Delineating Democracy: A Comprehensive Look At Indiana’s State Senate District Map
Delineating Democracy: A Comprehensive Look at Indiana’s State Senate District Map
Related Articles: Delineating Democracy: A Comprehensive Look at Indiana’s State Senate District Map
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Delineating Democracy: A Comprehensive Look at Indiana’s State Senate District Map. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Delineating Democracy: A Comprehensive Look at Indiana’s State Senate District Map
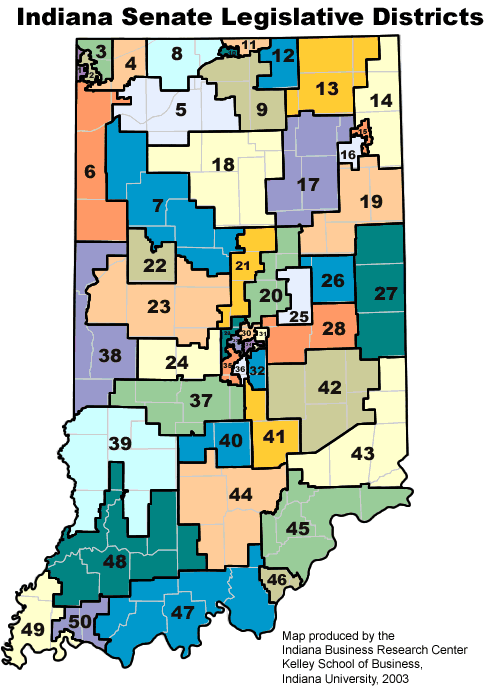
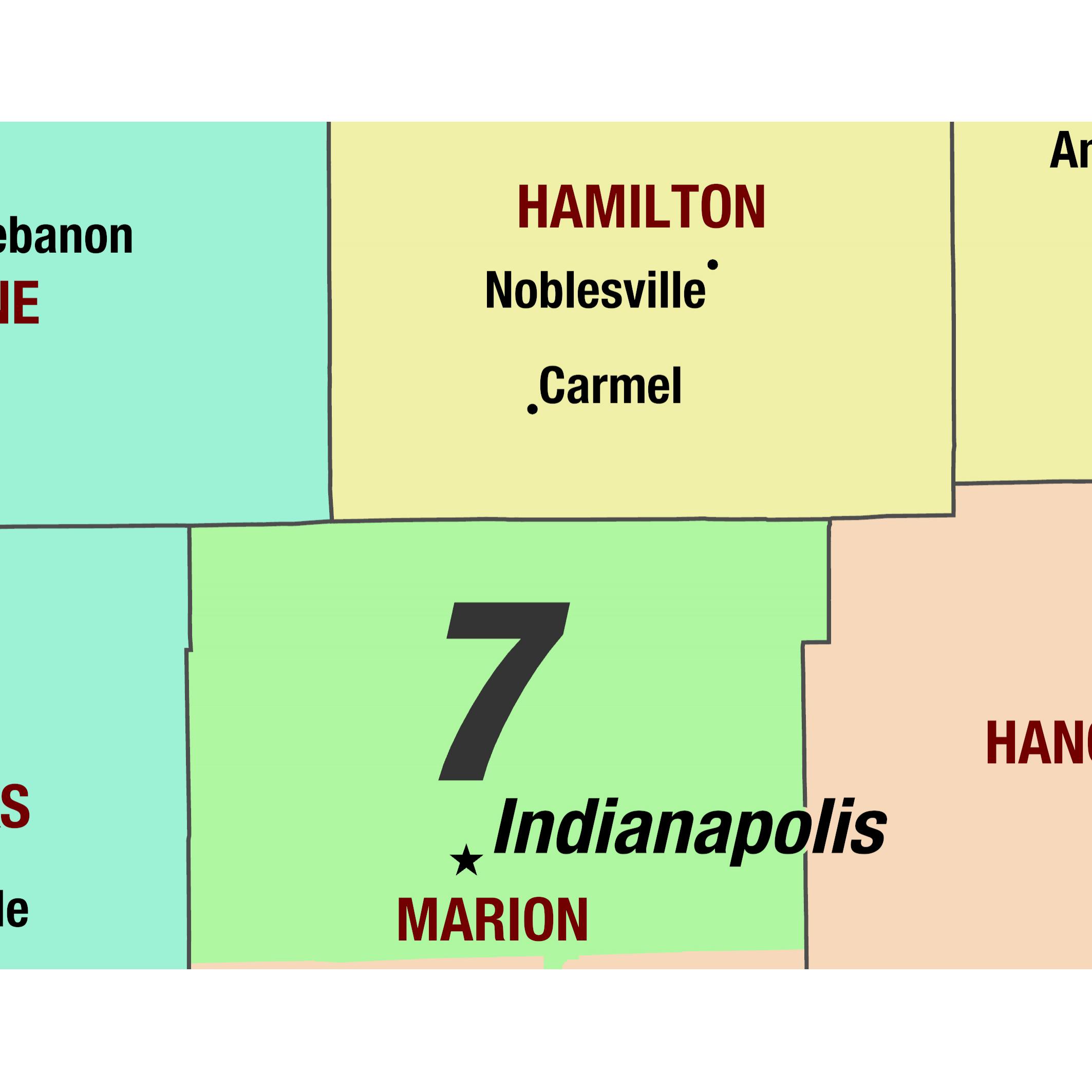
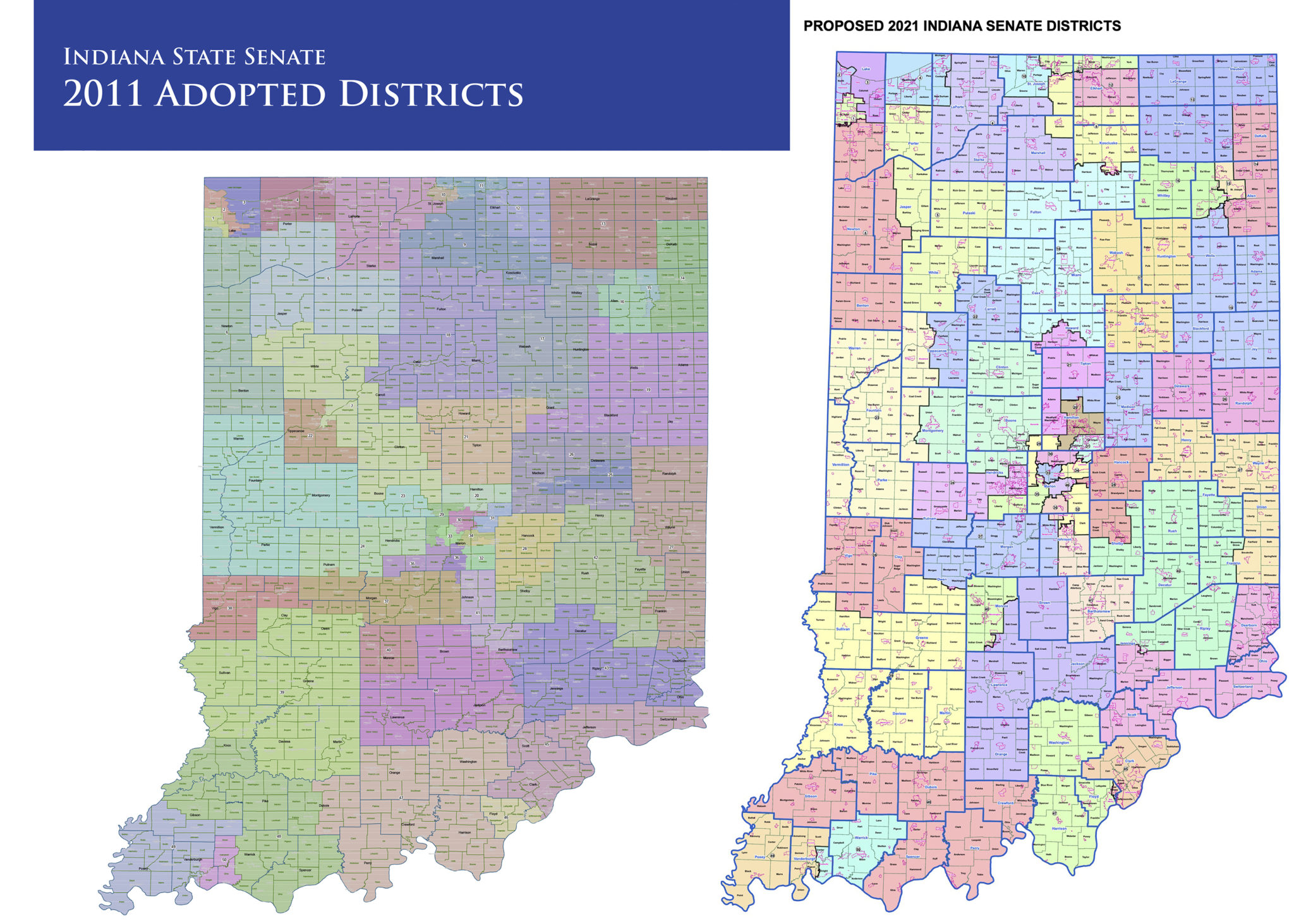
The Indiana State Senate district map serves as a foundational element of the state’s political landscape, defining the boundaries of electoral representation for the upper chamber of the Indiana General Assembly. This map, subject to periodic redrawing, directly impacts the political power dynamics within the state, influencing the composition of the Senate and, consequently, the legislative process itself.
