A Geographical Exploration Of The Israel Region: Historical Landscapes, Cultural Tapestry, And Geopolitical Significance
A Geographical Exploration of the Israel Region: Historical Landscapes, Cultural Tapestry, and Geopolitical Significance
Related Articles: A Geographical Exploration of the Israel Region: Historical Landscapes, Cultural Tapestry, and Geopolitical Significance
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to A Geographical Exploration of the Israel Region: Historical Landscapes, Cultural Tapestry, and Geopolitical Significance. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
A Geographical Exploration of the Israel Region: Historical Landscapes, Cultural Tapestry, and Geopolitical Significance

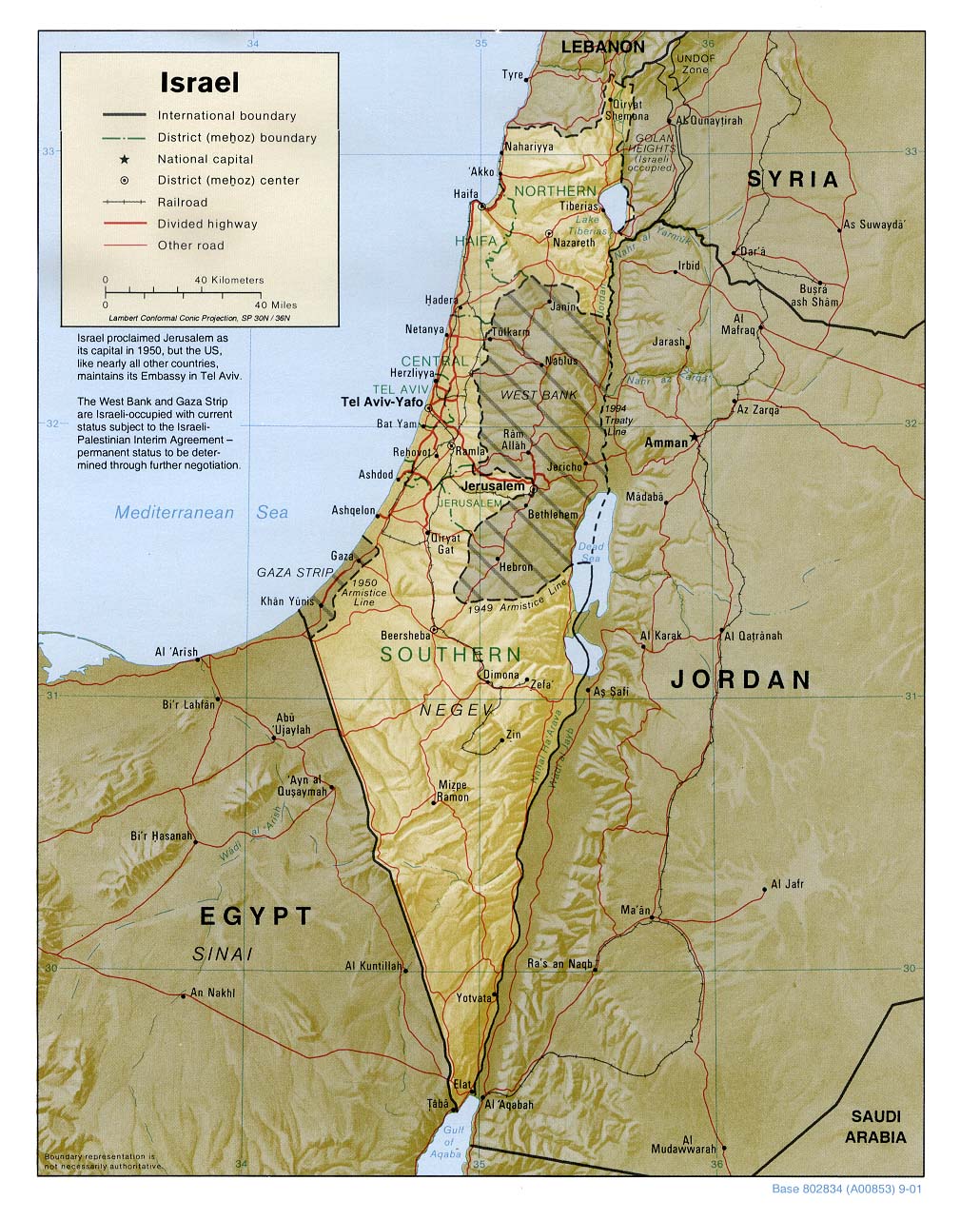
The Israel region, encompassing a landmass of approximately 22,094 square kilometers, holds a unique position on the world stage, interwoven with history, religion, and geopolitics. Its geographical features, from the fertile coastal plain to the arid Negev desert, have shaped its cultural landscape, fostering a diverse array of communities and traditions. Understanding the map of Israel, with its intricate political borders, historical sites, and natural wonders, is crucial for comprehending the region’s complex past, present, and future.
