Exploring The Geography And Significance Of Kenya On The Map Of Africa
Exploring the Geography and Significance of Kenya on the Map of Africa
Related Articles: Exploring the Geography and Significance of Kenya on the Map of Africa
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Exploring the Geography and Significance of Kenya on the Map of Africa. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Exploring the Geography and Significance of Kenya on the Map of Africa
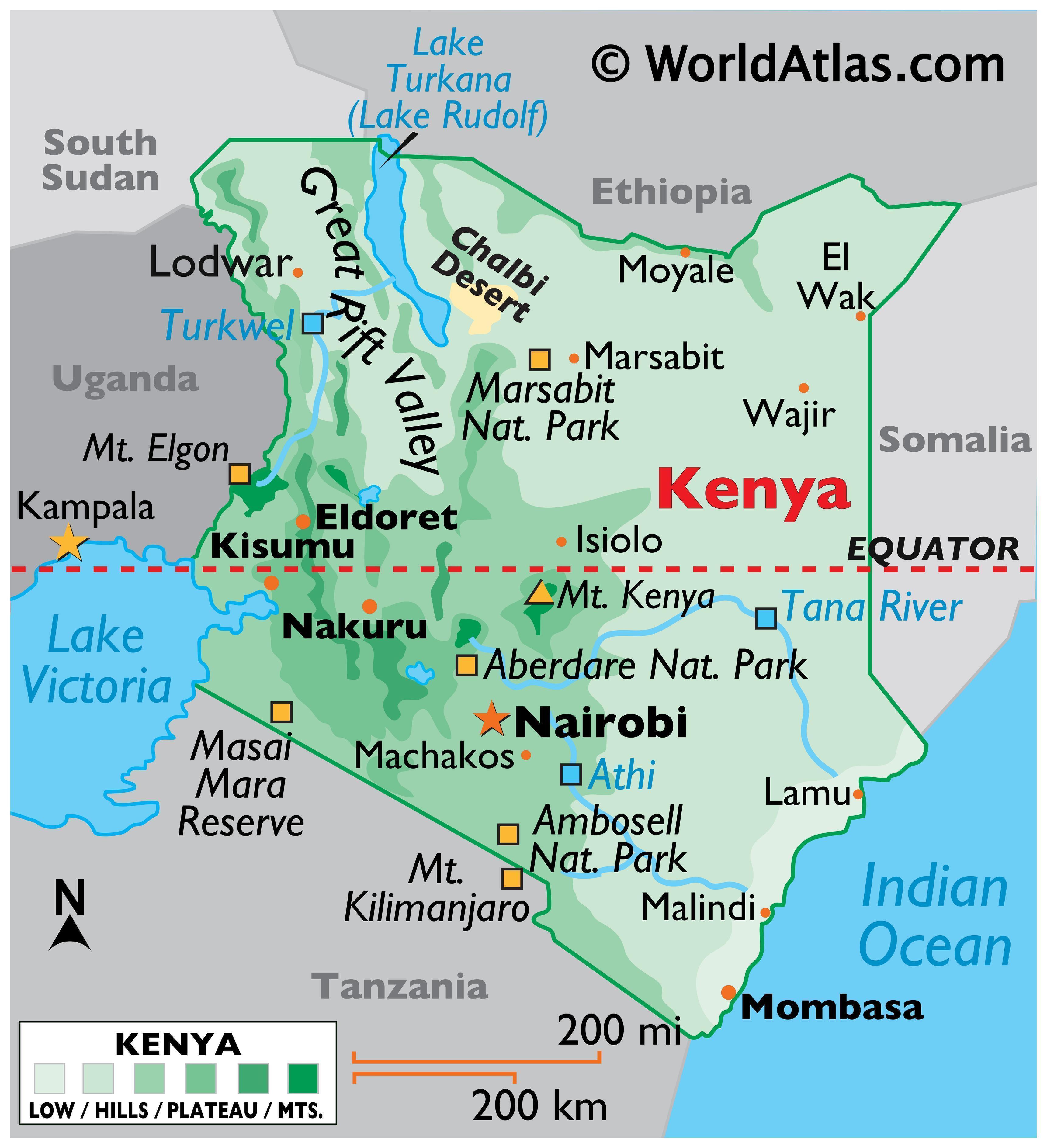
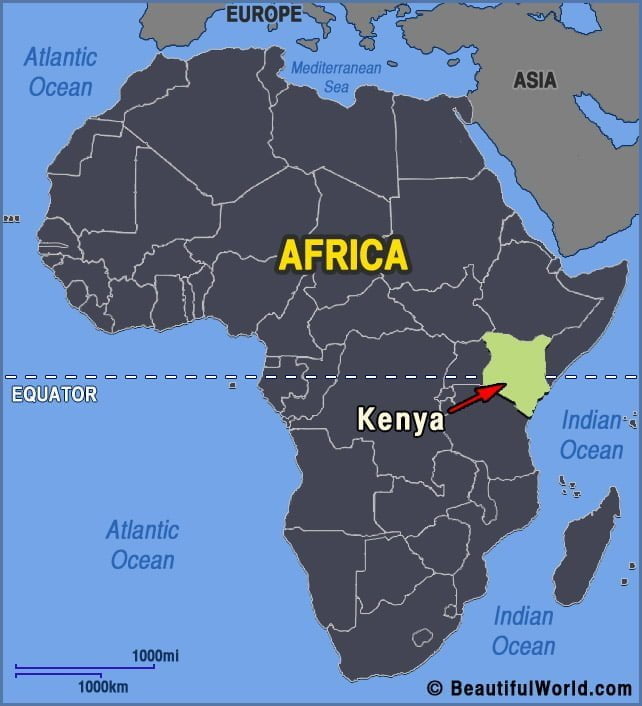
Kenya, a vibrant East African nation, occupies a prominent position on the map of Africa. Its diverse landscapes, rich cultural heritage, and strategic location have shaped its history, influenced its development, and contributed to its global significance. This article delves into the geographical features, cultural tapestry, and economic landscape of Kenya, providing a comprehensive understanding of its role in the African continent and the world.
Geographical Landscape: A Tapestry of Diversity
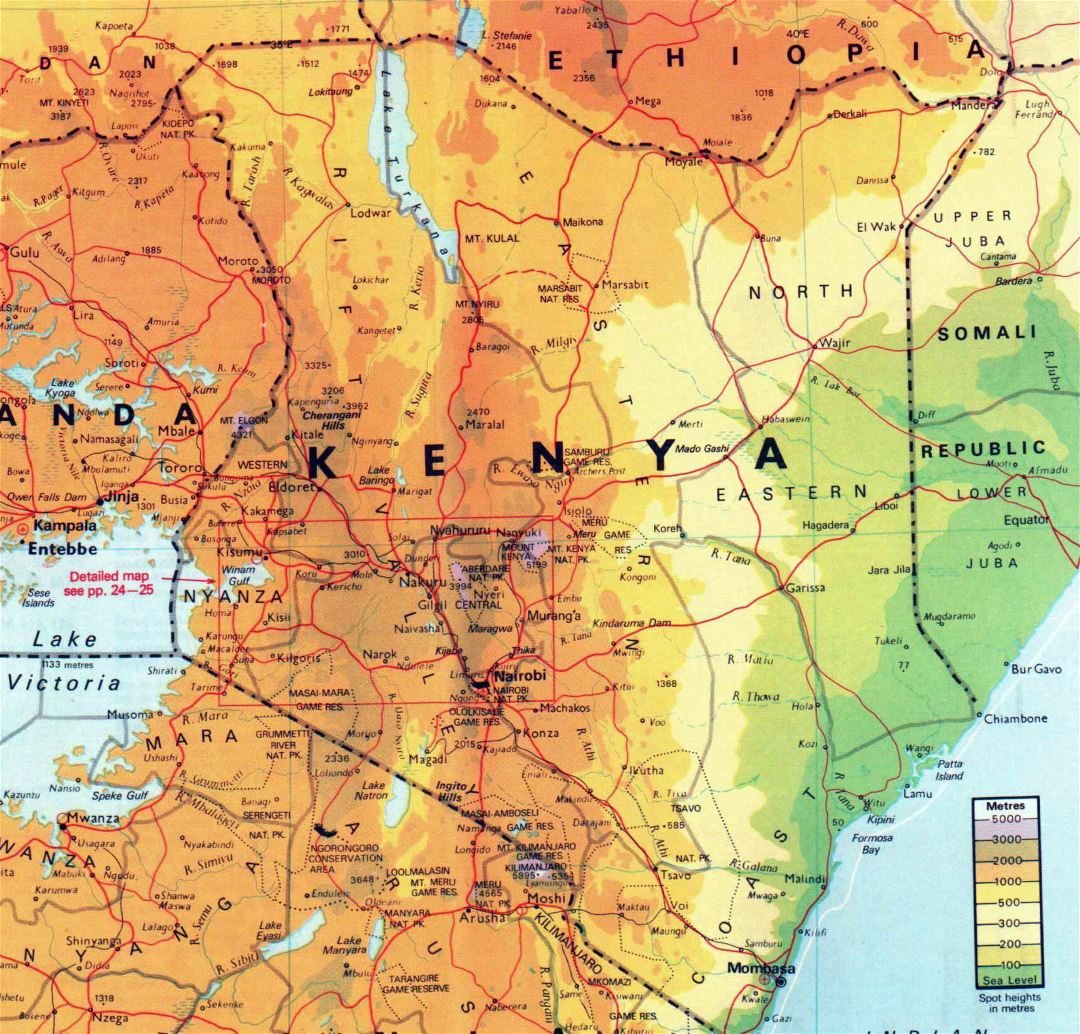
