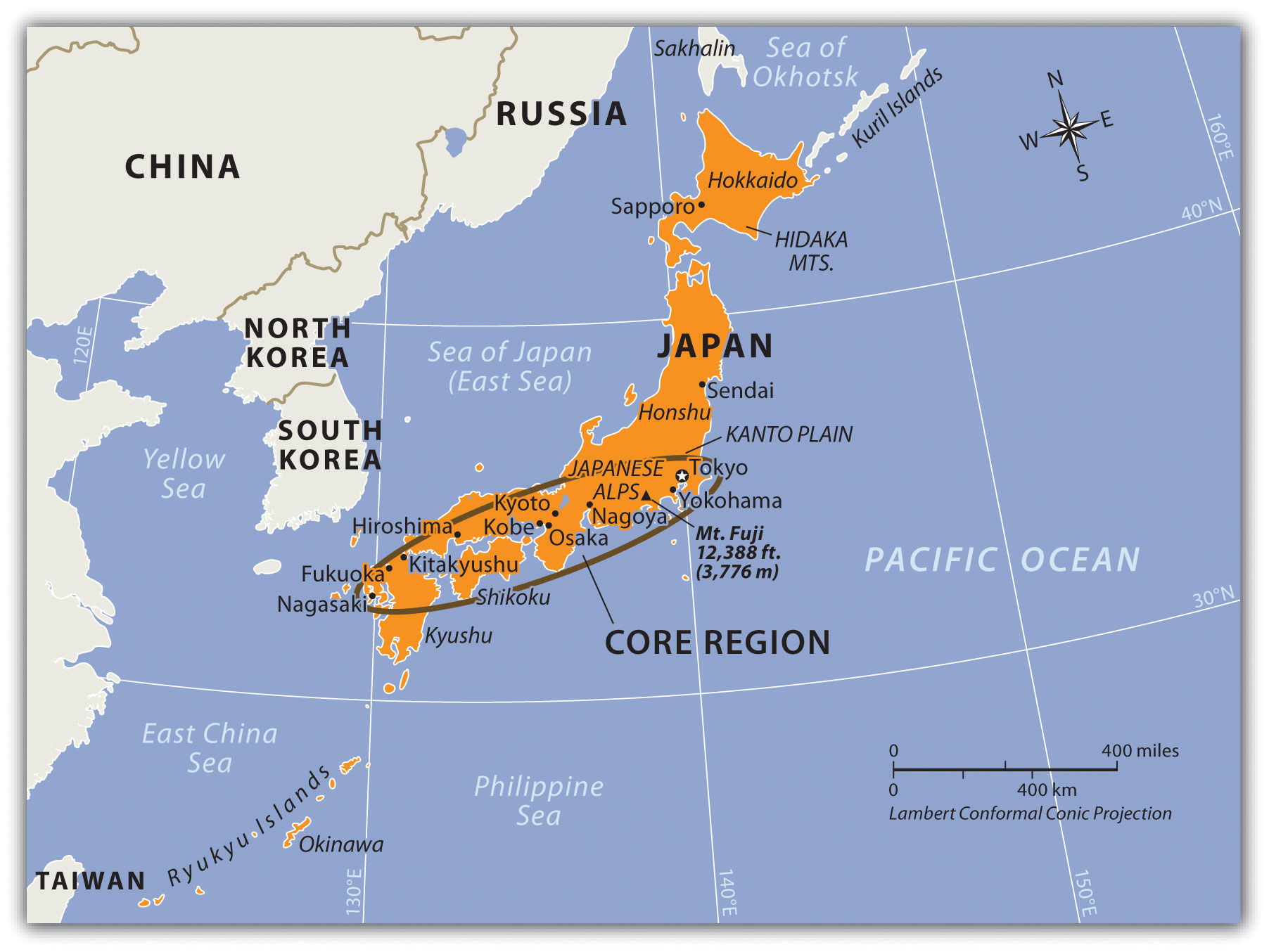
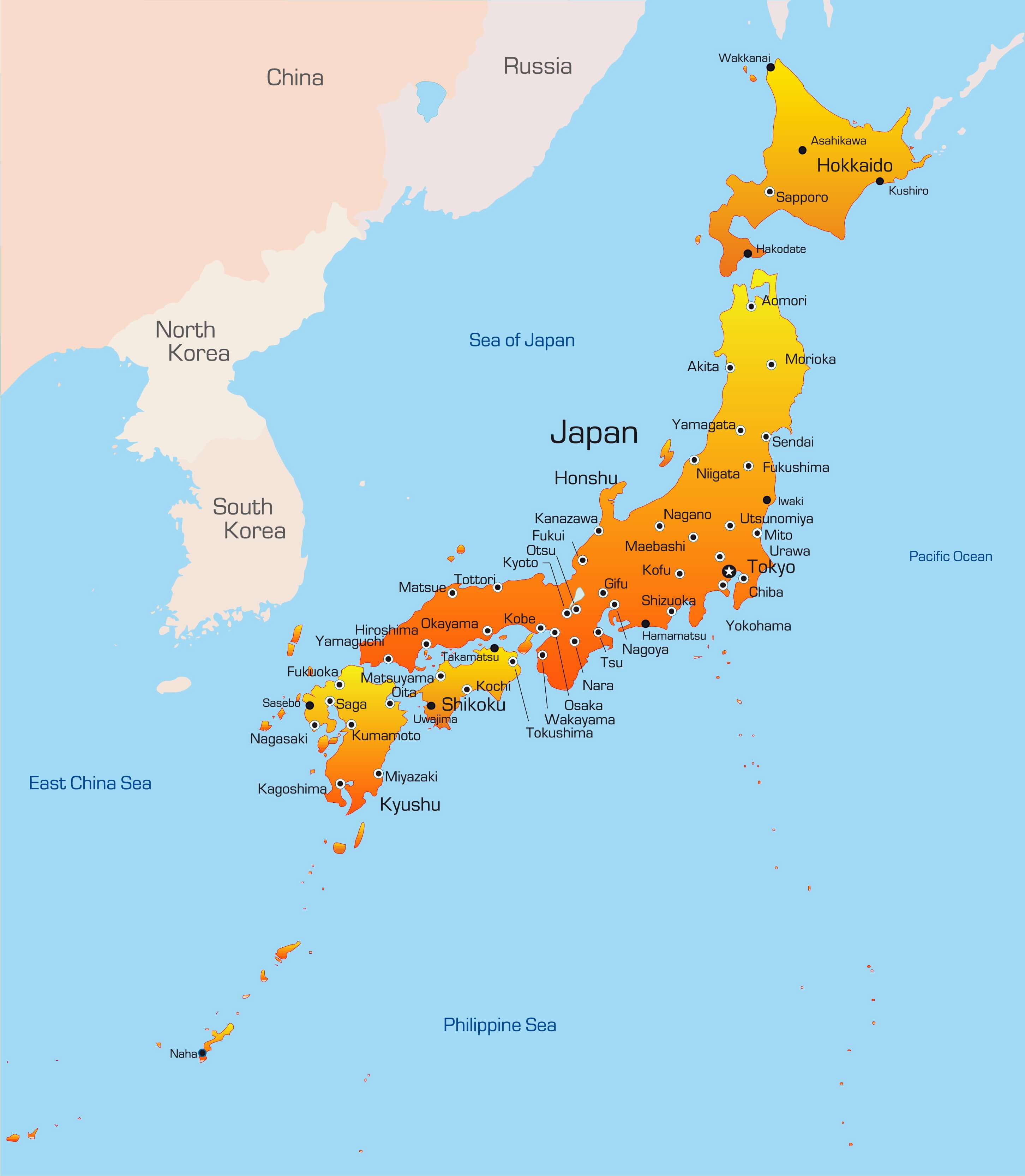
Japan’s geographical makeup is a defining characteristic. Comprised of four main islands – Hokkaido, Honshu, Shikoku, and Kyushu – and over 6,800 smaller islands, Japan’s landmass is predominantly mountainous, with approximately 73% of the country covered by forests. This mountainous terrain has historically posed challenges to transportation and development, but it has also fostered a deep appreciation for nature and a distinct sense of regional identity.
The Japanese archipelago sits on the Pacific Ring of Fire, a zone of intense seismic activity. This geographical reality has shaped Japan’s history, with frequent earthquakes, volcanic eruptions, and tsunamis. While these natural disasters can be devastating, they have also instilled a culture of resilience and preparedness, leading to advancements in disaster mitigation and infrastructure.