The Land and Its Features:
The Israel region is situated at the crossroads of three continents: Asia, Africa, and Europe. Its diverse topography encompasses:
- The Coastal Plain: This fertile strip of land along the Mediterranean Sea is home to major cities like Tel Aviv and Haifa, and serves as a vital agricultural hub.
- The Central Highlands: This hilly region, stretching from the Carmel Mountains to the Judean Hills, is characterized by rolling hills, vineyards, and ancient settlements. Jerusalem, the holy city, resides within these highlands.
- The Jordan Rift Valley: This geological depression, running along the eastern border, includes the Dead Sea, the lowest point on Earth, and the Jordan River, a vital water source.
- The Negev Desert: Covering over half of Israel’s landmass, the Negev is a vast desert landscape with unique geological formations and sparse vegetation.
Historical Significance:
The Israel region boasts an ancient history, dating back millennia. Its strategic location along trade routes and its fertile land have attracted civilizations for centuries, leaving behind a rich tapestry of archaeological sites and historical narratives.
- The Land of Canaan: In ancient times, the region was known as Canaan, inhabited by various Semitic tribes.
- The Kingdom of Israel: Around the 10th century BCE, the united Kingdom of Israel emerged, later dividing into the Kingdoms of Israel and Judah.
- Roman and Byzantine Rule: The region fell under Roman rule in the 1st century CE, followed by Byzantine rule in the 4th century CE.
- Islamic Conquest: In the 7th century CE, the region was conquered by the Muslim Rashidun Caliphate, marking the beginning of Islamic rule.
- Ottoman Empire: From the 16th to the 19th centuries, the region was part of the Ottoman Empire.
- British Mandate: Following World War I, the region came under British control as the British Mandate for Palestine.
The Modern State of Israel:
The establishment of the State of Israel in 1948 was a pivotal moment in the region’s history. It was followed by the Arab-Israeli War of 1948, leading to the displacement of Palestinian refugees and ongoing territorial disputes.
- The Six-Day War: The 1967 Six-Day War resulted in Israel’s control over the West Bank, East Jerusalem, Gaza Strip, Golan Heights, and Sinai Peninsula.
- The Oslo Accords: In the 1990s, the Oslo Accords aimed to establish a two-state solution, with an independent Palestinian state alongside Israel. However, these efforts have been hampered by ongoing violence and political disagreements.
The Palestinian Territories:
The Palestinian territories, encompassing the West Bank and Gaza Strip, are home to a large Palestinian population. They are under Israeli control, with varying degrees of autonomy. The Palestinian Authority (PA) governs the West Bank, while Hamas controls the Gaza Strip.
- The West Bank: Divided into Area A, B, and C, the West Bank is subject to Israeli security control and administrative restrictions.
- The Gaza Strip: A densely populated coastal territory, the Gaza Strip is under a tight Israeli blockade, leading to humanitarian challenges and economic hardship.
Geopolitical Significance:
The Israel region remains a focal point of international attention due to its geopolitical significance:
- Religious Importance: The region holds immense religious importance for Judaism, Christianity, and Islam, with Jerusalem being a sacred city for all three faiths.
- Strategic Location: Situated at the crossroads of three continents, the region holds strategic importance in terms of trade routes and military deployments.
- Resource Potential: The region possesses significant natural resources, including water, minerals, and energy reserves, making it a valuable asset in the global economy.
