A Geographical Journey Through Japan: Exploring The Regions Of The Land Of The Rising Sun
A Geographical Journey Through Japan: Exploring the Regions of the Land of the Rising Sun
Related Articles: A Geographical Journey Through Japan: Exploring the Regions of the Land of the Rising Sun
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to A Geographical Journey Through Japan: Exploring the Regions of the Land of the Rising Sun. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
A Geographical Journey Through Japan: Exploring the Regions of the Land of the Rising Sun
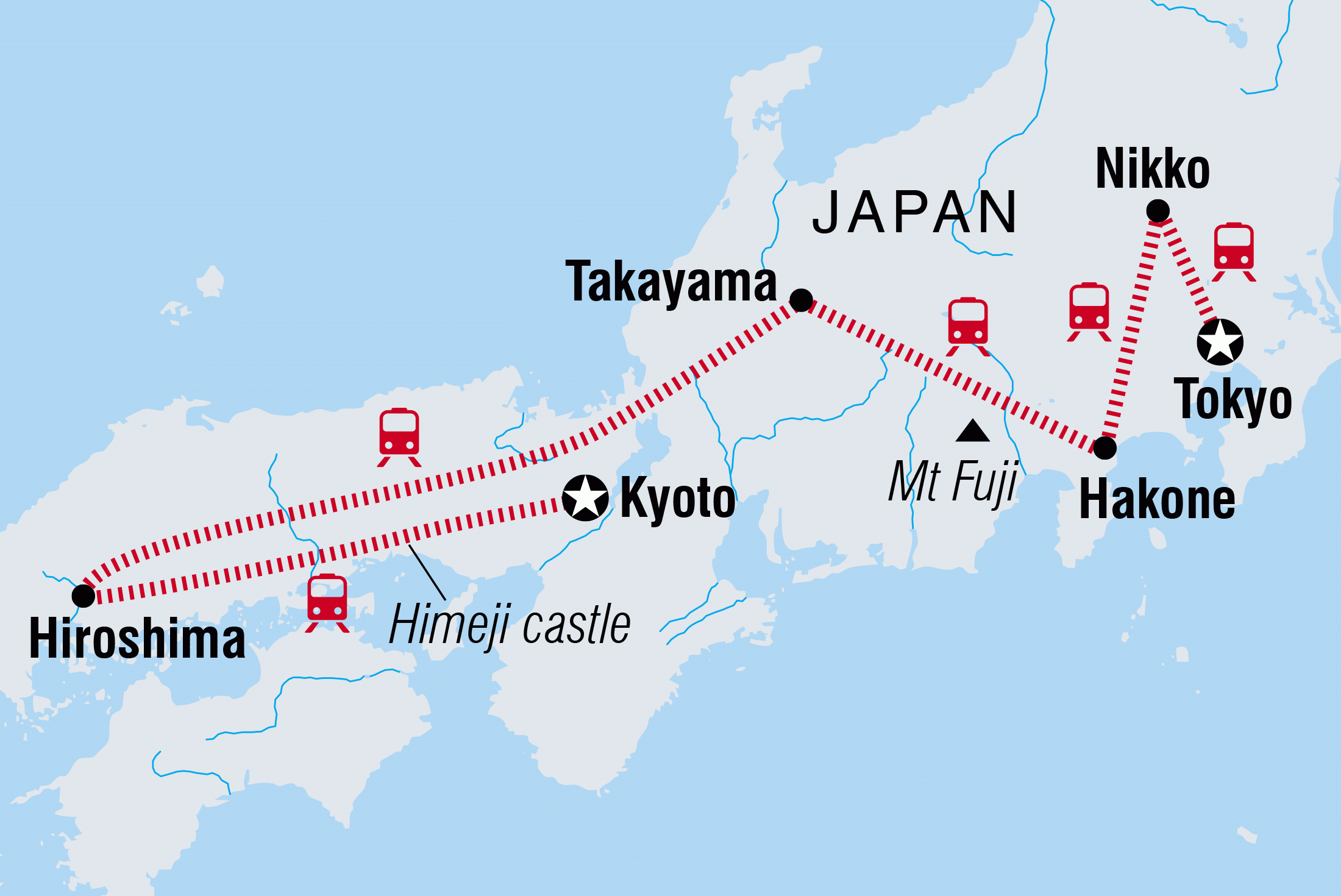
Japan, an archipelago nation nestled in the northwest Pacific Ocean, is renowned for its vibrant culture, technological prowess, and breathtaking landscapes. Its diverse geography, however, goes beyond these popular perceptions. A deeper understanding of Japan’s regional distinctions reveals a tapestry of unique cultural traditions, economic landscapes, and natural wonders that contribute to the nation’s multifaceted identity.
