Indonesia: A Maritime Archipelago At The Heart Of Southeast Asia
Indonesia: A Maritime Archipelago at the Heart of Southeast Asia
Related Articles: Indonesia: A Maritime Archipelago at the Heart of Southeast Asia
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Indonesia: A Maritime Archipelago at the Heart of Southeast Asia. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Indonesia: A Maritime Archipelago at the Heart of Southeast Asia
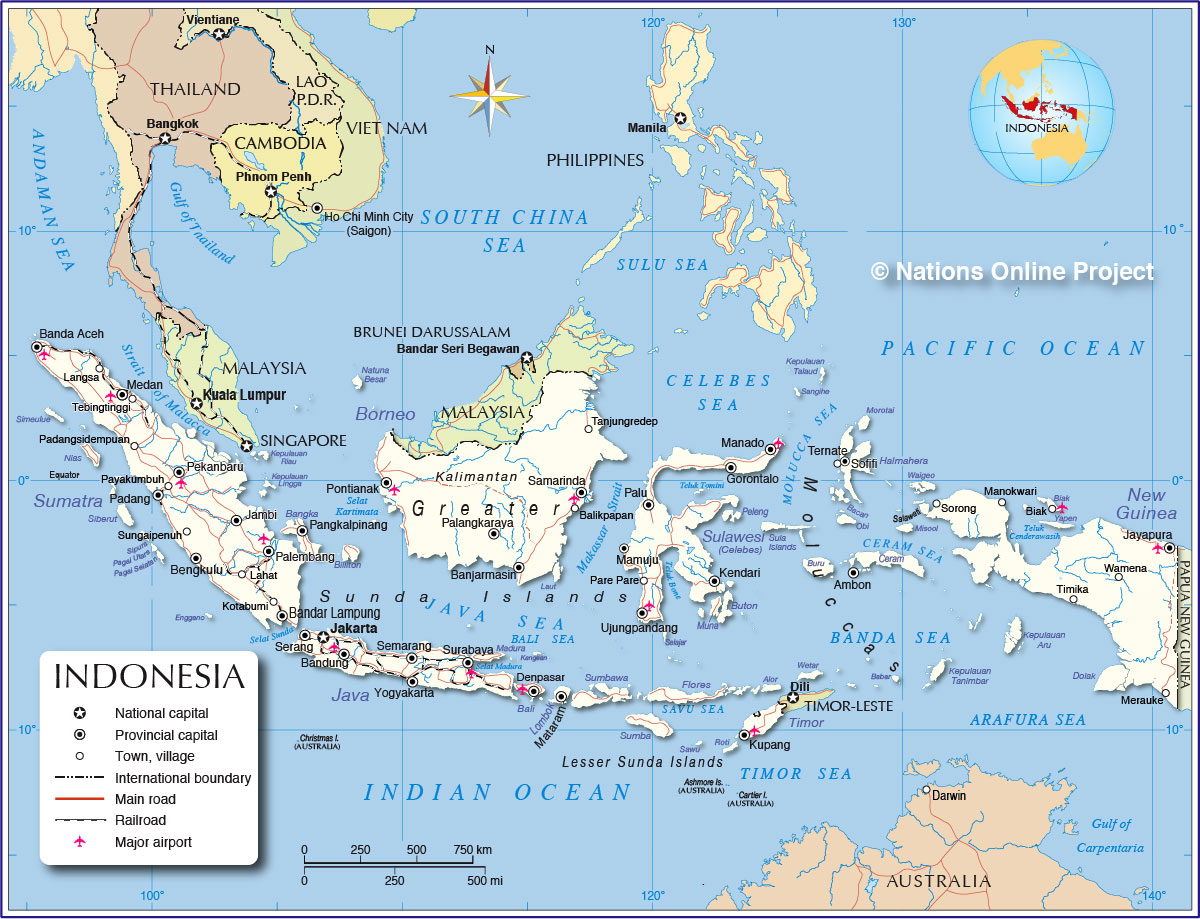
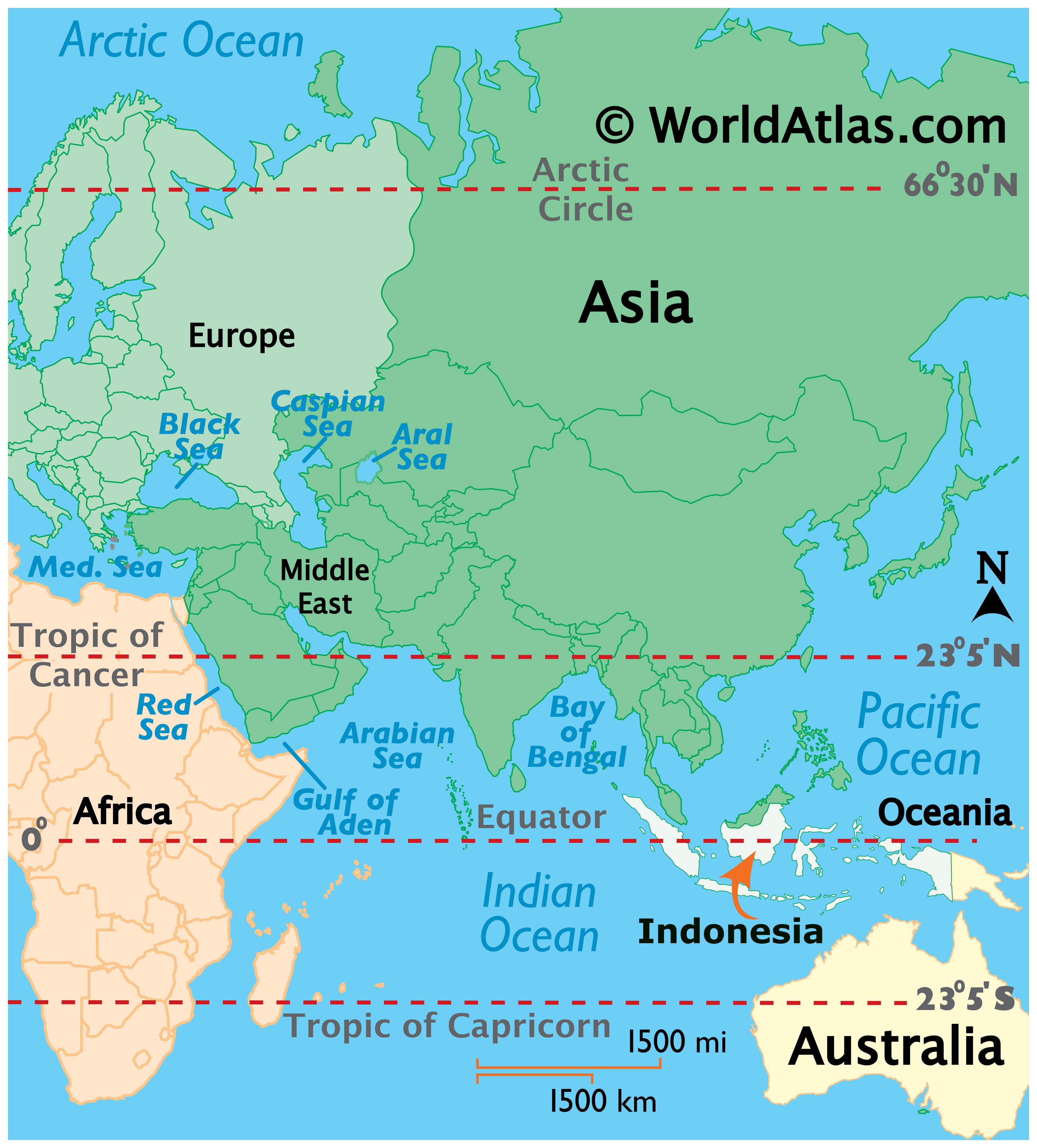
Indonesia, the world’s largest archipelago nation, sprawls across a vast expanse of the Earth’s surface, straddling the equator and encompassing over 17,000 islands. Its strategic location in Southeast Asia, nestled between the Indian and Pacific Oceans, has shaped its history, culture, and economy, making it a significant player in the global landscape.