A Cultural Tapestry:
Japan’s cultural landscape is as diverse as its geography. Centuries of isolation fostered a unique cultural identity, marked by traditions like calligraphy, tea ceremony, and the intricate art of bonsai. The influence of Buddhism and Shintoism, two major religions, can be seen in temples, shrines, and festivals throughout the country.
Modern Japan has embraced globalization, incorporating elements of Western culture while retaining its distinct traditions. This blend of old and new is evident in everything from fashion and cuisine to music and technology. Japan’s pop culture, known as "kawaii" (cute) and "otaku" (obsessive fan), has gained global recognition, highlighting the nation’s creativity and its ability to bridge cultural divides.
Economic Powerhouse:
Japan’s post-World War II economic miracle is a testament to its resilience and adaptability. The nation transformed from a war-torn country to a global economic powerhouse, driven by technological innovation, a skilled workforce, and strong manufacturing capabilities. Japan’s manufacturing prowess is evident in its production of automobiles, electronics, and robotics, making it a significant player in the global economy.
While facing economic challenges in recent decades, Japan continues to be a leader in technological advancements. Its commitment to research and development has resulted in innovations in areas like artificial intelligence, robotics, and renewable energy. Japan’s economic influence extends beyond its own borders, with strong trade ties and investments across the globe.
International Relations and Global Influence:
Japan’s strategic location in East Asia has made it a key player in regional and global affairs. The nation has a strong alliance with the United States, a relationship forged in the aftermath of World War II. Japan also maintains close ties with its neighbors in Asia, playing a significant role in promoting regional stability and economic cooperation.
Japan’s commitment to international development and humanitarian assistance has earned it global respect. The nation has been a leading donor to developing countries, providing aid in areas like disaster relief, education, and healthcare. Japan’s active role in international organizations like the United Nations further underscores its commitment to global peace and cooperation.
Challenges and Opportunities:
Despite its successes, Japan faces a number of challenges. An aging population and declining birth rate pose significant demographic and economic pressures. The nation is also grappling with issues like climate change, resource scarcity, and the need for economic diversification.
However, these challenges also present opportunities for innovation and growth. Japan’s technological advancements and its focus on sustainability can contribute to addressing global challenges. The nation’s strong cultural identity and its commitment to education can attract talent and investment from around the world.
FAQs on Japan on the Map:
Q: What is the official language of Japan?
A: The official language of Japan is Japanese.
Q: What is the currency of Japan?
A: The currency of Japan is the Japanese yen (JPY).
Q: What is the capital city of Japan?
A: The capital city of Japan is Tokyo.
Q: What are the major industries in Japan?
A: Major industries in Japan include manufacturing (automobiles, electronics, robotics), technology, finance, and tourism.
Q: What are the main religions in Japan?
A: The main religions in Japan are Shintoism and Buddhism.
Q: What are some popular tourist destinations in Japan?
A: Popular tourist destinations in Japan include Tokyo, Kyoto, Mount Fuji, Hiroshima Peace Memorial Park, and the ancient temples and shrines of Nara.
Tips for Visiting Japan:
- Learn basic Japanese phrases: While English is spoken in tourist areas, knowing a few basic Japanese phrases will enhance your experience.
- Respect cultural norms: Japanese culture places a high value on politeness and etiquette. Be mindful of your behavior and dress appropriately.
- Plan your itinerary: Japan has a lot to offer, so it’s important to plan your itinerary in advance to make the most of your trip.
- Try local cuisine: Japanese cuisine is renowned for its freshness and diversity. Be sure to try traditional dishes like sushi, ramen, and tempura.
- Take advantage of public transportation: Japan’s public transportation system is efficient and reliable.
Conclusion:
Japan’s position on the map is not merely a geographical location. It signifies a nation that has navigated a complex history, embracing both tradition and innovation. From its stunning natural beauty to its vibrant cultural tapestry, Japan offers a unique and captivating experience for visitors. As a global economic and technological leader, Japan continues to shape the world, showcasing the power of resilience, adaptability, and a deep respect for its rich heritage.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Japan on the Map: A Nation of Contrasts and Enduring Influence. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!