A Geopolitical Overview: Israel, Gaza, And Egypt
A Geopolitical Overview: Israel, Gaza, and Egypt
Related Articles: A Geopolitical Overview: Israel, Gaza, and Egypt
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to A Geopolitical Overview: Israel, Gaza, and Egypt. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
A Geopolitical Overview: Israel, Gaza, and Egypt
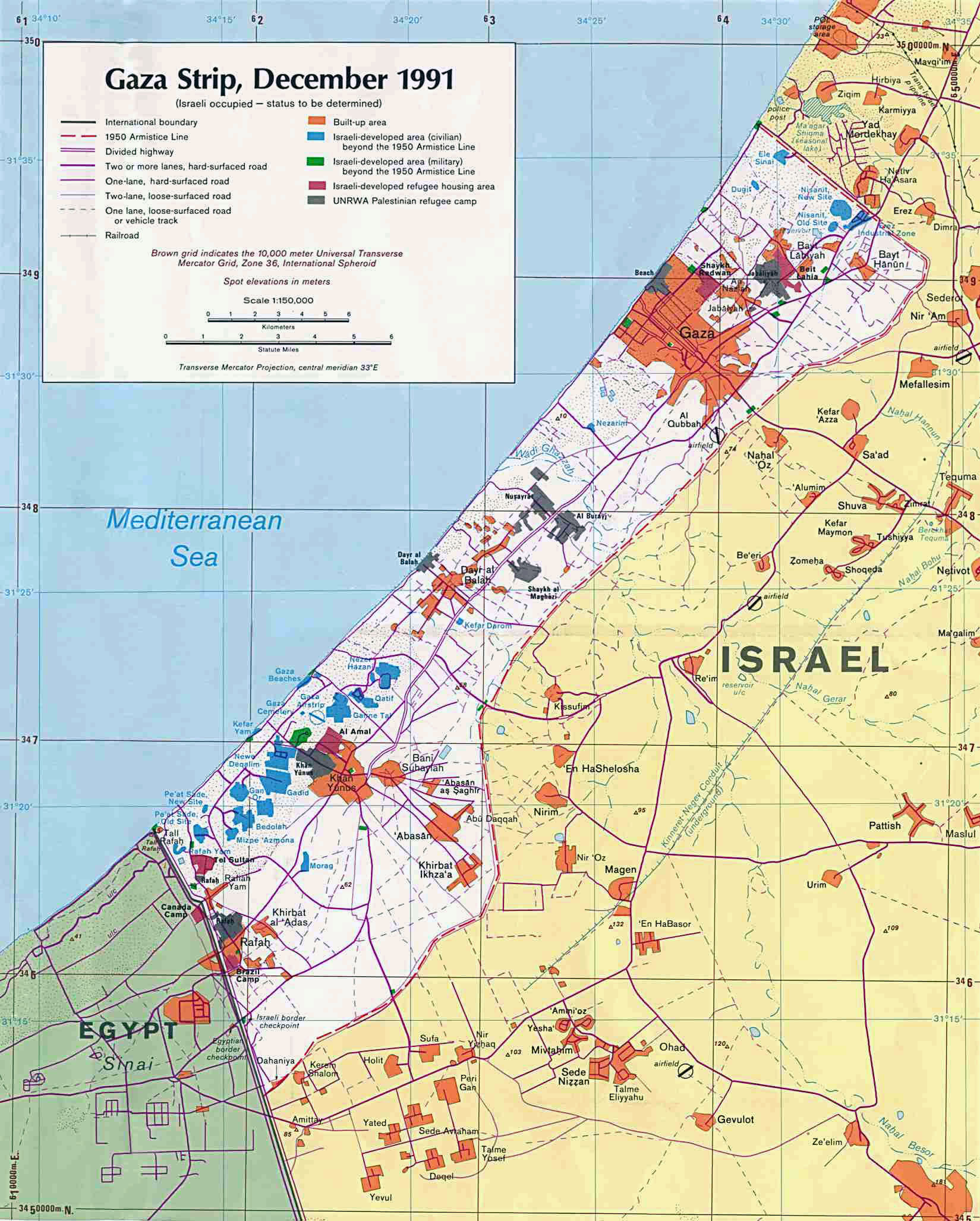
The intricate tapestry of the Middle East is woven with threads of history, culture, and conflict. Understanding the geopolitical landscape of Israel, Gaza, and Egypt is crucial for comprehending the region’s complexities and navigating the ongoing challenges. This article delves into the geographical, political, and historical nuances of this region, providing a comprehensive overview of the intricate relationships between these three entities.
