A Geopolitical Landscape: Israel And Its Surrounding Countries
A Geopolitical Landscape: Israel and Its Surrounding Countries
Related Articles: A Geopolitical Landscape: Israel and Its Surrounding Countries
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to A Geopolitical Landscape: Israel and Its Surrounding Countries. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
A Geopolitical Landscape: Israel and Its Surrounding Countries

The Middle East, a region steeped in history and often characterized by political complexities, holds within its borders a small nation with a disproportionately large global impact: Israel. Understanding the geographical context of Israel, its surrounding countries, and their intricate relationships is essential for comprehending the region’s dynamics, its history, and its future. This article delves into the geopolitical landscape of Israel and its neighbors, exploring their geographical features, historical connections, and ongoing challenges.
A Crossroads of Civilizations:
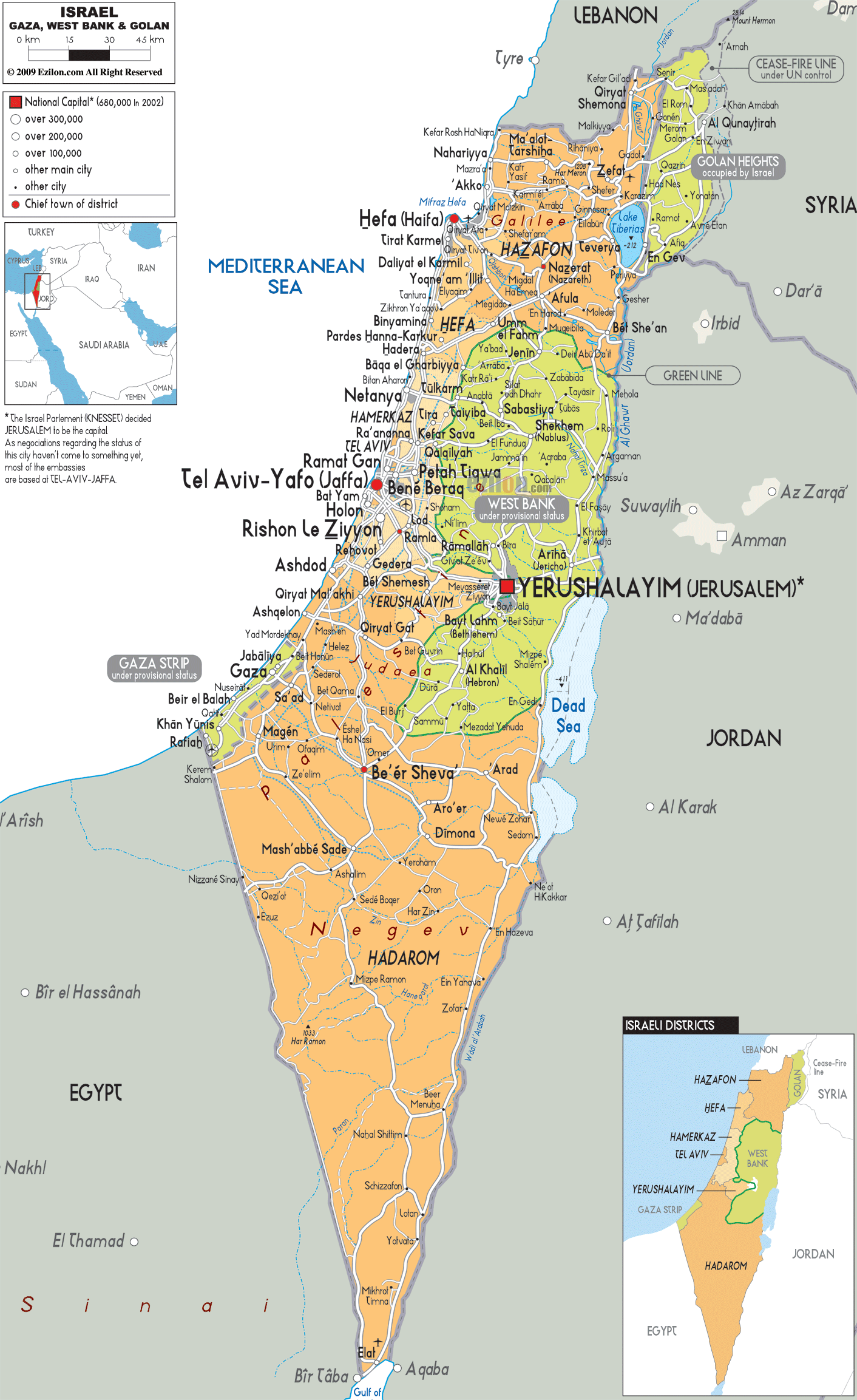
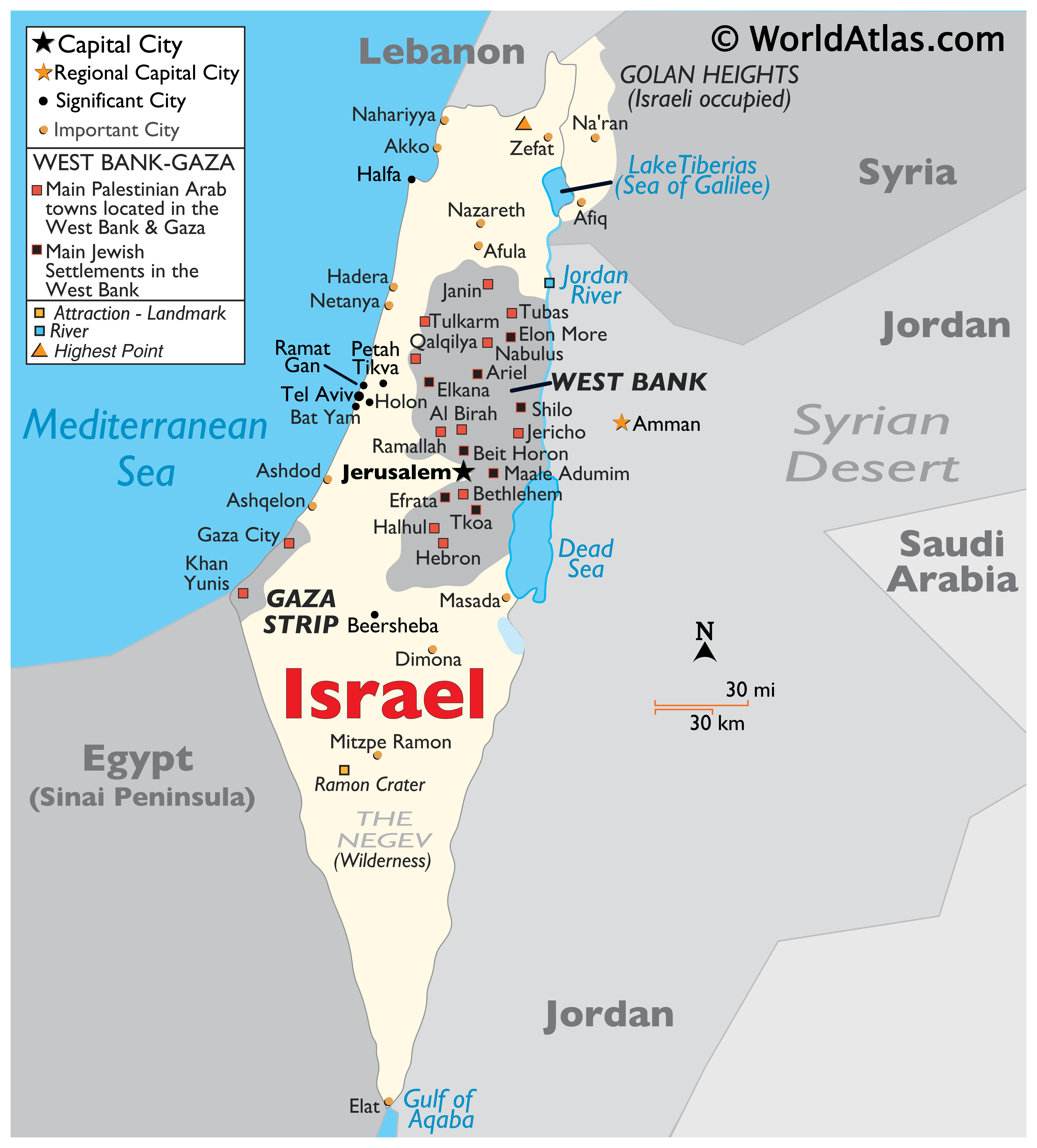
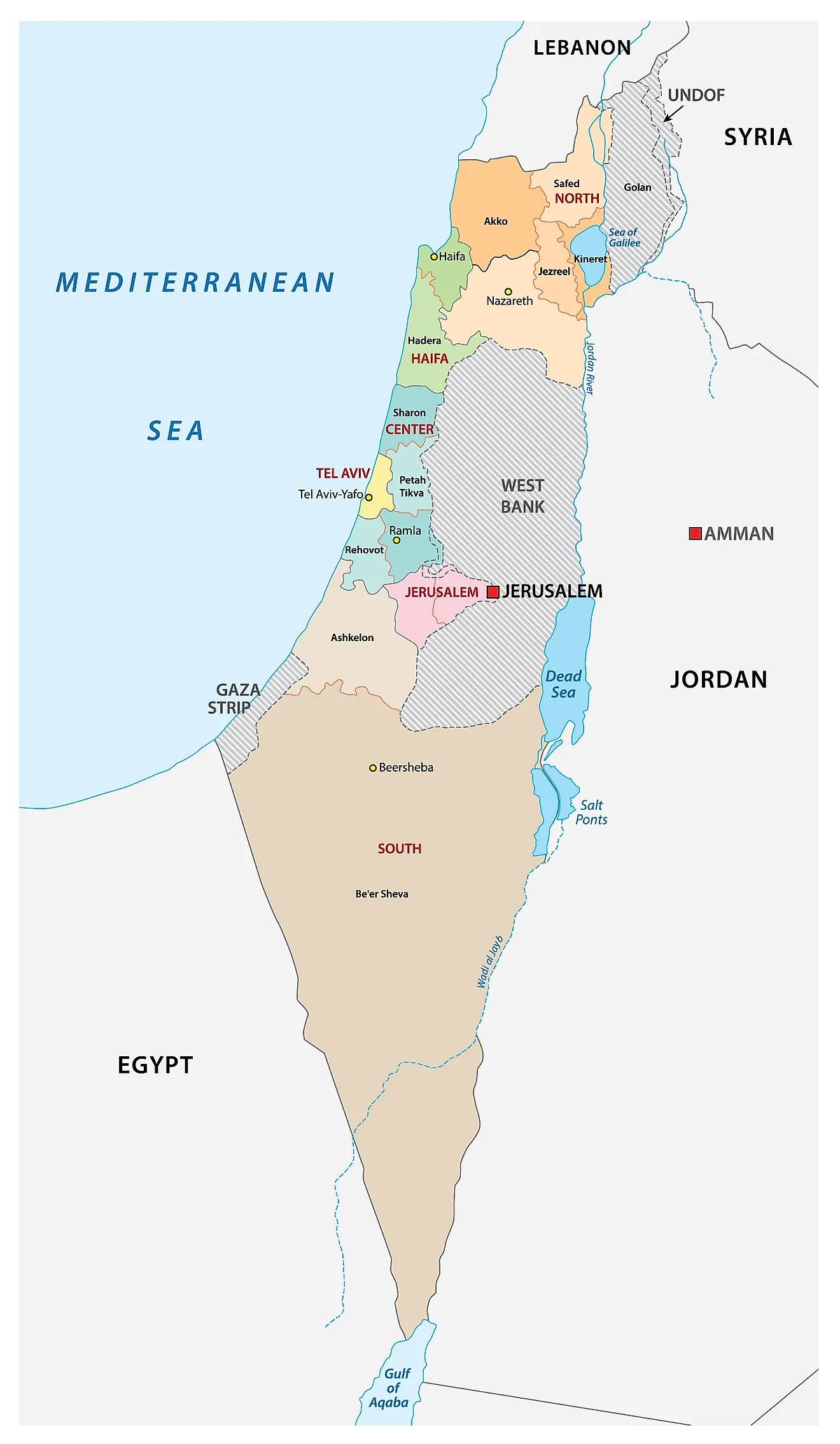
Israel, nestled on the eastern Mediterranean coast, occupies a strategically vital location. Its borders touch the Levant region, a historical crossroads of civilizations. This strategic position has played a significant role in shaping Israel’s history and its contemporary relationships with its neighbors.
Neighboring Nations:
Israel shares borders with several countries, each with its own unique history, culture, and political landscape. These include:
-
Lebanon: To the north, Lebanon borders Israel along a volatile frontier. The two countries have a history of conflict, with ongoing tensions stemming from the Israeli-Lebanese War (1982) and the presence of Hezbollah, a Lebanese Shia militant group.
