A Geographical Exploration Of Africa: Understanding The Continent’s Diverse Nations
A Geographical Exploration of Africa: Understanding the Continent’s Diverse Nations
Related Articles: A Geographical Exploration of Africa: Understanding the Continent’s Diverse Nations
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to A Geographical Exploration of Africa: Understanding the Continent’s Diverse Nations. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
A Geographical Exploration of Africa: Understanding the Continent’s Diverse Nations

Africa, the second-largest continent by both land and population, is a tapestry of diverse landscapes, cultures, and histories. Its 54 sovereign nations, each with its unique identity, contribute to the vibrant mosaic that defines the continent. Understanding the geographical distribution of these nations is crucial for comprehending the continent’s political, economic, and social dynamics.
The North: A Region of Contrast
North Africa, separated from the rest of the continent by the Sahara Desert, presents a unique blend of Arab and Berber influences. This region is home to five nations:
- Egypt: Straddling the Nile River, Egypt is the most populous country in the region and a historical powerhouse, renowned for its ancient civilization and iconic pyramids.
- Libya: A vast, arid country with significant oil reserves, Libya borders Egypt to the east and Tunisia to the west.
- Algeria: The largest country in Africa by land area, Algeria shares a long border with Morocco to the west and boasts a diverse landscape ranging from the Atlas Mountains to the Sahara Desert.
- Morocco: Located at the northwestern tip of Africa, Morocco is known for its beautiful coastline, vibrant cities, and rich cultural heritage.
- Tunisia: Situated on the Mediterranean Sea, Tunisia is a relatively small country with a rich history and a thriving tourism industry.
The West: A Tapestry of Cultures
West Africa, with its diverse ethnicities and languages, is a region characterized by its vibrant cultures, bustling cities, and rich natural resources. The region encompasses 17 nations:
- Mauritania: A vast desert country located on the Atlantic coast, Mauritania shares borders with several other West African nations.
- Senegal: Known for its beautiful beaches and vibrant capital city Dakar, Senegal is a key player in the West African economy.
- Gambia: A small, narrow country located along the Gambia River, Gambia is known for its rich culture and its abundance of wildlife.
- Guinea-Bissau: A coastal country with a rich cultural heritage, Guinea-Bissau was once a Portuguese colony.
- Guinea: A large country with diverse landscapes, Guinea is rich in natural resources and has a significant mining industry.
- Sierra Leone: Situated on the Atlantic coast, Sierra Leone has a rich history and is known for its beautiful beaches and its diverse wildlife.
- Liberia: Founded by freed American slaves, Liberia is a country with a unique history and a diverse population.
- Côte d’Ivoire: Located on the Atlantic coast, Côte d’Ivoire is a major producer of cocoa and coffee and has a vibrant economy.
- Ghana: Known for its rich gold deposits and its historical significance, Ghana is a key player in the West African economy.
- Togo: A small country with diverse landscapes, Togo is known for its beautiful beaches and its rich cultural heritage.
- Benin: Situated on the Gulf of Guinea, Benin is a country with a rich cultural heritage and a diverse population.
- Niger: A landlocked country with a vast desert landscape, Niger is known for its uranium deposits and its rich cultural heritage.
- Nigeria: The most populous country in Africa, Nigeria is a major producer of oil and has a thriving economy.
- Chad: A landlocked country with a diverse landscape, Chad is known for its oil reserves and its rich cultural heritage.
- Cameroon: A country with diverse landscapes, Cameroon is known for its biodiversity and its rich cultural heritage.
- Central African Republic: A landlocked country with a diverse landscape, the Central African Republic is rich in natural resources.
- Equatorial Guinea: A small country on the west coast of Central Africa, Equatorial Guinea is a major producer of oil and has a rapidly growing economy.
The Central: Heart of the Continent
Central Africa, characterized by dense rainforests and vast savannas, is home to a diverse array of wildlife and indigenous cultures. The region comprises 10 nations:
- Gabon: A country with diverse landscapes, Gabon is known for its rich biodiversity and its abundant oil reserves.
- Congo: A country with a vast rainforest, Congo is known for its rich biodiversity and its vast oil reserves.
- Democratic Republic of the Congo: The largest country in Central Africa, the Democratic Republic of the Congo is known for its rich mineral resources and its diverse population.
- Republic of the Congo: Located on the Atlantic coast, the Republic of the Congo is a country with diverse landscapes and abundant oil reserves.
- Angola: A country with a long coastline and a vast interior, Angola is a major producer of oil and diamonds.
- Zambia: A landlocked country with a diverse landscape, Zambia is known for its rich copper deposits and its abundant wildlife.
- Malawi: A landlocked country with a beautiful lake, Malawi is known for its rich biodiversity and its diverse population.
- Mozambique: A country with a long coastline and a diverse landscape, Mozambique is known for its beautiful beaches and its abundant seafood.
- Zimbabwe: A landlocked country with a diverse landscape, Zimbabwe is known for its rich history and its abundant wildlife.
- Botswana: A landlocked country with a vast desert landscape, Botswana is known for its diamond reserves and its abundant wildlife.
The East: Cradle of Humanity
East Africa, home to the Great Rift Valley and the source of the Nile River, is a region of diverse landscapes and cultures. The region encompasses 20 nations:
- Sudan: A vast country with diverse landscapes, Sudan is known for its rich history and its abundant oil reserves.
- South Sudan: A young nation formed in 2011, South Sudan is known for its rich oil reserves and its diverse population.
- Ethiopia: A country with a rich history and a diverse population, Ethiopia is known for its ancient churches and its beautiful landscapes.
- Eritrea: A country with a long coastline and a diverse landscape, Eritrea is known for its rich history and its diverse population.
