A Geographical Overview Of Africa: Understanding The Continent’s Diverse Nations
A Geographical Overview of Africa: Understanding the Continent’s Diverse Nations
Related Articles: A Geographical Overview of Africa: Understanding the Continent’s Diverse Nations
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to A Geographical Overview of Africa: Understanding the Continent’s Diverse Nations. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
A Geographical Overview of Africa: Understanding the Continent’s Diverse Nations
Africa, the second-largest continent on Earth, is a vibrant tapestry of diverse cultures, landscapes, and histories. Its vastness and complexity are reflected in its political landscape, home to 54 sovereign nations, each with its own unique identity. Understanding the geographical distribution of these nations is crucial for comprehending the continent’s multifaceted realities and appreciating the intricate connections that bind them.
Mapping Africa’s Nations: A Visual Guide to Diversity
A map of Africa is not merely a static representation of borders; it is a dynamic visual narrative of the continent’s rich tapestry of nations. It reveals the geographical distribution of diverse cultures, languages, religions, and histories that have shaped the African experience.
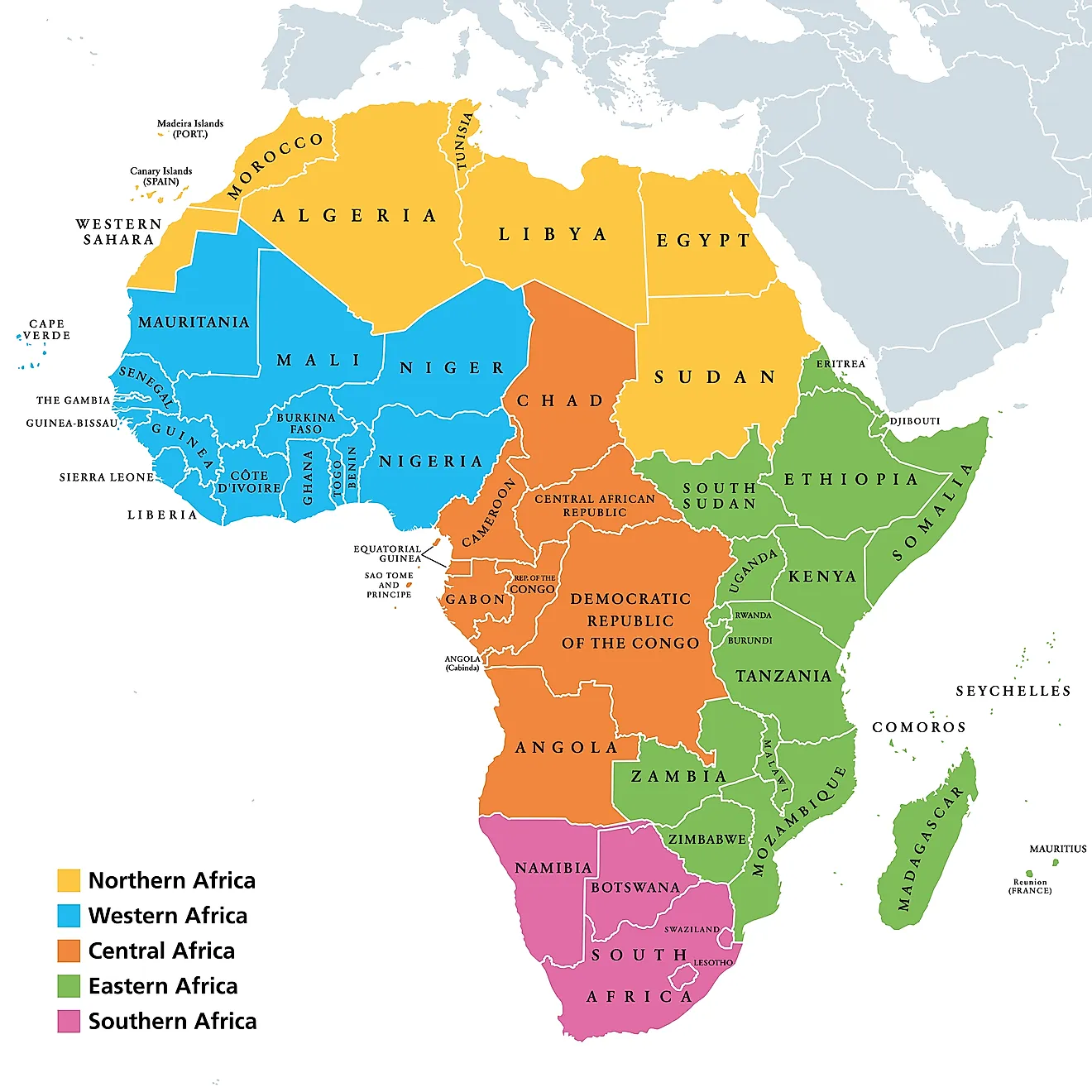
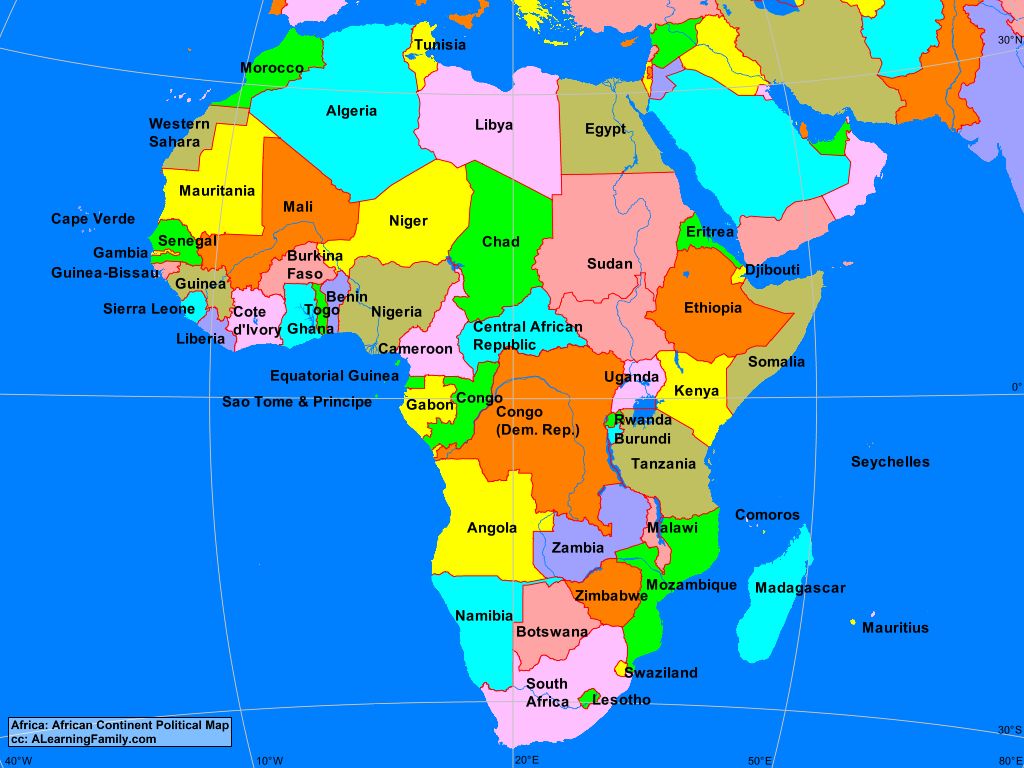
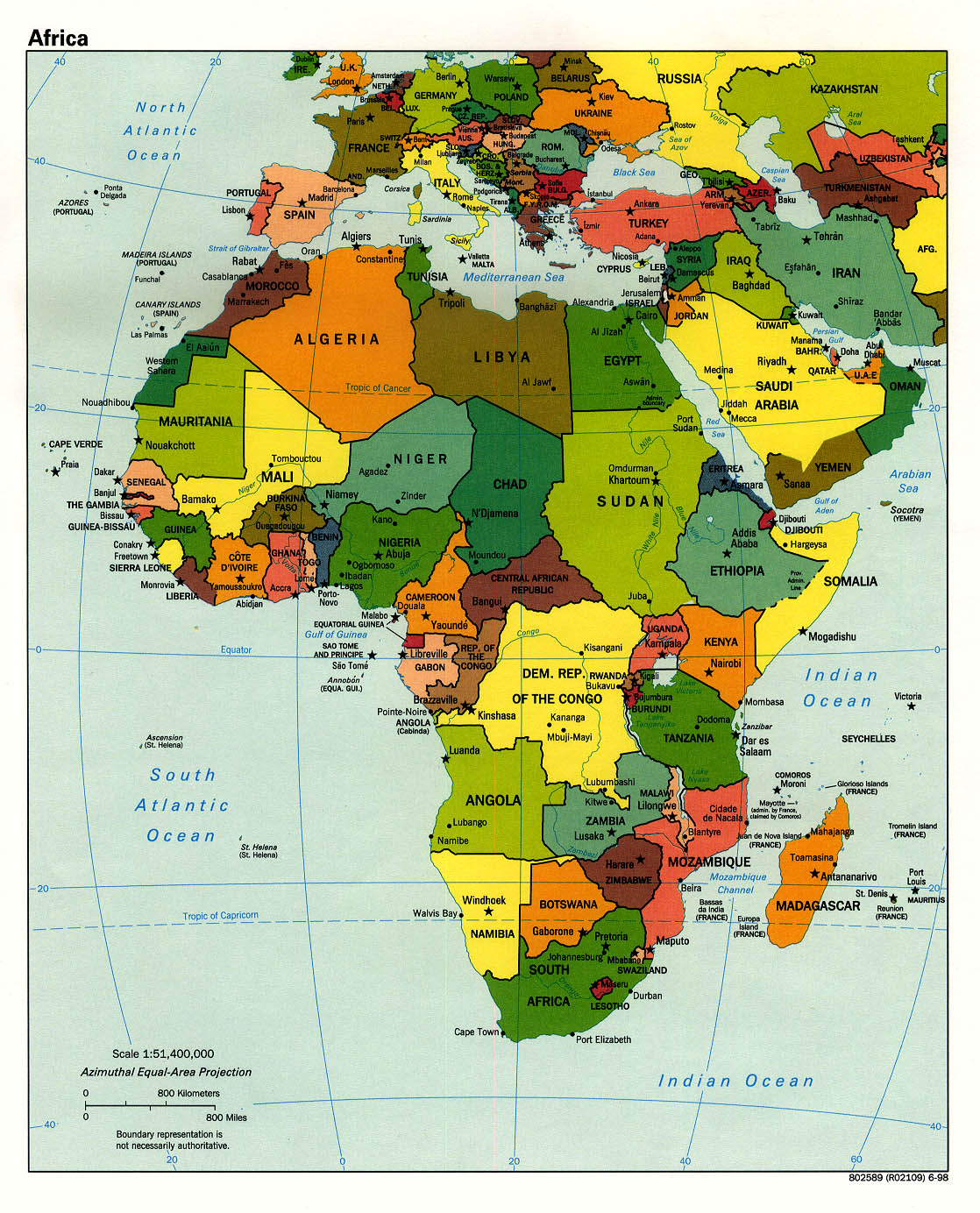
North Africa: This region, bordering the Mediterranean Sea, is characterized by its distinct cultural and historical ties to the Middle East and Europe. It encompasses countries like Egypt, Algeria, Morocco, Tunisia, and Libya, each with a unique blend of Arab, Berber, and other influences.