Kenya’s geography is a striking mosaic of contrasting landscapes, ranging from the snow-capped peaks of Mount Kenya to the arid plains of the Northern Frontier District. This diversity is reflected in its varied ecosystems, which support a rich biodiversity.
-
The Rift Valley: A defining feature of Kenya’s landscape, the Great Rift Valley stretches across the country, creating a series of dramatic escarpments, volcanic lakes, and fertile valleys. The valley is home to iconic landmarks like Lake Nakuru, known for its flamingo colonies, and the Maasai Mara National Reserve, renowned for its annual wildebeest migration.
-
Highlands: The central highlands, dominated by Mount Kenya and Mount Elgon, provide a cooler climate and fertile soils, ideal for agriculture. This region is also home to the country’s largest cities, Nairobi and Mombasa, and serves as a vital economic hub.
-
Coastal Plains: The Indian Ocean coastline, characterized by sandy beaches and coral reefs, offers breathtaking scenery and attracts tourists from around the world. The coastal region is also a vital economic engine, driven by tourism, fishing, and trade.
-
Arid and Semi-Arid Regions: The vast northern and eastern regions of Kenya are characterized by arid and semi-arid landscapes, with limited rainfall and sparse vegetation. This region is home to diverse nomadic communities, including the Samburu, Turkana, and Rendille, who have adapted to the harsh conditions.
Cultural Heritage: A Tapestry of Traditions
Kenya’s cultural heritage is as diverse as its landscape, reflecting the influence of its numerous ethnic groups and their unique traditions.
-
Ethnic Diversity: Kenya is home to over 40 distinct ethnic groups, each with its own language, customs, and beliefs. The largest groups include the Kikuyu, Luo, Luhya, and Kalenjin.
-
Traditional Practices: Traditional practices, such as music, dance, storytelling, and crafts, play a vital role in Kenyan culture. These traditions are often passed down through generations, preserving the rich heritage of the different communities.
-
Religious Diversity: Kenya is a religiously diverse country, with Christianity, Islam, and traditional African religions all being widely practiced. This diversity fosters a spirit of tolerance and understanding.