Geographical Context: A Land of Contrasts
The region encompasses a diverse range of landscapes, from the fertile Nile Delta to the arid Negev Desert. The Mediterranean Sea borders the region to the west, while the Sinai Peninsula serves as a bridge between Africa and Asia.
-
Israel: Occupying a relatively small area, Israel boasts a diverse topography, ranging from the coastal plains to the rugged highlands of the Galilee and the Judean Desert. Its location at the crossroads of three continents, Europe, Asia, and Africa, has historically shaped its identity and geopolitical significance.
-
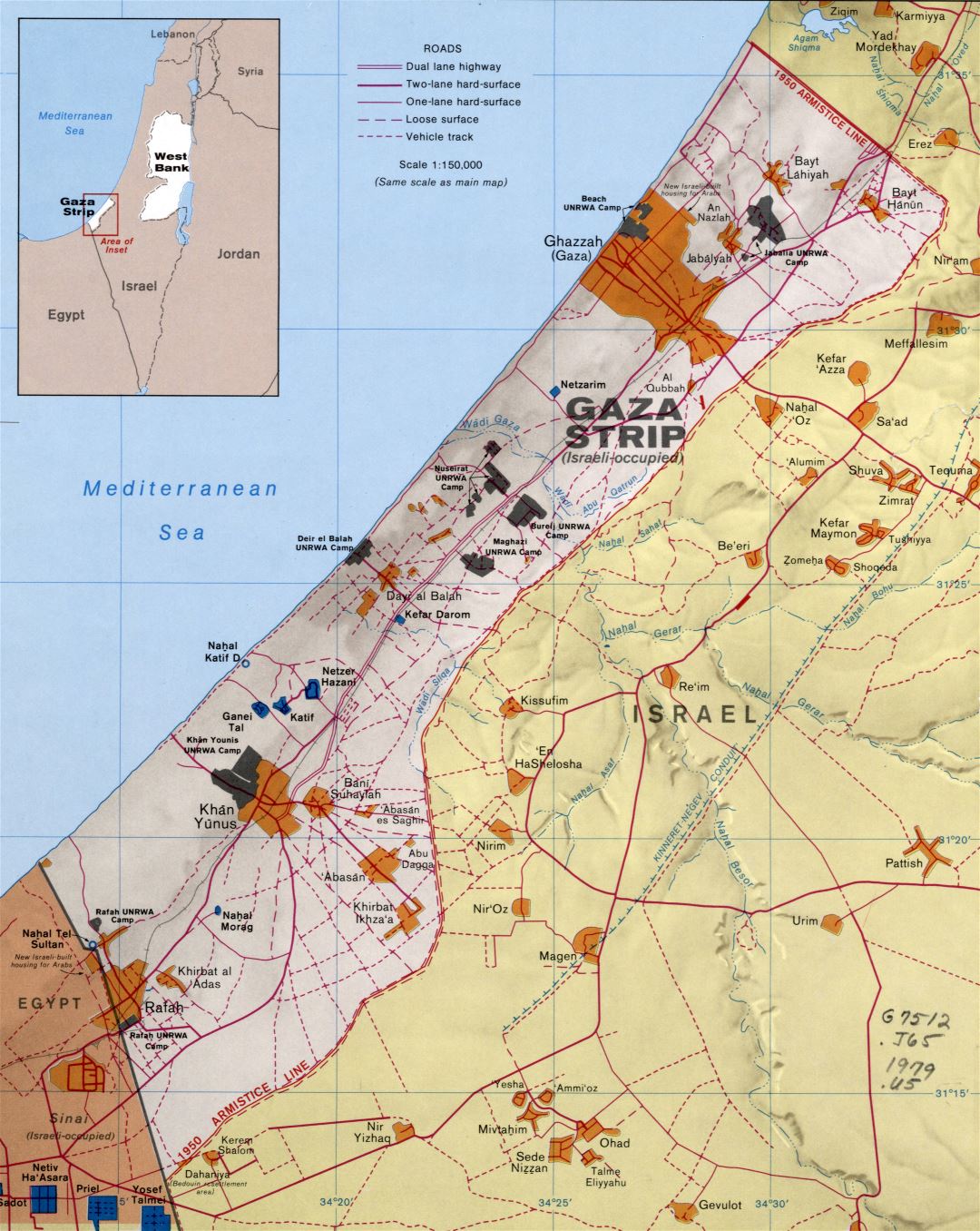
Gaza: Located on the Mediterranean coast, Gaza is a narrow strip of land bordering Israel to the east and Egypt to the south. It is characterized by a densely populated urban environment and limited agricultural potential.