West Africa: This region, bordering the Atlantic Ocean, is known for its rich cultural heritage, vibrant music and dance traditions, and bustling cities. It includes nations like Nigeria, Ghana, Senegal, Mali, and Ivory Coast, each with a distinct history and cultural landscape.
Central Africa: This region, encompassing the Congo Basin, is characterized by its dense rainforests, abundant biodiversity, and diverse indigenous communities. It includes countries like the Democratic Republic of Congo, Cameroon, Gabon, and Central African Republic, each with its own unique challenges and opportunities.
East Africa: This region, bordering the Indian Ocean, is known for its stunning landscapes, including the Great Rift Valley, Mount Kilimanjaro, and the Serengeti National Park. It encompasses countries like Kenya, Tanzania, Uganda, Ethiopia, and Somalia, each with a distinct history and cultural heritage.
Southern Africa: This region, encompassing the southern tip of the continent, is known for its diverse landscapes, from the Kalahari Desert to the Drakensberg Mountains. It includes countries like South Africa, Namibia, Botswana, Zimbabwe, and Mozambique, each with its own unique history and cultural identity.
Island Nations: Africa is also home to several island nations, including Madagascar, Cape Verde, São Tomé and Príncipe, and Comoros. These islands, each with its own unique history and culture, add to the continent’s diversity.
The Importance of Mapping Africa’s Nations
Understanding the geographical distribution of African nations is essential for several reasons:
- Understanding Political Dynamics: A map provides a visual representation of the continent’s political landscape, highlighting the relationships and potential conflicts between nations.
- Appreciating Cultural Diversity: It helps visualize the vast cultural diversity of Africa, showcasing the unique traditions, languages, and identities of each nation.
- Analyzing Economic Development: A map can be used to analyze the distribution of resources, infrastructure, and economic activity across the continent, revealing regional disparities and opportunities.
- Facilitating International Cooperation: By understanding the geographical context of African nations, international organizations and policymakers can better tailor development initiatives and address shared challenges.
FAQs on Mapping Africa’s Nations
Q: What are the largest and smallest nations in Africa by land area?
A: The largest nation in Africa by land area is Algeria, covering over 2,381,741 square kilometers. The smallest is Seychelles, covering only 455 square kilometers.
Q: What are the most populous nations in Africa?
A: The most populous nation in Africa is Nigeria, with a population exceeding 200 million. Other highly populated nations include Egypt, Ethiopia, and the Democratic Republic of Congo.
Q: How does the geographical distribution of Africa’s nations impact trade and development?
A: The geographical distribution of nations influences trade patterns, infrastructure development, and access to resources. For example, landlocked nations often face challenges in accessing international markets and accessing vital resources.
Q: What are some of the major geographical features that shape Africa’s nations?
A: Major geographical features like the Sahara Desert, the Nile River, the Great Rift Valley, and the Congo Basin have profoundly influenced the development of African nations, shaping their cultures, economies, and societies.
Tips for Understanding Map Africa Nations
- Use Interactive Maps: Interactive maps allow you to explore different layers of information, such as population density, economic activity, and cultural diversity.
- Focus on Regional Variations: Pay attention to the unique characteristics of each region, considering its history, culture, and geographical features.
- Consider Historical Context: Understanding the historical events that shaped the boundaries of African nations is crucial for interpreting their present-day realities.
- Engage with Diverse Sources: Consult various sources, including academic journals, news articles, and cultural materials, to gain a comprehensive understanding of the continent’s diverse nations.
Conclusion
A map of Africa is more than just a collection of lines and borders; it is a powerful tool for understanding the continent’s rich tapestry of nations. By exploring the geographical distribution of these nations, we can gain insights into their unique identities, historical experiences, and present-day challenges. This knowledge is essential for fostering understanding, promoting cooperation, and contributing to the continent’s continued development and progress.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into A Geographical Overview of Africa: Understanding the Continent’s Diverse Nations. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!