Understanding the Map’s Structure and Significance:
Indiana’s State Senate comprises 50 districts, each representing a geographically defined area within the state. These districts are not static, as the map undergoes a redistricting process every ten years following the decennial census. The redistricting process aims to ensure that each district contains roughly the same population, adhering to the principle of "one person, one vote." This process, however, is not devoid of political influence, as decisions regarding district boundaries can strategically favor certain political parties or incumbents.
Historical Context and Evolution:
The current Indiana State Senate district map is the product of a long and evolving history. The state’s first constitution, adopted in 1816, established a Senate with 50 members, each representing a county. Over time, as the state’s population grew and shifted, the need for a more equitable representation system became apparent. This led to the adoption of multi-county districts, with the number of senators remaining at 50.
The redistricting process, mandated by the federal Voting Rights Act of 1965, has undergone significant changes over the years. Initially, the process was largely controlled by state legislatures, often resulting in gerrymandering, the manipulation of district boundaries to favor a particular party. However, with the rise of judicial oversight and the increasing use of data-driven techniques, the redistricting process has become more complex and subject to greater scrutiny.
The Impact of Redistricting:
The redistricting process carries significant implications for Indiana’s political landscape. The redrawing of district boundaries can influence the following:
- Electoral Outcomes: By strategically drawing district lines, political parties can create safe seats for their candidates, potentially leading to a disproportionate representation of one party over another.
- Representation of Minority Groups: Redistricting can impact the representation of minority groups, either by creating districts with a majority of minority voters or diluting their voting power by spreading them across multiple districts.
- Legislative Power Dynamics: The composition of the Senate, determined by the district map, directly influences the legislative process. A dominant party in the Senate can shape the agenda, control committee assignments, and ultimately influence the passage of legislation.
The Challenges of Redistricting:
The redistricting process is inherently complex, involving balancing competing interests and navigating legal requirements. Some of the key challenges include:
- Fairness and Equality: Ensuring that each district contains roughly the same population while maintaining geographically coherent communities poses a significant challenge.
- Political Influence: The redistricting process is often influenced by political considerations, leading to accusations of gerrymandering and unfair advantage.
- Transparency and Public Participation: The redistricting process should be transparent and involve meaningful public participation to ensure that the concerns of all stakeholders are heard.
FAQs about the Indiana State Senate District Map:
1. How often is the Indiana State Senate district map redrawn?
The Indiana State Senate district map is redrawn every ten years following the decennial census. This is mandated by the federal Voting Rights Act of 1965 to ensure that each district contains roughly the same population.
2. Who is responsible for redrawing the Indiana State Senate district map?
The responsibility for redrawing the Indiana State Senate district map lies with the Indiana General Assembly. The legislature establishes a redistricting commission, typically composed of members from both the House and Senate, to oversee the process.
3. What are the criteria used for redrawing the Indiana State Senate district map?
The primary criterion for redrawing the Indiana State Senate district map is population equality. Each district must contain roughly the same number of people to ensure that each voter has an equal say in the electoral process. Other considerations include maintaining geographically coherent communities, respecting existing political boundaries, and minimizing the division of counties.
4. How can I get involved in the redistricting process?
The redistricting process is open to public participation. Individuals can engage with the redistricting commission by attending public hearings, submitting written testimony, and contacting their elected officials to express their concerns.
5. What are the potential consequences of gerrymandering?
Gerrymandering, the manipulation of district boundaries to favor a particular party, can lead to a number of negative consequences, including:
- Reduced competition in elections, leading to a lack of accountability and responsiveness from elected officials.
- Reduced representation of minority groups, as their voting power may be diluted or concentrated in a few districts.