Economic Landscape: A Dynamic and Growing Economy
Kenya’s economy is characterized by its growing services sector, vibrant agricultural industry, and burgeoning tourism sector.
-
Services Sector: The services sector, particularly finance, telecommunications, and tourism, plays a dominant role in Kenya’s economy. Nairobi has emerged as a regional financial hub, attracting foreign investment and driving economic growth.
-
Agriculture: Agriculture is a vital sector, employing a significant portion of the population and contributing to food security. Kenya is a major exporter of coffee, tea, and horticultural products.
-
Tourism: Kenya’s diverse landscapes and wildlife attract millions of tourists each year, making it a major contributor to the economy. The tourism sector supports a wide range of businesses, from hotels and lodges to safari operators and cultural attractions.
Strategic Location: A Gateway to East Africa
Kenya’s strategic location on the eastern coast of Africa has made it a vital trade and transport hub.
-
Port of Mombasa: Mombasa, Kenya’s largest port, serves as a gateway to the East African hinterland, facilitating trade with neighboring countries and the rest of the world.
-
Regional Hub: Kenya’s well-developed infrastructure, including its road, rail, and air networks, makes it a regional hub for trade, investment, and development.
-
Regional Integration: Kenya is a key member of regional organizations like the East African Community (EAC), promoting economic integration and cooperation within the region.
Challenges and Opportunities:
Despite its progress, Kenya faces a number of challenges, including poverty, inequality, and environmental degradation. However, the country also has significant opportunities for growth and development, fueled by its young and growing population, its entrepreneurial spirit, and its strategic location.
Conclusion:
Kenya’s journey on the map of Africa is one of remarkable diversity, resilience, and progress. Its unique geography, vibrant culture, and dynamic economy have shaped its identity and contributed to its growing influence on the continent and the world. As Kenya continues to navigate the challenges and opportunities of the 21st century, its position on the map of Africa will undoubtedly continue to evolve, reflecting its enduring spirit and its commitment to progress.
FAQs about Kenya:
Q: What is the capital city of Kenya?
A: The capital city of Kenya is Nairobi.
Q: What is the currency of Kenya?
A: The currency of Kenya is the Kenyan shilling (KES).
Q: What are the main languages spoken in Kenya?
A: The official languages of Kenya are English and Swahili. However, over 40 different languages are spoken across the country.
Q: What is the population of Kenya?
A: The population of Kenya is estimated to be around 54 million.
Q: What are some of the major industries in Kenya?
A: Kenya’s major industries include agriculture, tourism, services (finance, telecommunications), manufacturing, and energy.
Q: What are some of the major tourist attractions in Kenya?
A: Kenya’s major tourist attractions include the Maasai Mara National Reserve, Amboseli National Park, Tsavo National Parks, Mount Kenya, Lake Nakuru National Park, and the coastal beaches of Mombasa and Diani.
Tips for Visiting Kenya:
- Obtain a visa: Most visitors to Kenya require a visa. It is advisable to apply for a visa in advance of your trip.
- Pack for the climate: Kenya’s climate varies significantly depending on the region. Pack appropriate clothing for both hot and cool temperatures.
- Respect local customs: Kenya is a culturally diverse country. It is important to be respectful of local customs and traditions.
- Be aware of health risks: Before traveling to Kenya, consult with your doctor about necessary vaccinations and health precautions.
- Plan your itinerary: Kenya offers a wide range of attractions and activities. It is advisable to plan your itinerary in advance to make the most of your trip.
Conclusion:
Kenya is a fascinating and dynamic country with a rich history, diverse culture, and vibrant economy. Its strategic location on the map of Africa makes it a vital hub for trade, investment, and development. By understanding its geography, culture, and economic landscape, we can appreciate the unique contributions Kenya makes to the African continent and the world. As Kenya continues to evolve and progress, its presence on the map of Africa will undoubtedly continue to grow in importance, reflecting its resilience, its entrepreneurial spirit, and its commitment to a brighter future.
