Decoding Japan’s Climate Zones: A Comprehensive Guide
Decoding Japan’s Climate Zones: A Comprehensive Guide
Related Articles: Decoding Japan’s Climate Zones: A Comprehensive Guide
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Decoding Japan’s Climate Zones: A Comprehensive Guide. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: Decoding Japan’s Climate Zones: A Comprehensive Guide
- 2 Introduction
- 3 Decoding Japan’s Climate Zones: A Comprehensive Guide
- 3.1 Understanding Japan’s Climate Zones: A Geographical Perspective
- 3.2 A Deeper Dive into Japan’s Climate Zones: The Köppen-Geiger Classification System
- 3.3 The Significance of Japan’s Climate Zones: Understanding the Impacts
- 3.4 FAQs: Exploring the Nuances of Japan’s Climate Zones
- 3.5 Tips: Navigating Japan’s Climate Zones for a Seamless Experience
- 3.6 Conclusion: The Importance of Understanding Japan’s Climate Zones
- 4 Closure
Decoding Japan’s Climate Zones: A Comprehensive Guide

Japan, an archipelago nation nestled in the northwest Pacific Ocean, experiences a diverse range of climates. This climatic variation, shaped by geographical features and prevailing weather patterns, is crucial for understanding the country’s unique ecosystems, agricultural practices, and even cultural nuances. This article delves into the intricacies of Japan’s climate zones, providing a comprehensive overview of their characteristics, influencing factors, and implications.
Understanding Japan’s Climate Zones: A Geographical Perspective
Japan’s climate zones are primarily determined by its geographical position, encompassing a range of latitudes and altitudes. The country’s elongated shape, stretching from north to south, exposes it to varying levels of solar radiation, influencing temperature patterns. Moreover, the presence of mountainous terrain, including the iconic Japanese Alps, creates distinct microclimates, further diversifying the country’s climatic landscape.
1. The Influence of Latitude:
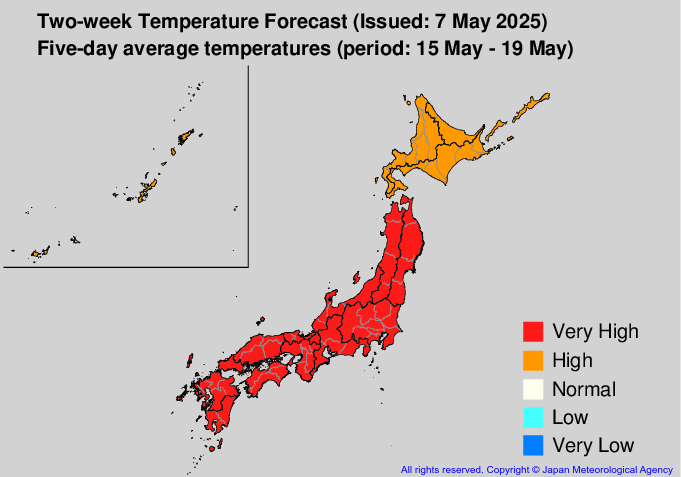
- Northern Japan: Located in higher latitudes, this region experiences colder temperatures and longer winters compared to the south. The northernmost island of Hokkaido is characterized by a subarctic climate with significant snowfall during the winter months.
- Central Japan: This region, encompassing the main island of Honshu, experiences a temperate climate with four distinct seasons. Winters are relatively cold, while summers are warm and humid.
- Southern Japan: The southern islands of Shikoku and Kyushu, situated in lower latitudes, enjoy a subtropical climate with warm winters and hot, humid summers. The southernmost island of Okinawa boasts a tropical climate with year-round warm temperatures and high humidity.
2. The Impact of Altitude:
- Mountainous Regions: Elevations in Japan’s mountainous regions significantly influence temperature and precipitation patterns. Higher altitudes experience colder temperatures, increased snowfall, and a shorter growing season. The iconic Mount Fuji, for instance, exhibits a distinct alpine climate with snow-capped peaks even during the summer months.
- Coastal Regions: Coastal areas experience a moderating effect from the surrounding ocean, resulting in milder temperatures and less extreme weather fluctuations. The presence of ocean currents, such as the warm Kuroshio Current, further influences coastal climates.