A Tapestry of Diverse Landscapes:
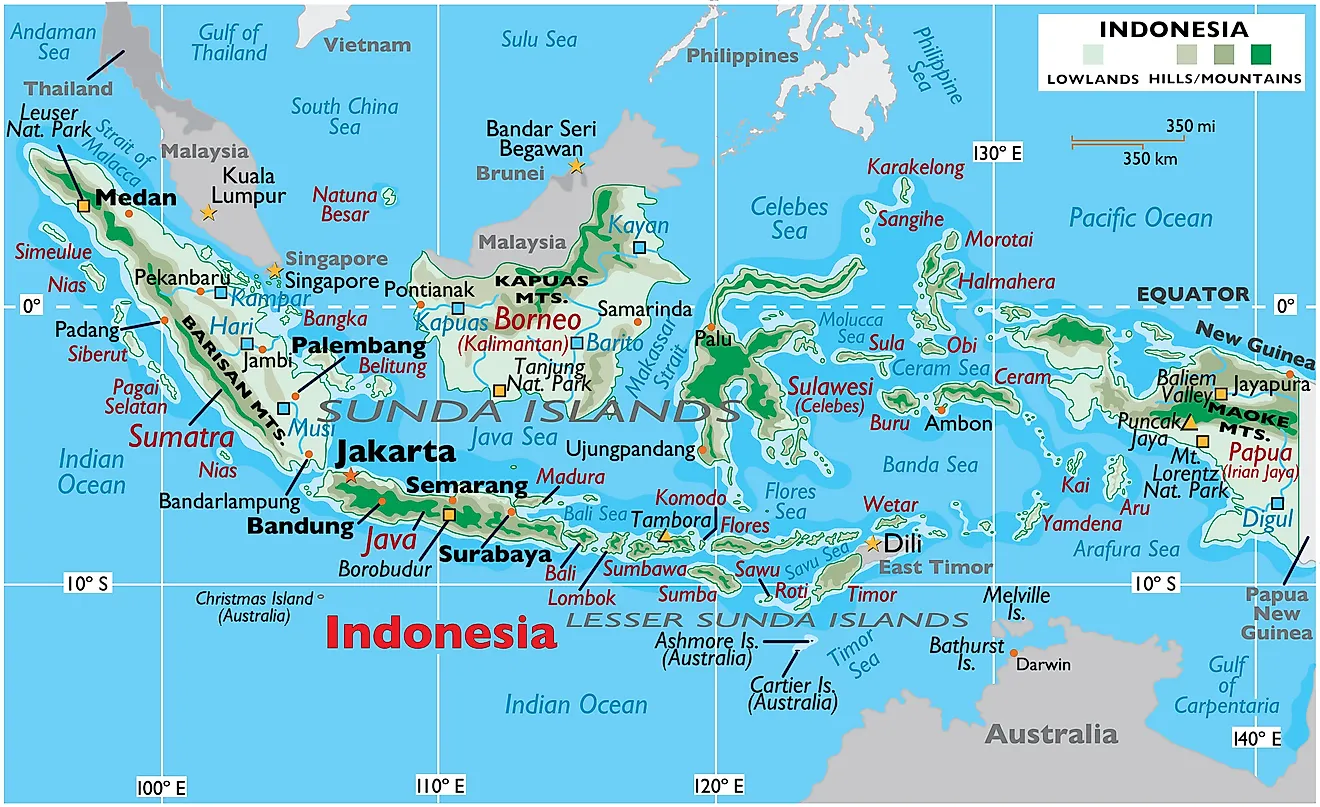
Indonesia’s geography is a testament to its geological dynamism, boasting diverse landscapes that range from towering volcanic peaks to lush rainforests, serene beaches, and sprawling rice paddies. The iconic Mount Merapi, a stratovolcano in Java, serves as a powerful reminder of the country’s volcanic origins. The island of Sumatra is home to the dense, biodiverse rainforests of Gunung Leuser National Park, while the Komodo National Park in Nusa Tenggara offers a glimpse into the prehistoric world of the Komodo dragon.