- Political Instability: The ongoing Israeli-Palestinian conflict, coupled with regional tensions, contributes to political instability and security concerns.
Cultural Tapestry:
The Israel region is a vibrant tapestry of cultures, shaped by its diverse history and population:
- Jewish Culture: With a strong emphasis on tradition, religious observance, and a rich literary and artistic heritage, Jewish culture is deeply intertwined with the region’s identity.
- Arab Culture: Arab culture, with its distinct linguistic, culinary, and artistic traditions, plays a significant role in the region’s social fabric.
- Bedouin Culture: The Bedouin people, known for their nomadic lifestyle and resilience in harsh desert environments, contribute a unique cultural dimension to the region.
- International Influences: Due to its historical connections and modern-day immigration, the region has absorbed influences from various cultures, contributing to its diverse cultural landscape.
Challenges and Opportunities:
The Israel region faces numerous challenges, including:
- The Israeli-Palestinian Conflict: The unresolved conflict remains a major obstacle to peace and stability in the region.
- Water Scarcity: The region experiences water shortages, exacerbated by climate change and population growth.
- Economic Disparities: Income inequality and social disparities persist, particularly between Jewish and Arab populations.
- Security Threats: The region faces various security threats, including terrorism and regional instability.
Despite these challenges, the Israel region also presents significant opportunities:
- Technological Innovation: Israel is a global leader in technology, with a thriving start-up ecosystem and expertise in fields like agriculture, cybersecurity, and renewable energy.
- Tourism Potential: The region attracts millions of tourists annually, drawn to its historical sites, religious significance, and diverse cultural offerings.
- Economic Growth: The region has a dynamic economy, driven by industries like technology, tourism, and agriculture.
- Regional Cooperation: There is potential for increased cooperation between Israel and its neighboring countries, particularly in areas like water management and economic development.
FAQs on the Israel Region:
Q: What is the current political situation in the Israel region?
A: The political situation in the Israel region remains complex and volatile. The Israeli-Palestinian conflict remains unresolved, with ongoing tensions and disputes over land, resources, and security. The Israeli government faces internal divisions, while the Palestinian Authority struggles with internal fragmentation and external pressures.
Q: What is the significance of Jerusalem in the Israel region?
A: Jerusalem holds immense religious significance for Judaism, Christianity, and Islam. It is considered the holy city for all three faiths, with sacred sites like the Western Wall, the Church of the Holy Sepulchre, and the Dome of the Rock. Its status as a contested city remains a major point of contention in the Israeli-Palestinian conflict.
Q: What are the main challenges facing the Israel region?
A: The Israel region faces numerous challenges, including the unresolved Israeli-Palestinian conflict, water scarcity, economic disparities, and security threats. These challenges require complex and multifaceted solutions involving political dialogue, economic development, and social reconciliation.
Q: What are the potential opportunities for the Israel region?
A: The Israel region offers significant potential for economic growth, technological innovation, tourism development, and regional cooperation. Its strategic location, diverse population, and entrepreneurial spirit provide opportunities for collaboration and progress.
Tips for Understanding the Israel Region:
- Engage with diverse perspectives: Seek out information from various sources, including Israeli, Palestinian, and international perspectives.
- Study the history: Understand the historical context of the region, including its ancient origins, colonial periods, and modern-day conflicts.
- Explore cultural nuances: Appreciate the diverse cultural traditions and identities that contribute to the region’s richness.
- Follow current events: Stay informed about ongoing developments and political dynamics in the region.
- Support peace initiatives: Encourage and support efforts aimed at resolving conflicts and promoting peace and reconciliation.
Conclusion:
The Israel region is a complex and dynamic landscape, shaped by its history, geography, and diverse populations. Understanding its map, with its intricate political borders, historical sites, and natural wonders, is essential for comprehending the region’s past, present, and future. Despite the challenges it faces, the Israel region also holds significant potential for progress, collaboration, and a more peaceful future. By fostering dialogue, promoting understanding, and encouraging cooperation, the region can work towards a future where its diverse communities can thrive in peace and prosperity.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into A Geographical Exploration of the Israel Region: Historical Landscapes, Cultural Tapestry, and Geopolitical Significance. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!