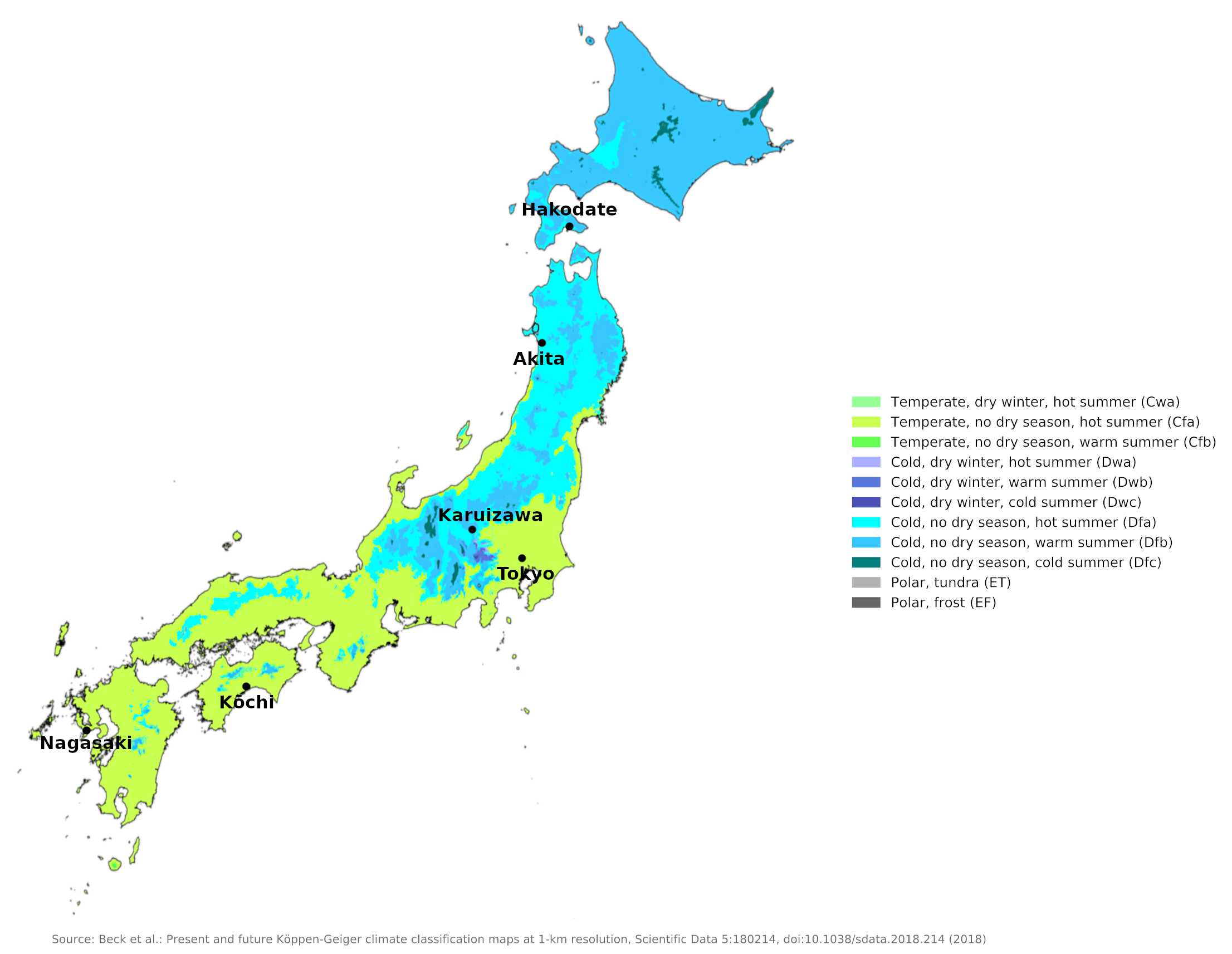
A Deeper Dive into Japan’s Climate Zones: The Köppen-Geiger Classification System
To understand the nuances of Japan’s climate, it’s essential to refer to the Köppen-Geiger climate classification system. This widely accepted system categorizes climates based on temperature and precipitation patterns, providing a more detailed understanding of regional variations. Japan falls primarily within the following climate zones:
1. Humid Subtropical Climate (Cfa): This zone, encompassing much of central and southern Japan, experiences warm, humid summers and mild, wet winters. Precipitation is relatively evenly distributed throughout the year, with a distinct rainy season (tsuyu) during June and July.