A Mosaic of Cultures:
Indonesia’s vast archipelago is home to over 250 million people, representing a breathtaking tapestry of ethnicities, languages, and religions. This cultural richness is reflected in the country’s vibrant traditions, art forms, and cuisine. From the intricate dances of Bali to the intricate batik patterns of Java, the artistic heritage of Indonesia is a testament to its diverse cultural heritage. The country’s culinary scene is equally diverse, offering a range of flavors and ingredients, from the spicy rendang of Sumatra to the savory nasi goreng of Java.
Economic Powerhouse in Southeast Asia:
Indonesia’s strategic location and diverse resources have propelled it to become a leading economic force in Southeast Asia. Its vast natural resources, including oil, gas, tin, and rubber, have fueled its industrial growth. The country’s manufacturing sector is also booming, producing a wide range of goods, from textiles and electronics to automobiles and pharmaceuticals.
Navigating Challenges and Opportunities:
Despite its economic progress, Indonesia faces a number of challenges, including poverty, inequality, and environmental degradation. The country’s rapid economic growth has put a strain on its natural resources, leading to deforestation and pollution. Addressing these challenges will require sustainable development strategies that prioritize environmental protection and social inclusion.
Global Significance and International Relations:
Indonesia plays a significant role in international affairs, actively engaging in global issues such as climate change, terrorism, and economic development. As a member of the Association of Southeast Asian Nations (ASEAN), Indonesia advocates for regional cooperation and stability. Its commitment to multilateralism and international cooperation has earned it respect and recognition on the global stage.
FAQs
1. What is Indonesia’s geographical location?
Indonesia is located in Southeast Asia, straddling the equator and encompassing over 17,000 islands. It is situated between the Indian Ocean and the Pacific Ocean.
2. What are some of Indonesia’s major islands?
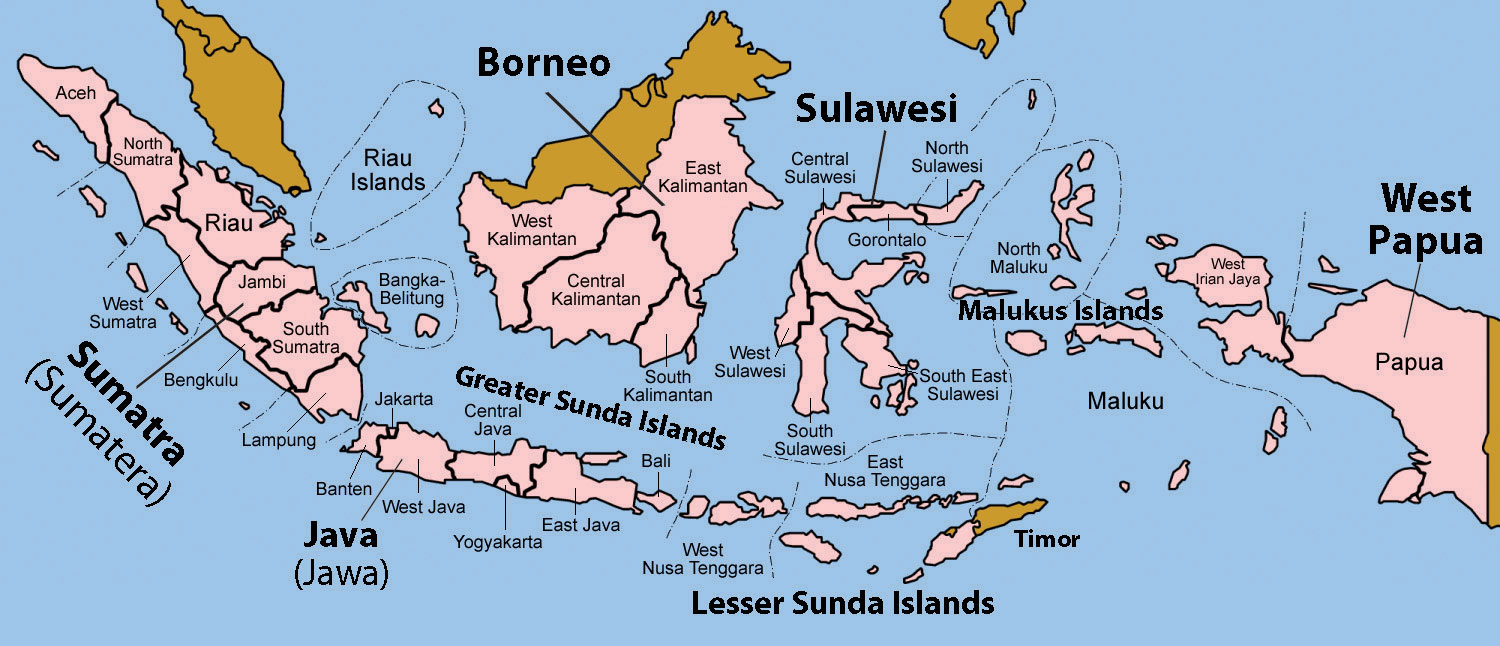
Indonesia’s major islands include Java, Sumatra, Borneo (shared with Malaysia and Brunei), Sulawesi, Papua (shared with Papua New Guinea), and the islands of Bali and Lombok.
3. What is Indonesia’s population?
Indonesia has a population of over 250 million people, making it the world’s fourth most populous country.
4. What is Indonesia’s official language?