- A lack of diversity in the legislature, as one party may dominate the chamber.
Tips for Understanding and Engaging with the Indiana State Senate District Map:
- Stay informed: Follow news coverage and reports about the redistricting process.
- Engage with your elected officials: Contact your state senators and representatives to express your views on redistricting.
- Participate in public hearings: Attend public hearings held by the redistricting commission to provide input on the process.
- Educate yourself about the redistricting process: Learn about the criteria used for redrawing district boundaries and the potential consequences of gerrymandering.
Conclusion:
The Indiana State Senate district map plays a vital role in shaping the state’s political landscape. It determines the boundaries of electoral representation, influencing the composition of the Senate and, consequently, the legislative process itself. Understanding the structure, significance, and challenges of the redistricting process is crucial for informed civic engagement and ensuring a fair and equitable representation system in Indiana. By staying informed, engaging with elected officials, and participating in the process, citizens can contribute to shaping the future of the state’s political landscape.
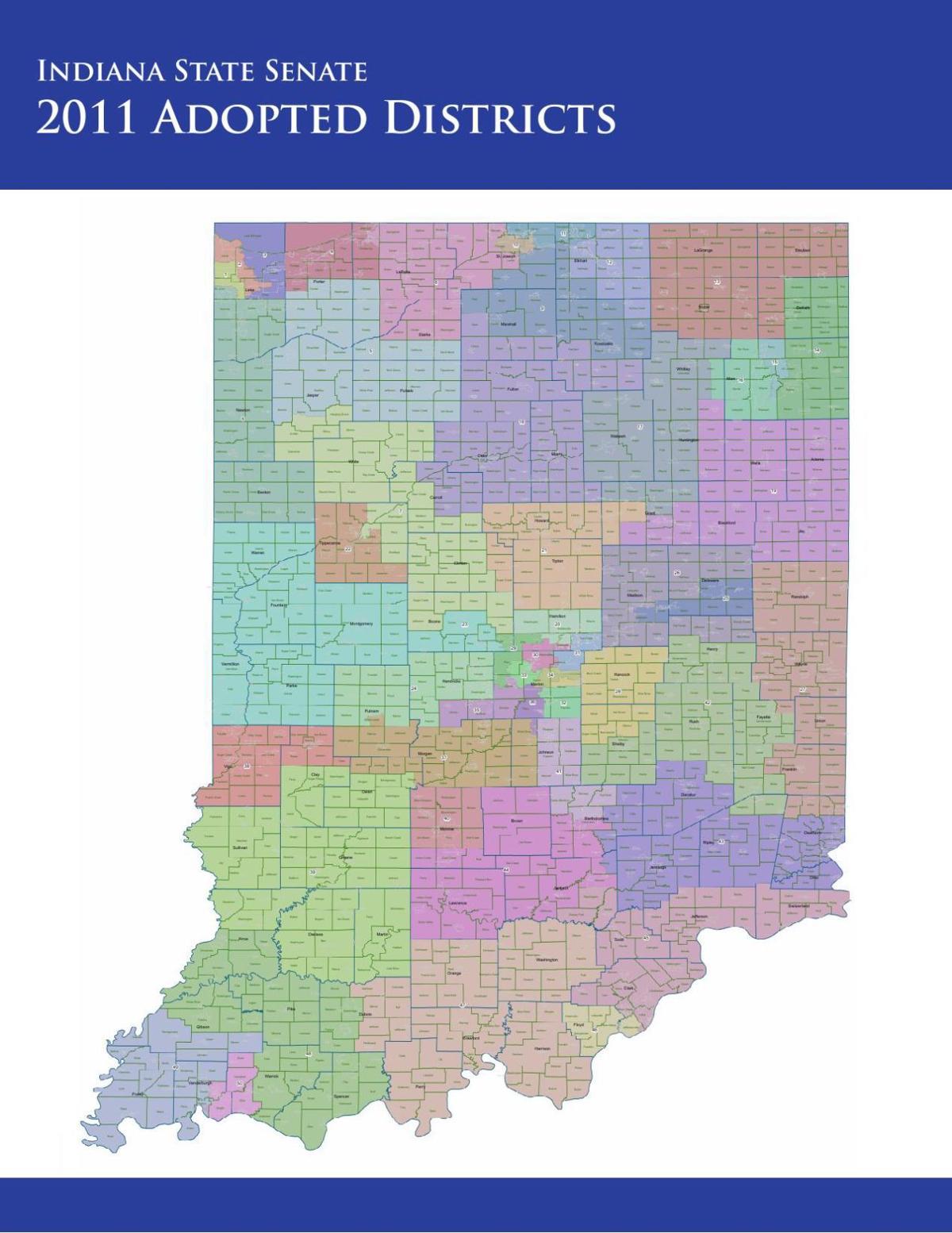
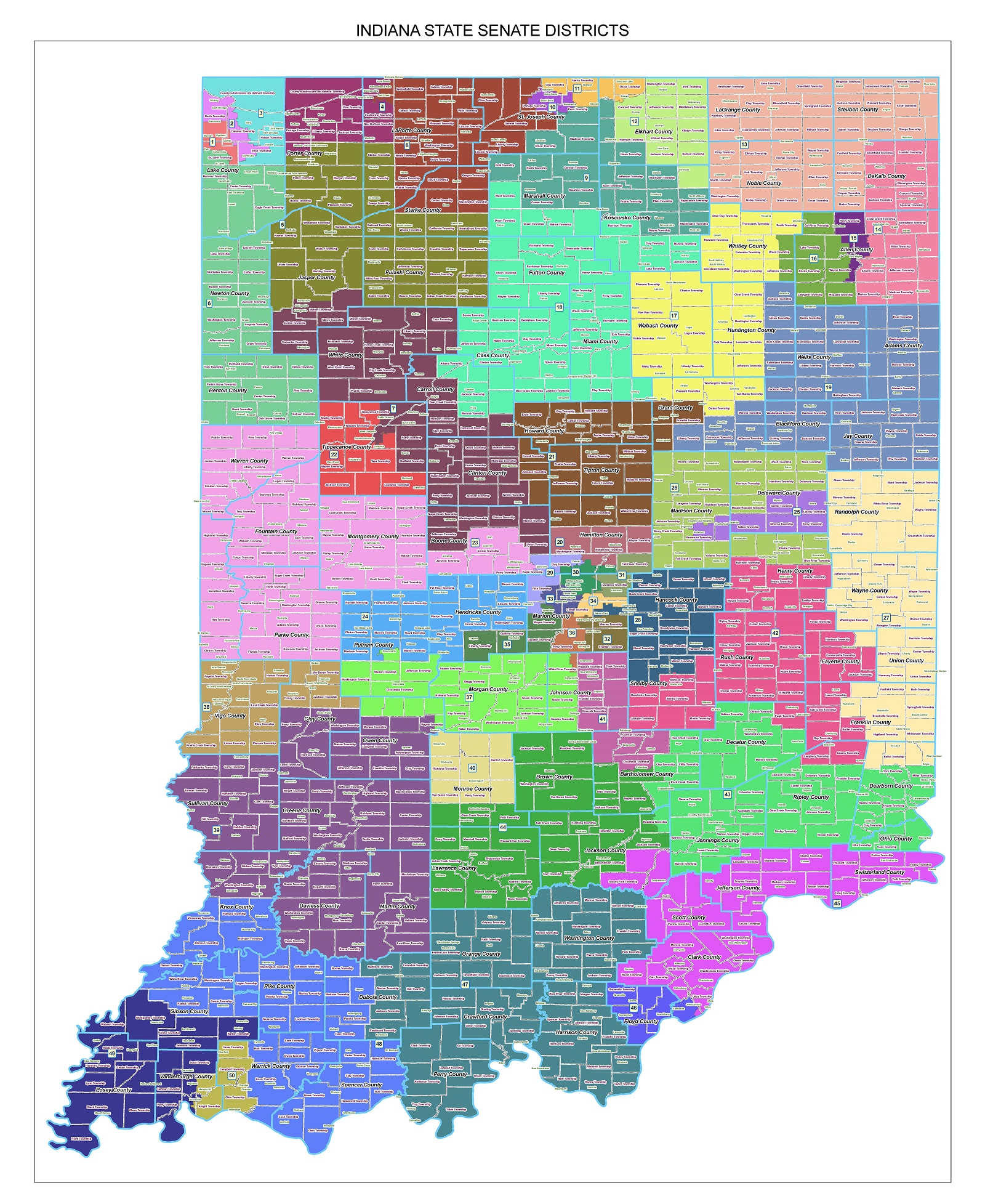


Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Delineating Democracy: A Comprehensive Look at Indiana’s State Senate District Map. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!