-
Syria: Situated to the northeast, Syria shares a contentious border with Israel. The two nations have been locked in a state of war since 1948, with sporadic clashes and the Golan Heights, a strategically important plateau, remaining a point of contention.
-
Jordan: To the east, Jordan shares a relatively stable border with Israel. The two countries signed a peace treaty in 1994, marking a significant step towards regional stability. However, ongoing disputes over water resources and the Palestinian issue continue to pose challenges.
-
Egypt: To the southwest, Egypt borders Israel along the Sinai Peninsula. The two nations signed a peace treaty in 1979, ending decades of conflict. Despite the peace accord, the relationship remains complex, with unresolved issues concerning the Gaza Strip and the Palestinian territories.
-
The Palestinian Territories: The West Bank and the Gaza Strip, collectively known as the Palestinian Territories, are situated within the Israeli-occupied territories. This region is home to a large Palestinian population and is the subject of ongoing conflict and negotiations.
The Palestinian Issue:
The Palestinian issue stands as a central factor in the region’s complexities. The Israeli-Palestinian conflict, rooted in competing claims to the same land, has been a source of conflict for decades. The ongoing struggle for Palestinian self-determination and the establishment of an independent state remains a critical issue with global implications.
Geopolitical Challenges:
The geopolitical landscape of Israel and its surrounding countries is marked by a number of significant challenges:
-
Conflict and Instability: The region has witnessed numerous conflicts, including wars, armed clashes, and ongoing tensions. This instability poses a significant threat to peace and security in the region.
-
Resource Scarcity: The Middle East is characterized by water scarcity, a critical resource for both human and agricultural needs. Competition over water resources can lead to tensions and conflicts between countries.
-
Religious and Cultural Differences: The region is home to diverse religious and cultural groups, including Jews, Muslims, and Christians. These differences can lead to religious and cultural tensions, further complicating the region’s political dynamics.
-
International Involvement: The region has attracted significant international involvement, with various countries and organizations playing active roles in peace processes and conflict resolution efforts. This involvement can sometimes exacerbate tensions and complicate the situation.
The Importance of Understanding the Region:
Understanding the geopolitical landscape of Israel and its surrounding countries is crucial for several reasons:
-
Global Security: The region’s instability has global ramifications, impacting international relations, energy security, and global peace efforts.
-
Regional Stability: The region’s stability is crucial for economic development, social progress, and the well-being of its people.
-
Conflict Resolution: Understanding the region’s complexities is essential for facilitating dialogue, promoting peace, and finding lasting solutions to ongoing conflicts.
-
Historical Context: The region’s history is rich and complex, with its past shaping its present and future. Understanding this historical context is essential for comprehending the region’s dynamics.
FAQs:
- What are the main challenges facing Israel and its surrounding countries?
The main challenges include ongoing conflicts, resource scarcity, religious and cultural differences, and international involvement.
- What is the Palestinian issue?
The Palestinian issue refers to the long-standing conflict between Israel and the Palestinians over the control of the same land.
- How does the Palestinian issue affect the region?
The Palestinian issue is a central factor in the region’s complexities, contributing to instability, violence, and tensions between countries.
- What are the prospects for peace in the region?
The prospects for peace are uncertain, with ongoing negotiations and efforts to reach a lasting solution facing significant challenges.
Tips for Understanding the Region:
-
Study the history: Understanding the historical context is crucial for comprehending the region’s dynamics.
-
Follow the news: Stay informed about current events and developments in the region.
-
Engage in respectful dialogue: Be open to different perspectives and engage in respectful discussions about the region’s complexities.
-
Support peace initiatives: Support organizations and initiatives working towards peace and reconciliation in the region.
Conclusion:
The geopolitical landscape of Israel and its surrounding countries is a complex and dynamic one, characterized by historical connections, ongoing challenges, and the potential for both conflict and cooperation. Understanding the region’s unique features, its historical context, and its current challenges is crucial for fostering peace, promoting stability, and ensuring the well-being of its people. By engaging in informed dialogue, promoting understanding, and supporting peace initiatives, we can contribute to a more peaceful and prosperous future for the region.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into A Geopolitical Landscape: Israel and Its Surrounding Countries. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!