Indonesia’s official language is Bahasa Indonesia, a standardized form of Malay. However, hundreds of regional languages and dialects are also spoken throughout the country.
5. What are some of Indonesia’s major religions?
Islam is the dominant religion in Indonesia, followed by Christianity, Hinduism, and Buddhism.
6. What are some of Indonesia’s major industries?
Indonesia’s major industries include oil and gas, mining, agriculture, manufacturing, and tourism.
7. What are some of the challenges facing Indonesia?
Indonesia faces challenges such as poverty, inequality, environmental degradation, and corruption.
8. What is Indonesia’s role in international affairs?
Indonesia plays a significant role in international affairs, actively engaging in global issues such as climate change, terrorism, and economic development. It is a member of the Association of Southeast Asian Nations (ASEAN) and advocates for regional cooperation and stability.
Tips for Visiting Indonesia:
- Plan your itinerary carefully: Indonesia is a vast country with diverse landscapes and cultures. Allocate sufficient time to explore the regions that interest you.
- Respect local customs: Indonesia is a predominantly Muslim country. Dress modestly and be mindful of local customs and traditions.
- Learn some basic Indonesian phrases: Even a few basic phrases can go a long way in enhancing your travel experience.
- Try the local cuisine: Indonesian cuisine is a delicious and diverse culinary adventure. Be sure to sample the local specialties.
- Enjoy the natural beauty: Indonesia is home to some of the most stunning natural landscapes in the world. Take the opportunity to explore its beaches, rainforests, and mountains.
- Be prepared for the weather: Indonesia is a tropical country with a humid climate. Pack lightweight clothing and be prepared for frequent rain showers.
- Stay safe: Be aware of your surroundings and take precautions to protect yourself from crime and scams.
Conclusion:
Indonesia, with its diverse landscapes, vibrant culture, and strategic location, is a country of immense beauty and significance. Its rich history, diverse ethnicities, and economic potential make it a fascinating and dynamic nation. While it faces challenges, Indonesia’s commitment to sustainable development and its active role in international affairs offer hope for a brighter future. As a nation that continues to evolve and grow, Indonesia’s position on the world map is sure to remain prominent and influential for generations to come.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Indonesia: A Maritime Archipelago at the Heart of Southeast Asia. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!