2. Temperate Oceanic Climate (Cfb): This zone, primarily found in coastal regions of central Japan, is characterized by mild temperatures and ample rainfall throughout the year. Winters are relatively short and mild, while summers are cool and humid.
3. Humid Continental Climate (Dfa): This zone, primarily found in northern Japan, experiences warm, humid summers and cold, snowy winters. Precipitation is more concentrated in the summer months, with occasional snowfall during the winter.
4. Subarctic Climate (Dfb): This zone, primarily found in the northernmost island of Hokkaido, features long, cold winters with significant snowfall and short, cool summers. Precipitation is relatively evenly distributed throughout the year.
5. Tropical Monsoon Climate (Am): This zone, primarily found in the southernmost islands of Okinawa and Amami, experiences warm, humid temperatures year-round. Precipitation is concentrated during the summer months, with a distinct dry season during the winter.
The Significance of Japan’s Climate Zones: Understanding the Impacts
The diverse climate zones of Japan play a crucial role in shaping the country’s natural environment, agricultural practices, and cultural landscape.
1. Environmental Impact:
- Biodiversity: Japan’s diverse climates support a rich array of plant and animal life. From the lush forests of central Japan to the alpine meadows of the Japanese Alps, each climate zone boasts unique ecosystems.
- Natural Disasters: Japan is prone to natural disasters, such as typhoons, earthquakes, and volcanic eruptions. The country’s climate zones influence the frequency and intensity of these disasters, impacting infrastructure and human life.
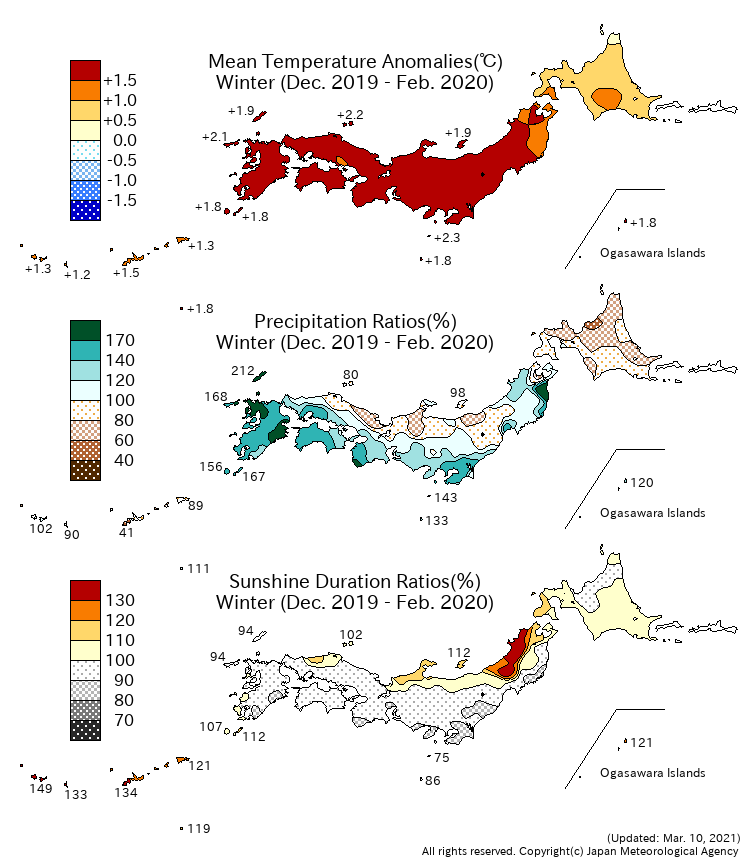
- Climate Change: Japan’s climate is undergoing significant changes due to global warming. Rising temperatures, changes in precipitation patterns, and increased frequency of extreme weather events are impacting ecosystems, agriculture, and human health.