Hokkaido: The Northern Frontier
Hokkaido, Japan’s second-largest island, is a land of untamed beauty. Its mountainous terrain, vast stretches of wilderness, and volcanic landscapes offer a stark contrast to the more densely populated mainland. Hokkaido is known for its abundant natural resources, including timber, fisheries, and agriculture, particularly dairy farming. Its capital, Sapporo, is a thriving metropolis renowned for its annual Snow Festival, a testament to the region’s distinct climate.
Tohoku: The Northeast Region
Tohoku, situated on the northernmost part of Honshu, Japan’s largest island, is a region of rugged beauty and rich cultural heritage. It boasts a dramatic coastline, volcanic mountains, and fertile valleys. Tohoku is known for its traditional crafts, such as lacquerware and textiles, and its unique culinary delights, including the famous Sendai beef. The region is also home to several UNESCO World Heritage sites, including the historic temples and gardens of Hiraizumi.
Kanto: The Heart of Japan
Kanto, encompassing the eastern portion of Honshu, is Japan’s most populous and economically influential region. It is home to the capital city, Tokyo, a bustling metropolis that serves as the nation’s financial, cultural, and political center. Kanto is also known for its diverse landscapes, ranging from the snow-capped Mount Fuji to the scenic Hakone National Park. The region’s rich history is reflected in the numerous castles, shrines, and temples scattered throughout its cities and towns.
Chubu: The Central Region
Chubu, situated in the center of Honshu, is a region of diverse landscapes and cultural heritage. It is home to the majestic Japanese Alps, a popular destination for hiking and skiing. Chubu is also known for its hot springs, traditional crafts, and unique culinary traditions, including the famed Hida beef. The region boasts several UNESCO World Heritage sites, including the Shirakawa-go village, famous for its traditional gassho-style houses.
Kansai: The Cultural Hub
Kansai, encompassing the western portion of Honshu, is renowned as Japan’s cultural heartland. Its capital, Osaka, is a vibrant city known for its lively atmosphere, delicious street food, and bustling entertainment district. Kansai is also home to Kyoto, the ancient capital of Japan, a city renowned for its traditional temples, gardens, and geisha districts. The region is known for its unique cultural traditions, including the tea ceremony and the Noh theater.
Chugoku: The Western Frontier
Chugoku, located on the western side of Honshu, is a region of diverse landscapes, from the scenic Seto Inland Sea to the rugged mountains of the Chugoku Mountains. Chugoku is known for its historical sites, including the ancient ruins of Hiroshima, a city devastated by the atomic bomb during World War II. The region is also home to the beautiful Itsukushima Shrine, a UNESCO World Heritage site located on Miyajima Island.
Shikoku: The Island of Pilgrimage
Shikoku, the smallest of Japan’s four main islands, is known for its spiritual significance. It is home to the 88-temple pilgrimage route, a sacred journey undertaken by Buddhist devotees. Shikoku is also known for its beautiful natural landscapes, including the Shikoku Mountains and the Uwajima Castle, a historical landmark overlooking the city of Uwajima.
