A Geographical Overview: Israel And Its Surrounding Countries
A Geographical Overview: Israel and its Surrounding Countries
Related Articles: A Geographical Overview: Israel and its Surrounding Countries
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to A Geographical Overview: Israel and its Surrounding Countries. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
A Geographical Overview: Israel and its Surrounding Countries

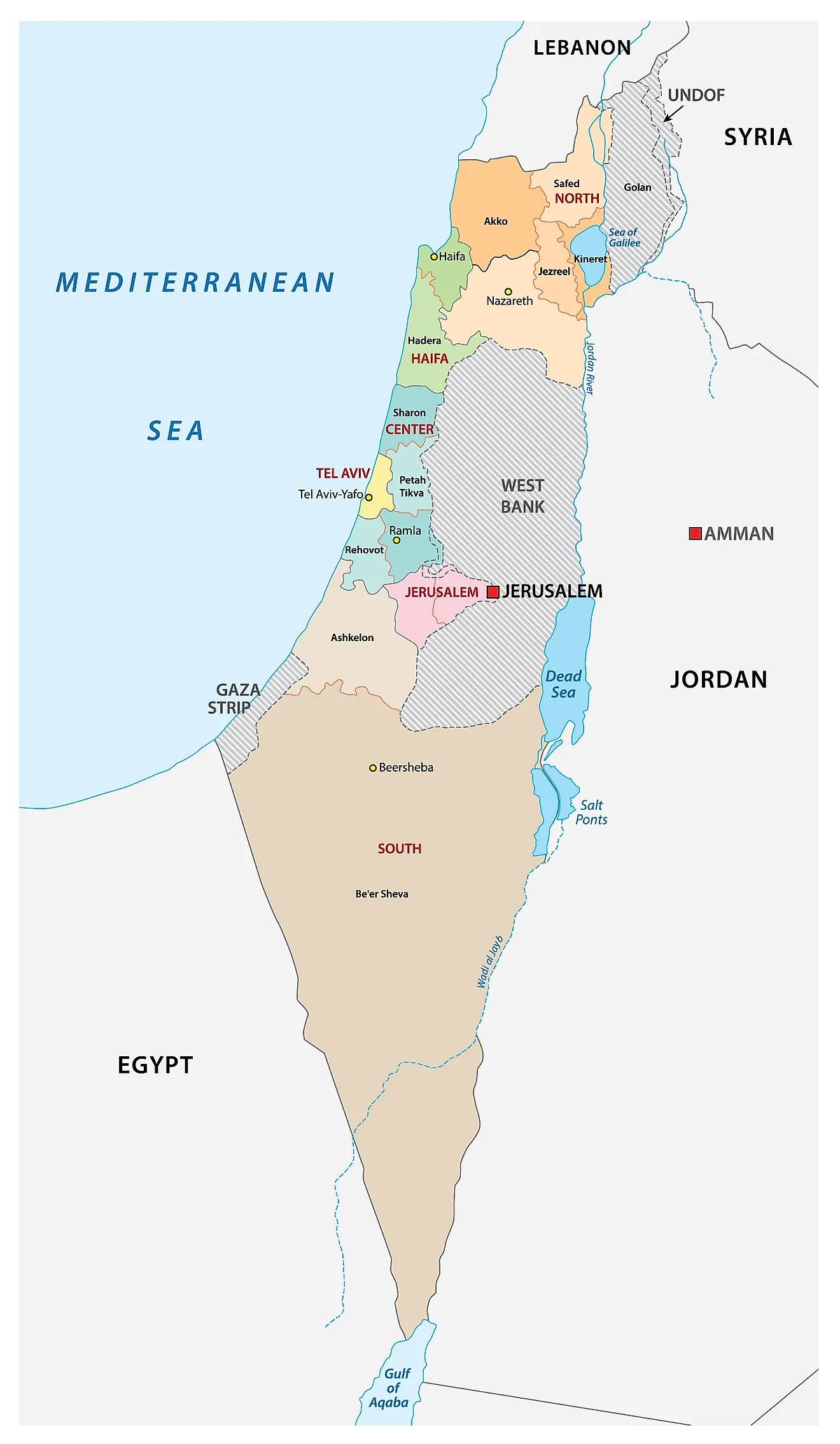
The intricate tapestry of the Middle East is woven with diverse cultures, religions, and histories. At its heart lies Israel, a nation with a long and complex past, nestled between the Mediterranean Sea and the Jordan River, surrounded by a constellation of countries each bearing its own unique weight in the region’s dynamics. Understanding the geography of this area is crucial to comprehending the political, social, and economic complexities that define the region.
