A Tapestry Of Continents: Exploring The Intertwined Histories And Futures Of Africa And Asia
A Tapestry of Continents: Exploring the Intertwined Histories and Futures of Africa and Asia
Related Articles: A Tapestry of Continents: Exploring the Intertwined Histories and Futures of Africa and Asia
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to A Tapestry of Continents: Exploring the Intertwined Histories and Futures of Africa and Asia. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
A Tapestry of Continents: Exploring the Intertwined Histories and Futures of Africa and Asia
Africa and Asia, two vast and diverse continents, have long been intertwined in a complex web of history, geography, and culture. While geographically separated by the Red Sea and the Suez Canal, their destinies have been deeply interconnected for centuries. Understanding the dynamics between these two continents is crucial for comprehending the global landscape and its future trajectory.
A Shared History of Trade and Exchange:
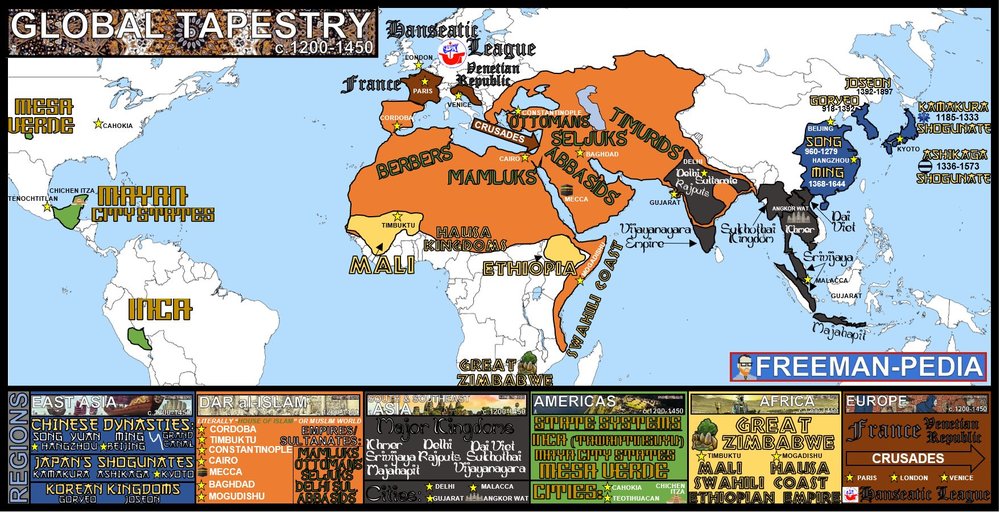
The historical ties between Africa and Asia date back to antiquity. The ancient Silk Road, a network of trade routes connecting East Asia to the Mediterranean, fostered extensive exchange of goods, ideas, and cultures between the two continents. African goods, including ivory, gold, and slaves, were transported eastward, while Asian commodities like silk, spices, and porcelain flowed westward. This trade played a significant role in shaping the economic and cultural landscapes of both continents.
The Indian Ocean, a vital trade route connecting Africa, Asia, and the Middle East, served as a conduit for cultural and religious diffusion. Islam, originating in the Arabian Peninsula, spread to Africa through trade and conquest, leaving a lasting impact on the continent’s religious and cultural fabric. Similarly, Hinduism and Buddhism found their way to Southeast Asia, contributing to the region’s diverse spiritual landscape.
The Impact of Colonialism and its Aftermath:
The era of colonialism, beginning in the 15th century, profoundly impacted both Africa and Asia. European powers, driven by economic ambitions and a quest for resources, carved up vast swathes of both continents, imposing their political and economic systems. This period witnessed the exploitation of natural resources, the displacement of indigenous populations, and the introduction of new social and political structures.
The legacy of colonialism continues to shape the relationship between Africa and Asia. Both continents face challenges related to poverty, inequality, and the need for economic development. However, the shared experience of colonialism has also fostered a sense of solidarity and a desire to forge a new future based on cooperation and mutual respect.
A Complex Web of Interdependence:
Africa and Asia are increasingly interdependent in the 21st century. Economic globalization has intensified trade and investment between the two continents, creating new opportunities for growth and development. China, a major economic power in Asia, has emerged as a key investor in Africa, supporting infrastructure projects and fostering economic ties.
The rise of Asian economies has also created new markets for African goods and services. The demand for agricultural products, minerals, and energy resources from Africa is steadily growing, presenting opportunities for economic diversification and job creation.
Challenges and Opportunities:
Despite the growing interdependence, challenges remain. Political instability, conflict, and poverty persist in parts of both continents. Climate change poses a significant threat to both regions, requiring collaborative efforts to mitigate its impact.
However, the challenges also present opportunities for cooperation. Africa and Asia can leverage their combined resources and expertise to address shared challenges, such as climate change, poverty, and disease. Joint initiatives in areas like infrastructure development, technology transfer, and human resource development can foster sustainable growth and prosperity.
Conclusion: Towards a Shared Future
The relationship between Africa and Asia is multifaceted and dynamic. Their shared history, intertwined economies, and common challenges create a unique context for collaboration and mutual benefit. By fostering closer ties, promoting trade and investment, and addressing shared concerns, Africa and Asia can build a more prosperous and sustainable future for both continents and the world.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q: How has the relationship between Africa and Asia evolved over time?
A: The relationship between Africa and Asia has evolved from ancient trade routes to colonial exploitation and, more recently, to a growing interdependence driven by economic globalization. This evolution reflects the changing dynamics of power, trade, and technology throughout history.
Q: What are the key drivers of economic interdependence between Africa and Asia?
A: Key drivers include the increasing demand for African resources by Asian economies, particularly China’s investment in infrastructure and development projects in Africa, and the growing trade in goods and services between the two continents.
Q: What are some of the challenges facing Africa and Asia in the 21st century?
A: Challenges include poverty, inequality, political instability, conflict, climate change, and the need for sustainable development. These challenges are often interconnected and require collaborative solutions.
Q: How can Africa and Asia collaborate to address shared challenges?
A: Collaboration can take many forms, including joint initiatives in areas like infrastructure development, technology transfer, human resource development, and climate change mitigation. These initiatives can foster sustainable growth and prosperity for both continents.
Tips for Understanding the Relationship Between Africa and Asia:
- Focus on historical context: Understanding the shared history of trade, colonialism, and cultural exchange is crucial for comprehending the current relationship.
- Analyze economic interdependence: Examine the growing trade and investment flows between the two continents, particularly the role of China in Africa’s development.
- Recognize shared challenges: Identify common challenges like poverty, conflict, and climate change, and explore how collaboration can address these issues.
- Explore diverse perspectives: Seek out perspectives from both continents, including voices from different regions, ethnicities, and socioeconomic backgrounds.
Conclusion:
The relationship between Africa and Asia is complex and constantly evolving. Recognizing the historical, economic, and cultural connections between these two continents is essential for understanding the global landscape and its future trajectory. By fostering collaboration, addressing shared challenges, and leveraging their combined resources, Africa and Asia can work together to build a more prosperous and sustainable future for both continents and the world.







Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into A Tapestry of Continents: Exploring the Intertwined Histories and Futures of Africa and Asia. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!