-
Egypt: The largest country in the region, Egypt stretches across the northeast corner of Africa. It encompasses a vast desert landscape, the fertile Nile Valley, and the Sinai Peninsula. Its strategic location and control over the Suez Canal have made it a pivotal player in regional and global affairs.
Historical Intertwining: A Century of Conflict and Cooperation
The historical relationship between Israel, Gaza, and Egypt is marked by periods of conflict and cooperation.
-
The British Mandate: After World War I, Britain gained control of Palestine, a region encompassing modern-day Israel, the West Bank, and Gaza. The establishment of a Jewish homeland in Palestine, as outlined in the Balfour Declaration, sparked conflict with the Arab population.
-
The 1948 Arab-Israeli War: The establishment of the State of Israel in 1948 triggered a war with neighboring Arab states, including Egypt. This war resulted in the displacement of hundreds of thousands of Palestinians and the occupation of the Gaza Strip by Egypt.
-
The Six-Day War (1967): Israel’s decisive victory in the Six-Day War led to its control over the Sinai Peninsula, the West Bank, and East Jerusalem. Egypt’s defeat prompted a period of intense hostility and military confrontation.
-
The Camp David Accords (1978): The landmark peace treaty signed by Israel and Egypt in 1978, brokered by President Jimmy Carter, marked a turning point in the region’s history. The treaty resulted in the return of the Sinai Peninsula to Egypt and the establishment of diplomatic relations between the two countries.
-
The Oslo Accords (1993): The Oslo Accords, signed between Israel and the Palestine Liberation Organization (PLO), aimed to establish a Palestinian state in the West Bank and Gaza Strip. However, the peace process faltered, and tensions escalated.
-
The Second Intifada (2000-2005): A wave of violence erupted in 2000, known as the Second Intifada, which further strained relations between Israel and the Palestinians.
-
The Hamas Takeover of Gaza (2007): The Islamist group Hamas seized control of Gaza in 2007, leading to a blockade imposed by Israel and Egypt. This has significantly impacted the economic and humanitarian situation in Gaza.
Political Landscape: A Complex and Dynamic Region
The political landscape of Israel, Gaza, and Egypt is characterized by a complex web of internal and external forces.
-
Israel: Israel’s political system is a parliamentary democracy with a multi-party system. However, the country has experienced a prolonged period of political instability, with several consecutive elections failing to produce a stable government.
-
Gaza: The Gaza Strip is governed by Hamas, a Palestinian Islamist group classified as a terrorist organization by many countries. Hamas’s control has led to a humanitarian crisis, with limited access to essential resources and a high unemployment rate.
-
Egypt: Egypt has transitioned from a military dictatorship to a more democratic system. However, the country’s political landscape remains fragile, with ongoing challenges to stability and human rights.
The Importance of Understanding the Region
Understanding the complex geopolitical landscape of Israel, Gaza, and Egypt is crucial for several reasons:
-
Regional Stability: The region’s stability is intricately linked to the resolution of the Israeli-Palestinian conflict. Continued violence and instability pose a threat to the entire region, impacting economic development and international relations.
-
International Security: The region’s strategic location and the presence of major international powers, such as the United States and Russia, make it a focal point for global security concerns.
-
Humanitarian Crisis: The humanitarian situation in Gaza is dire, with a high poverty rate and limited access to essential services. The ongoing conflict and blockade have exacerbated the crisis.
-
Economic Development: The region’s economic potential is hindered by political instability and conflict. Peace and stability are essential for attracting foreign investment and promoting economic growth.
FAQs on the Geopolitical Landscape of Israel, Gaza, and Egypt
1. What is the current status of the Israeli-Palestinian conflict?
The Israeli-Palestinian conflict remains unresolved, with ongoing tensions and violence. The two-state solution, which envisions the establishment of an independent Palestinian state alongside Israel, has been the subject of extensive negotiations but has yet to be realized.
2. What are the main challenges facing the region?
The region faces numerous challenges, including political instability, economic disparities, the humanitarian crisis in Gaza, and the ongoing Israeli-Palestinian conflict.