Kyushu: The Southern Gateway
Kyushu, Japan’s third-largest island, is a region of volcanic landscapes, hot springs, and vibrant cities. Its capital, Fukuoka, is a bustling metropolis known for its bustling nightlife and delicious street food. Kyushu is also home to the iconic Mount Aso, one of Japan’s most active volcanoes, and the beautiful Kumamoto Castle, a historical landmark that survived the Kumamoto earthquake.
Okinawa: The Tropical Paradise
Okinawa, a chain of islands located south of Kyushu, is a tropical paradise known for its beautiful beaches, turquoise waters, and vibrant coral reefs. Okinawa has a distinct culture, influenced by its history as the Ryukyu Kingdom. The region is known for its unique cuisine, including the famous Okinawa soba noodles, and its traditional crafts, such as the Ryukyu bingata dyeing technique.
Understanding the Importance of Regional Distinctions
Understanding the regional distinctions within Japan is crucial for appreciating its rich history, diverse culture, and unique natural beauty. Each region possesses its own unique identity, shaped by its geographical features, historical experiences, and cultural traditions.
Economic Diversification and Regional Development
Japan’s regional differences are also reflected in its economic landscape. While Tokyo and its surrounding areas dominate the nation’s economy, each region possesses its own unique strengths and contributes to the country’s overall economic growth.
Tourism and Cultural Exchange
The regional distinctions within Japan also contribute to the nation’s thriving tourism industry. Each region offers unique experiences, from exploring ancient temples and gardens in Kyoto to hiking in the Japanese Alps or relaxing on the beaches of Okinawa. The diversity of Japan’s regions makes it a destination that can cater to a wide range of interests and preferences.
Regional Distinctions and National Identity
Understanding the regional distinctions within Japan is essential for appreciating the nation’s complex and multifaceted identity. While Japan is often perceived as a homogenous society, its regional diversity plays a crucial role in shaping its cultural landscape and national identity.
FAQs
Q: What are the major geographical features of Japan?
A: Japan is an archipelago nation consisting of four main islands: Hokkaido, Honshu, Shikoku, and Kyushu, and over 6,800 smaller islands. The islands are mountainous, with volcanic activity being a prominent feature. The nation also has a long coastline and numerous rivers.
Q: What are the major cultural differences between Japan’s regions?
A: Each region in Japan possesses its own distinct cultural identity, shaped by its history, traditions, and local customs. This includes differences in dialect, cuisine, traditional crafts, and festivals.
Q: What are some of the major economic differences between Japan’s regions?
A: The Kanto region, with Tokyo as its center, is the most economically developed region in Japan. However, each region has its own economic strengths, ranging from agriculture and fishing in Hokkaido to manufacturing and tourism in other regions.
Q: How does understanding Japan’s regional distinctions benefit travelers?
A: Understanding Japan’s regional differences allows travelers to tailor their itinerary to their interests and preferences, exploring different landscapes, cultural experiences, and culinary delights.
Tips for Exploring Japan by Region
- Research the unique characteristics of each region: Explore its history, culture, cuisine, and natural attractions to plan your itinerary effectively.
- Consider using regional transportation: Utilize local trains and buses to explore the region more thoroughly and experience local life.
- Engage with local communities: Interact with locals, try regional specialties, and immerse yourself in the unique culture of each region.
- Respect local customs and traditions: Be mindful of cultural differences and show respect for local customs and traditions.
Conclusion
Japan’s regional distinctions are a testament to the nation’s rich history, diverse culture, and unique natural beauty. From the snow-capped mountains of Hokkaido to the tropical beaches of Okinawa, each region offers a unique and unforgettable experience. Understanding these regional differences allows for a deeper appreciation of Japan’s multifaceted identity and provides a richer and more rewarding travel experience.








Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into A Geographical Journey Through Japan: Exploring the Regions of the Land of the Rising Sun. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!