The Land and Its Boundaries:
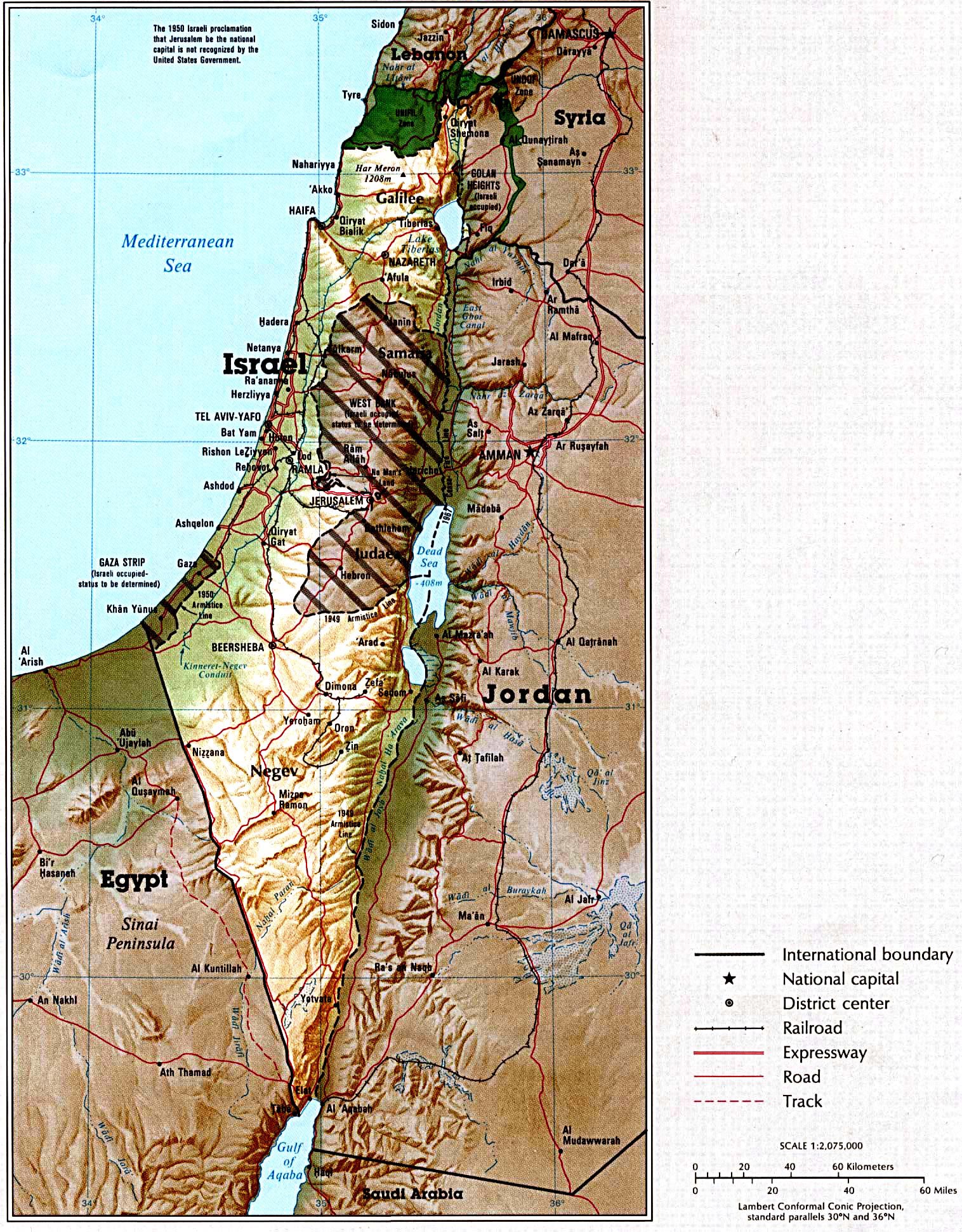
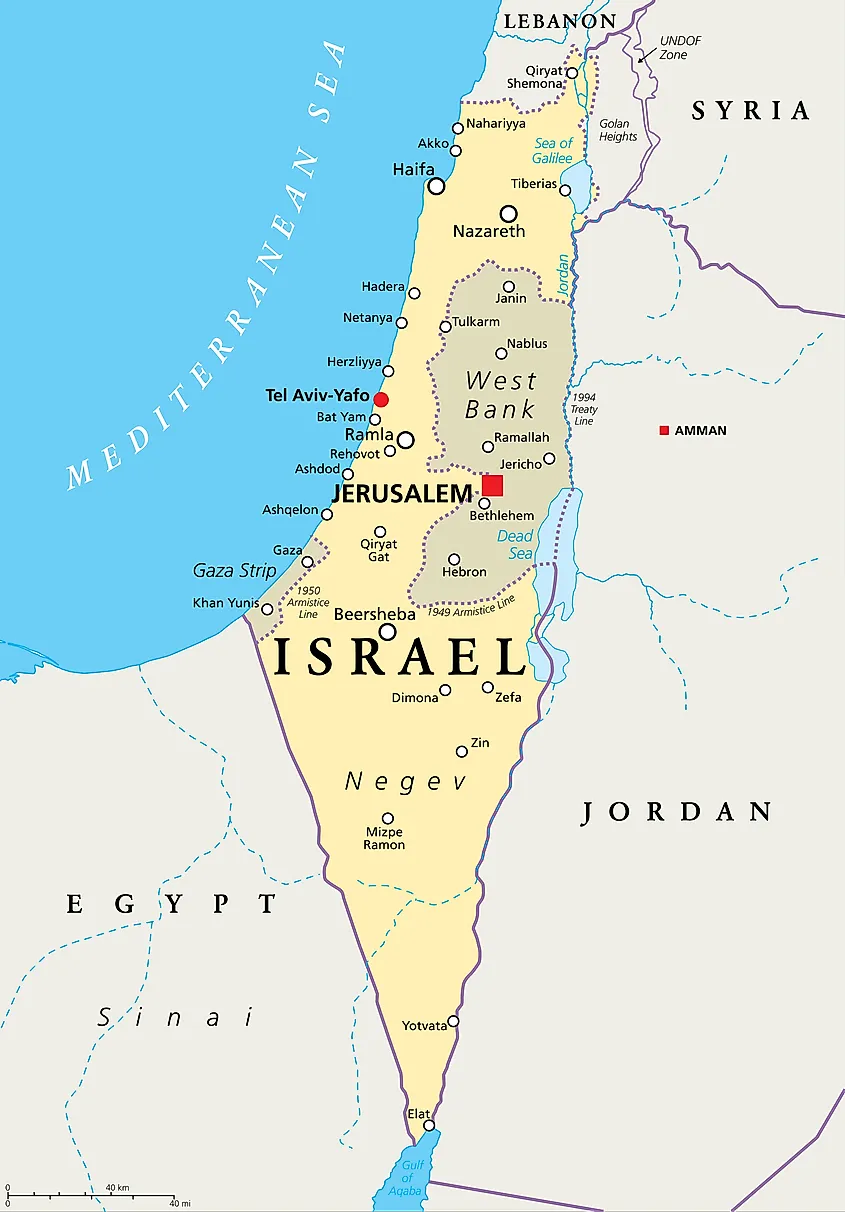
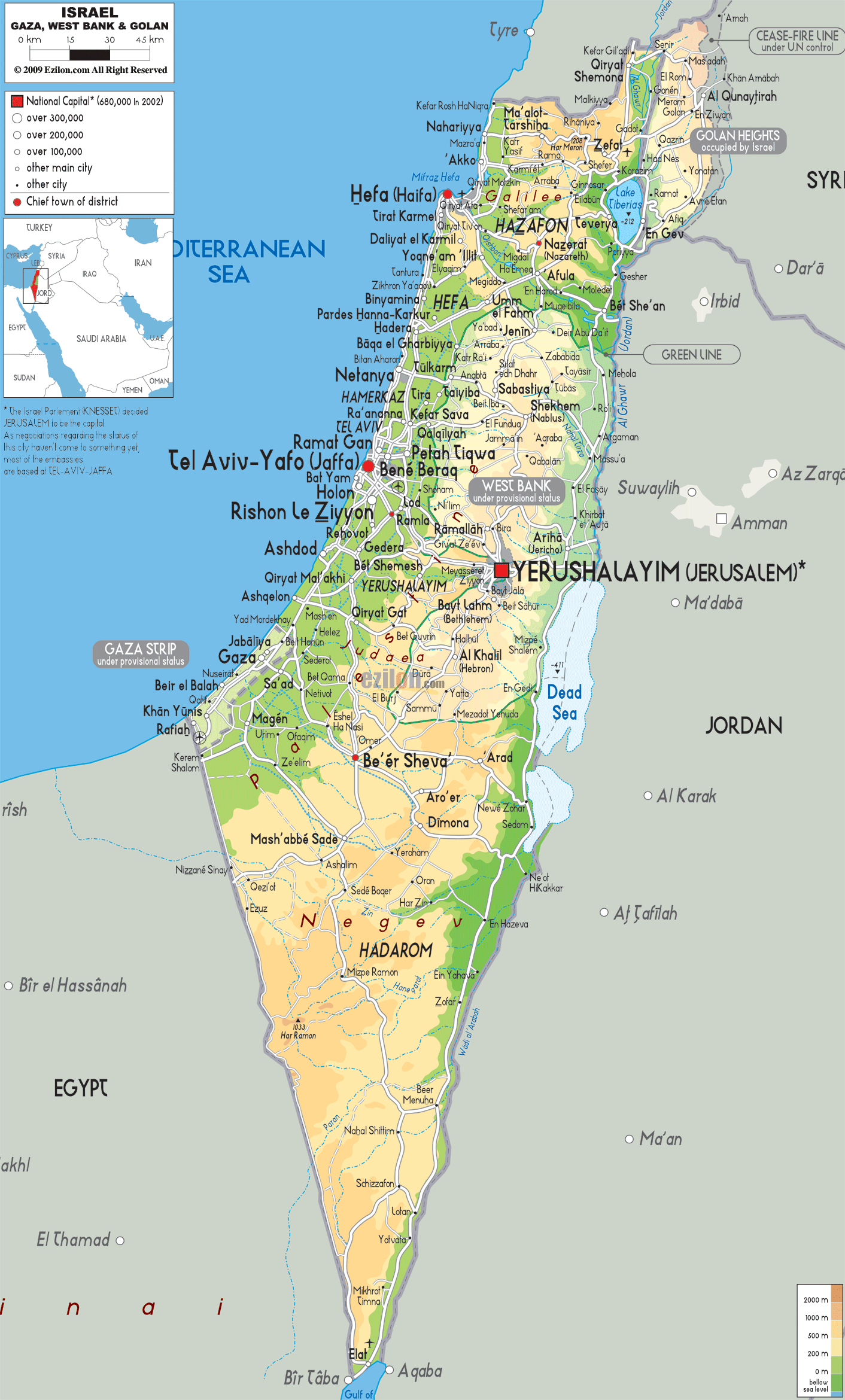
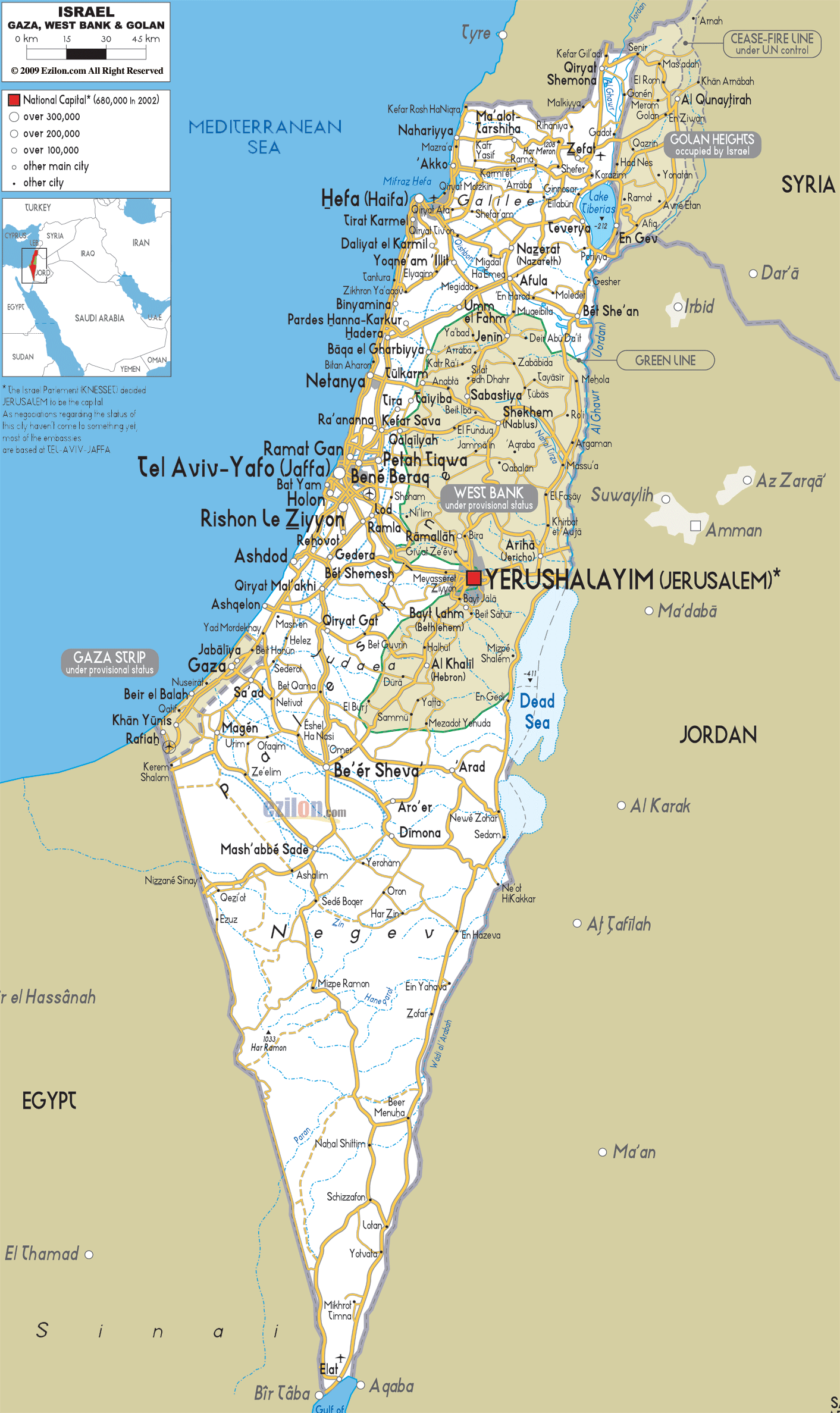
Israel occupies a landmass of approximately 22,072 square kilometers, encompassing diverse landscapes ranging from the fertile coastal plains to the arid Negev Desert. Its borders are defined by:
- To the west: The Mediterranean Sea, providing access to international trade and maritime routes.
- To the north: Lebanon, a country with a complex history and political landscape, bordering Israel along the Litani River.
- To the east: Syria, a nation with significant strategic importance due to its proximity to the Golan Heights, a contested region claimed by both Syria and Israel.
- To the south: Egypt, a vast country with a long history and cultural heritage, sharing a border with Israel in the Sinai Peninsula.