3. What is the role of the United States in the region?
The United States has been a major player in the Middle East for decades, providing significant military and economic aid to Israel and Egypt. The US has also played a role in peace negotiations between Israel and the Palestinians.
4. What is the role of the European Union in the region?
The European Union is a major donor to the Palestinian Authority and has been a vocal advocate for a two-state solution. The EU also plays a role in mediating between Israel and the Palestinians.
5. What are the prospects for peace in the region?
The prospects for peace in the region remain uncertain, with no immediate solutions in sight. However, there are ongoing efforts to promote dialogue and build trust between the parties involved.
Tips for Understanding the Geopolitical Landscape of Israel, Gaza, and Egypt
-
Engage with diverse perspectives: Seek out information from a variety of sources, including news outlets, think tanks, and academic publications.
-
Understand the historical context: Studying the region’s history is crucial for comprehending the current situation.
-
Stay informed about current events: Keep abreast of developments in the region through reliable news sources.
-
Engage in constructive dialogue: Participate in discussions about the region and share your insights with others.
-
Support organizations working for peace and development: Contribute to organizations working to promote peace, humanitarian aid, and economic development in the region.
Conclusion
The geopolitical landscape of Israel, Gaza, and Egypt is a complex and dynamic one, shaped by historical events, political ideologies, and ongoing conflicts. Understanding the region’s complexities is essential for navigating the challenges and opportunities it presents. The pursuit of peace, security, and economic prosperity for all parties involved remains a critical goal, requiring continued dialogue, diplomacy, and a commitment to a just and lasting solution.


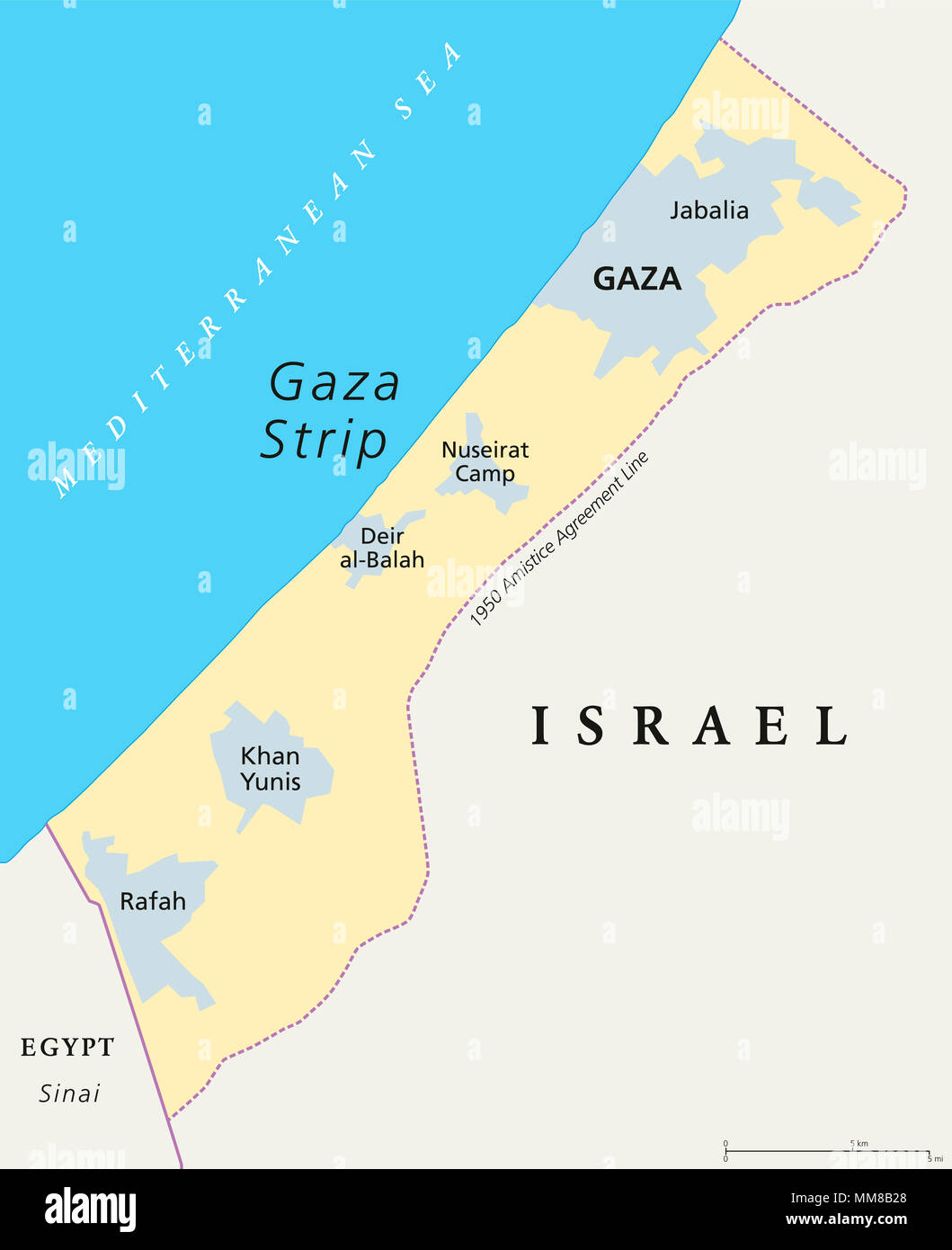
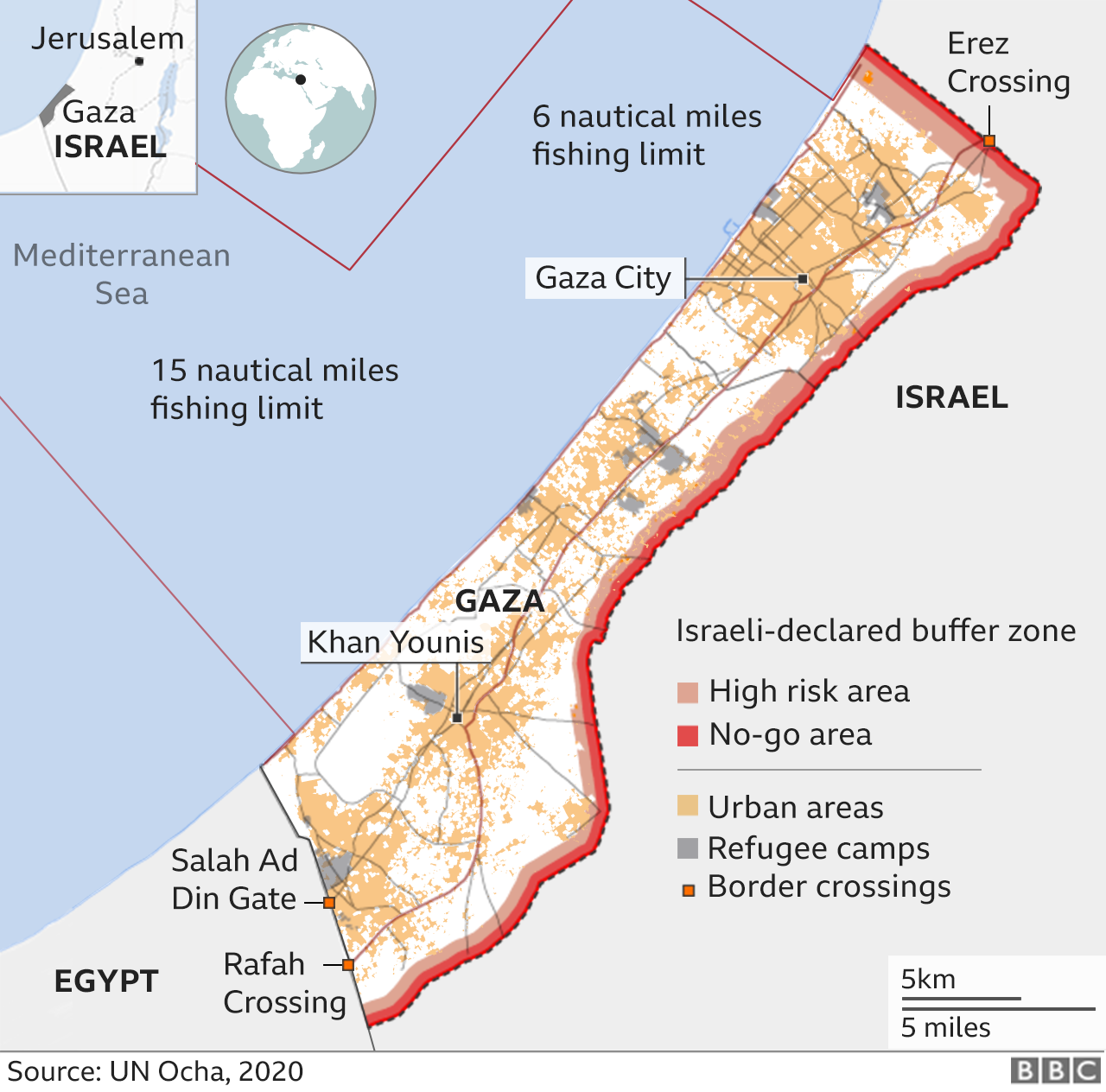


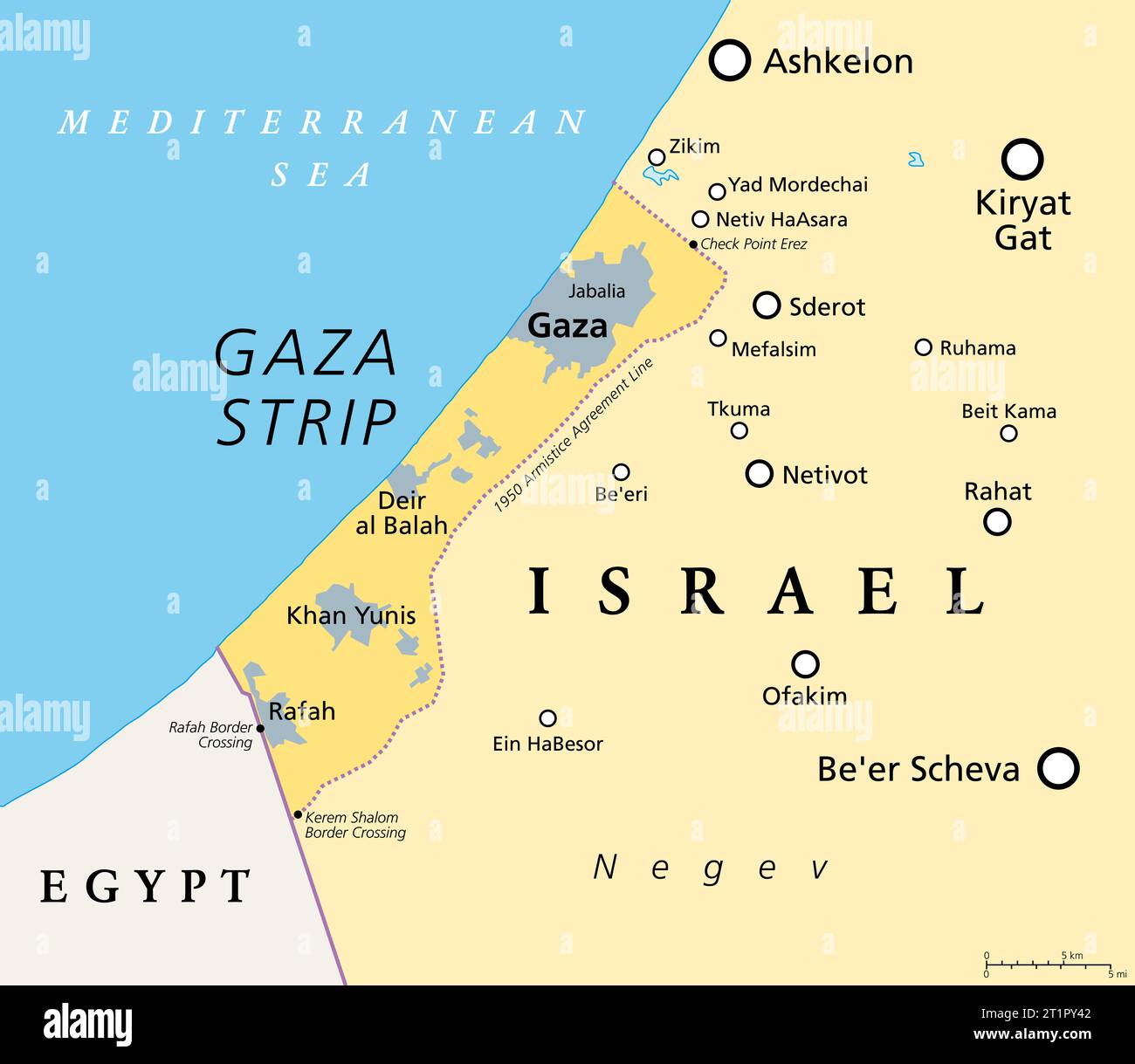
Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into A Geopolitical Overview: Israel, Gaza, and Egypt. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!