2. Agricultural Impact:
- Crop Diversity: Japan’s diverse climates support a wide variety of crops, from rice and tea in the south to apples and potatoes in the north. Each climate zone has its own unique agricultural products, contributing to the country’s food security and cultural identity.
- Seasonal Variation: Japan’s distinct seasons influence agricultural practices, with different crops being planted and harvested throughout the year. This seasonal variation is reflected in the country’s cuisine and cultural traditions.
- Climate Change Adaptation: Farmers in Japan are facing challenges due to climate change, including increased temperatures, droughts, and floods. Adapting to these changes is crucial for maintaining agricultural productivity and ensuring food security.
3. Cultural Impact:
- Traditional Architecture: Japan’s traditional architecture has evolved in response to the country’s climate. For instance, the use of tatami mats in homes provides insulation and a cool environment in the summer.
- Festivals and Traditions: Many Japanese festivals and traditions are deeply rooted in the country’s climate. For example, the cherry blossom festival (hanami) celebrates the arrival of spring, while the autumn foliage festival (momijigari) marks the changing colors of leaves.
- Lifestyle: Japan’s climate influences daily life, with people adapting their clothing, food, and activities to the changing seasons. The concept of "seasonal eating" (shun) emphasizes consuming foods that are in season, promoting health and sustainability.
FAQs: Exploring the Nuances of Japan’s Climate Zones
1. What is the hottest region in Japan?
The southernmost islands of Okinawa and Amami, located in the tropical monsoon climate zone, experience the hottest temperatures in Japan.
2. Which region in Japan receives the most rainfall?
The mountainous regions of central Japan, particularly the Chubu region, receive the most rainfall due to the influence of the monsoon winds and orographic lift.
3. How does Japan’s climate influence its architecture?
Traditional Japanese architecture incorporates design elements that respond to the country’s climate, such as wide eaves to provide shade from the sun and sliding doors for ventilation.
4. How does climate change impact Japan’s agriculture?
Climate change is affecting Japan’s agriculture in various ways, including increased temperatures, changes in precipitation patterns, and the emergence of new pests and diseases.
5. What are the main natural disasters that affect Japan?
Japan is prone to natural disasters such as typhoons, earthquakes, volcanic eruptions, and tsunamis. The frequency and intensity of these disasters are influenced by the country’s climate and geographical features.
Tips: Navigating Japan’s Climate Zones for a Seamless Experience
1. Pack for All Seasons: Japan’s climate is diverse, so pack accordingly for the season you are visiting. Be prepared for rain, especially during the rainy season (tsuyu) in June and July.
2. Stay Informed about Weather Forecasts: Check the weather forecast regularly, especially if you are planning outdoor activities. Be aware of potential natural disasters, such as typhoons and earthquakes.
3. Dress in Layers: Japan’s climate can change rapidly, so dressing in layers is recommended. This allows you to adjust to changing temperatures throughout the day.
4. Embrace Seasonal Experiences: Take advantage of the unique seasonal experiences that Japan offers, such as cherry blossom viewing in spring and autumn foliage viewing in fall.
5. Learn about Local Customs: Be aware of local customs and traditions related to the climate, such as the use of fans during the summer and the appreciation for hot springs (onsen) in winter.
Conclusion: The Importance of Understanding Japan’s Climate Zones
The diverse climate zones of Japan are a defining feature of the country, shaping its natural environment, agricultural practices, and cultural identity. Understanding these climate zones is crucial for appreciating the country’s unique beauty, navigating its diverse landscapes, and appreciating the rich cultural traditions that have evolved in response to its climate. As Japan faces the challenges of climate change, understanding its climate zones is more important than ever for developing sustainable practices and ensuring the well-being of its people and its environment.

![Eight Japanese Climate Zones [from Mizutani (2015)] Download Scientific Diagram](https://www.researchgate.net/publication/312386940/figure/fig5/AS:451310815322116@1484612291921/Eight-Japanese-Climate-Zones-from-Mizutani-2015.png)



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Decoding Japan’s Climate Zones: A Comprehensive Guide. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!