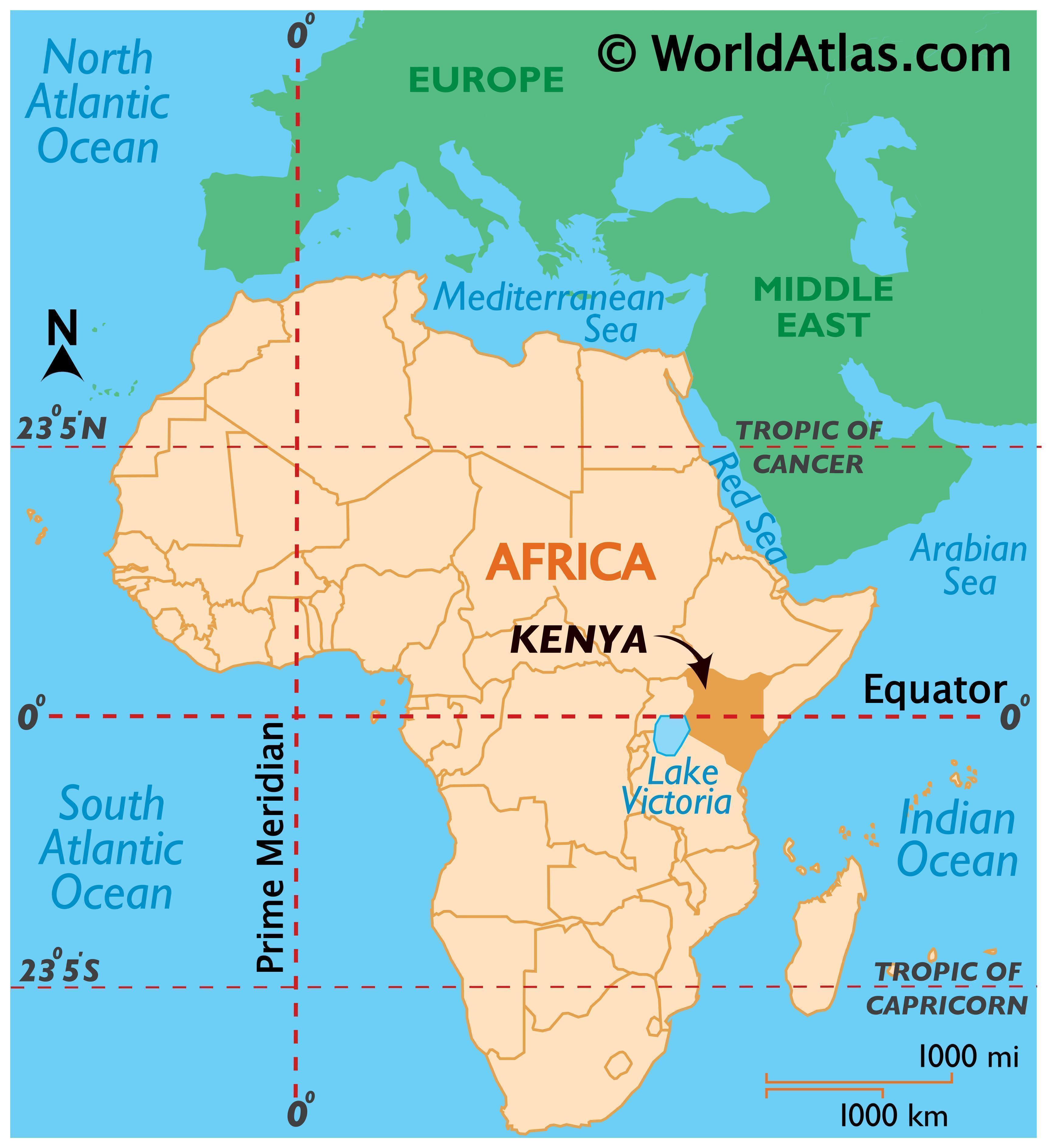
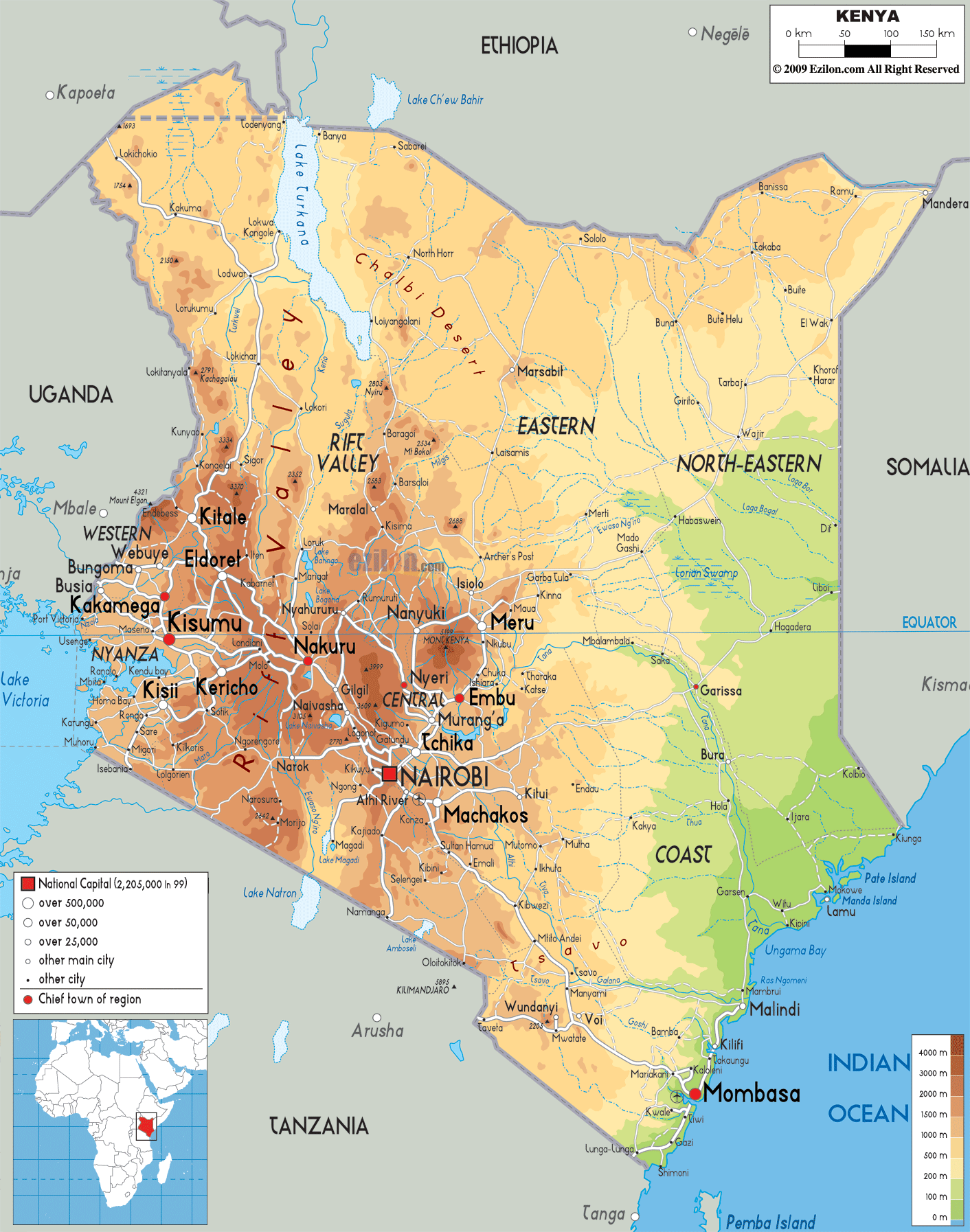


Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Exploring the Geography and Significance of Kenya on the Map of Africa. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!