- To the east: Jordan, a kingdom with a close historical connection to Israel, bordering it along the Jordan River.
The Significance of Geography:
The geography of Israel and its surrounding countries is inextricably linked to their history, culture, and present-day realities. The region’s strategic location at the crossroads of continents has shaped its political landscape and influenced its economic development.
- Historical Crossroads: The land has witnessed the rise and fall of empires, serving as a bridge between Africa, Asia, and Europe. The region’s significance is reflected in its rich archaeological heritage, with ancient cities like Jerusalem, Jericho, and Petra bearing testament to millennia of human history.
- Religious Significance: The region holds profound religious importance for Judaism, Christianity, and Islam, with holy sites like Jerusalem, Bethlehem, and Nazareth attracting pilgrims from around the globe. These shared religious sites have also been a source of tension and conflict, underscoring the complexities of the region’s religious landscape.
- Economic Importance: The region’s strategic location offers potential for economic growth, facilitating trade and investment between different continents. The access to the Mediterranean Sea, coupled with the presence of natural resources like natural gas and oil, creates opportunities for economic development.
- Security Concerns: The history of conflict and political instability in the region has created a complex security landscape, with ongoing tensions and border disputes posing challenges to stability and peace. The proximity of countries with diverse political ideologies and military capabilities adds another layer of complexity to the security situation.
The Impact of Political Dynamics:
The political landscape of the region is characterized by a web of interconnected issues, including:
- The Israeli-Palestinian Conflict: This long-standing conflict over land, resources, and political rights has been a major source of instability in the region, affecting both internal and external relations.
- The Syrian Civil War: The ongoing civil war in Syria has had a profound impact on the region, creating a humanitarian crisis and contributing to the flow of refugees and the rise of extremist groups.
- The Arab-Israeli Conflict: This broader conflict, encompassing multiple wars and peace agreements, has shaped the region’s political landscape for decades.
- Regional Alliances: The complex web of alliances and rivalries between regional powers, including Iran, Saudi Arabia, and Turkey, adds another layer of complexity to the political landscape.
The Role of International Actors:
International actors play a significant role in shaping the region’s political and economic landscape. The United States, European Union, and United Nations have been involved in peacemaking efforts, providing humanitarian aid, and supporting economic development.
FAQs:
1. What are the main geographical features of Israel?
Israel’s geography is diverse, encompassing coastal plains, mountainous regions, valleys, and deserts. The country is divided into four main regions: the coastal plain, the central highlands, the Jordan Valley, and the Negev Desert.
2. What is the significance of the Jordan River?
The Jordan River is a vital water source for Israel and its neighboring countries. It holds religious significance for Judaism, Christianity, and Islam, and its banks have been the site of numerous historical events.
3. What is the Golan Heights and why is it important?
The Golan Heights is a plateau strategically located on the border between Israel and Syria. It is a source of water and has strategic military importance, leading to disputes over its control.
4. What are the main challenges facing the region?
The region faces numerous challenges, including political instability, conflict, poverty, environmental degradation, and the lack of economic opportunities.
5. What are the potential for economic development in the region?
The region has potential for economic development in areas like agriculture, tourism, and technology. However, the political instability and lack of infrastructure pose significant challenges.
Tips:
- Study the history of the region: Understanding the historical context is crucial for comprehending the present-day political and social landscape.
- Explore the cultural diversity: The region is home to a rich tapestry of cultures, religions, and languages. Engaging with this diversity can foster understanding and empathy.
- Follow the news and current events: Stay informed about the latest developments in the region to gain a deeper understanding of the ongoing challenges and potential solutions.
- Support peace initiatives: Engage in initiatives promoting dialogue, reconciliation, and cooperation between different communities in the region.
Conclusion:
The map of Israel and its surrounding countries offers a window into a complex and dynamic region. Understanding the geographical features, historical context, political dynamics, and economic challenges is crucial for appreciating the region’s complexities and potential for change. By fostering dialogue, promoting peace, and working towards sustainable development, the region can move towards a future of stability and prosperity.



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into A Geographical Overview: Israel and its Surrounding Countries. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!