- Djibouti: A small country on the Horn of Africa, Djibouti is a strategic location with a thriving port.
- Somalia: A country with a long coastline and a diverse landscape, Somalia is known for its rich history and its diverse population.
- Kenya: A country with diverse landscapes, Kenya is known for its abundant wildlife and its beautiful beaches.
- Uganda: A landlocked country with a diverse landscape, Uganda is known for its abundant wildlife and its rich cultural heritage.
- Tanzania: A country with diverse landscapes, Tanzania is known for its abundant wildlife and its beautiful beaches.
- Rwanda: A small country with a mountainous landscape, Rwanda is known for its rich cultural heritage and its diverse population.
- Burundi: A small country with a mountainous landscape, Burundi is known for its rich cultural heritage and its diverse population.
- Seychelles: A group of islands in the Indian Ocean, Seychelles is known for its beautiful beaches and its diverse marine life.
- Comoros: A group of islands in the Indian Ocean, Comoros is known for its beautiful beaches and its rich cultural heritage.
- Mauritius: An island nation in the Indian Ocean, Mauritius is known for its beautiful beaches and its diverse population.
- Madagascar: A large island off the coast of Africa, Madagascar is known for its unique biodiversity and its rich cultural heritage.
The South: A Land of Beauty and Resources
Southern Africa, home to the iconic Table Mountain and the vast Kalahari Desert, is a region of diverse landscapes and cultures. The region encompasses 15 nations:
- Namibia: A country with diverse landscapes, Namibia is known for its vast desert landscapes and its abundant wildlife.
- South Africa: The most developed country in Africa, South Africa is known for its diverse population, its beautiful landscapes, and its rich history.
- Lesotho: A mountainous country entirely surrounded by South Africa, Lesotho is known for its beautiful landscapes and its rich cultural heritage.
- Swaziland: A small country surrounded by South Africa, Swaziland is known for its rich cultural heritage and its beautiful landscapes.
- Mozambique: A country with a long coastline and a diverse landscape, Mozambique is known for its beautiful beaches and its abundant seafood.
- Zimbabwe: A landlocked country with a diverse landscape, Zimbabwe is known for its rich history and its abundant wildlife.
- Botswana: A landlocked country with a vast desert landscape, Botswana is known for its diamond reserves and its abundant wildlife.
- Zambia: A landlocked country with a diverse landscape, Zambia is known for its rich copper deposits and its abundant wildlife.
- Malawi: A landlocked country with a beautiful lake, Malawi is known for its rich biodiversity and its diverse population.
- Angola: A country with a long coastline and a vast interior, Angola is a major producer of oil and diamonds.
- Republic of the Congo: Located on the Atlantic coast, the Republic of the Congo is a country with diverse landscapes and abundant oil reserves.
- Democratic Republic of the Congo: The largest country in Central Africa, the Democratic Republic of the Congo is known for its rich mineral resources and its diverse population.
- Gabon: A country with diverse landscapes, Gabon is known for its rich biodiversity and its abundant oil reserves.
- Equatorial Guinea: A small country on the west coast of Central Africa, Equatorial Guinea is a major producer of oil and has a rapidly growing economy.
- Cameroon: A country with diverse landscapes, Cameroon is known for its biodiversity and its rich cultural heritage.
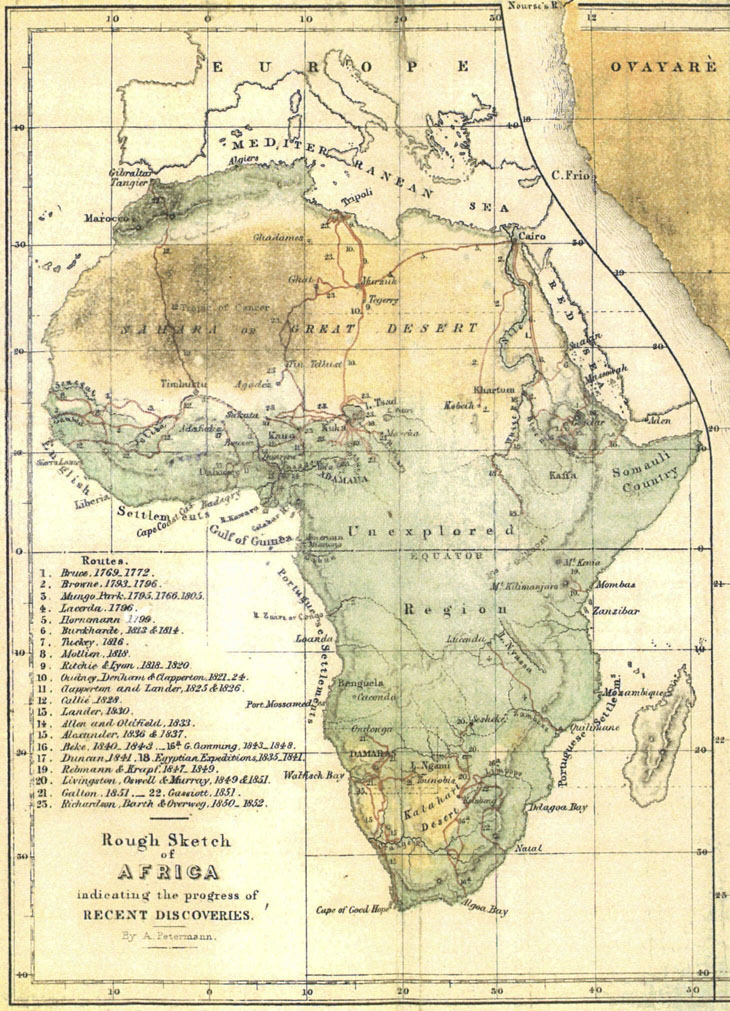
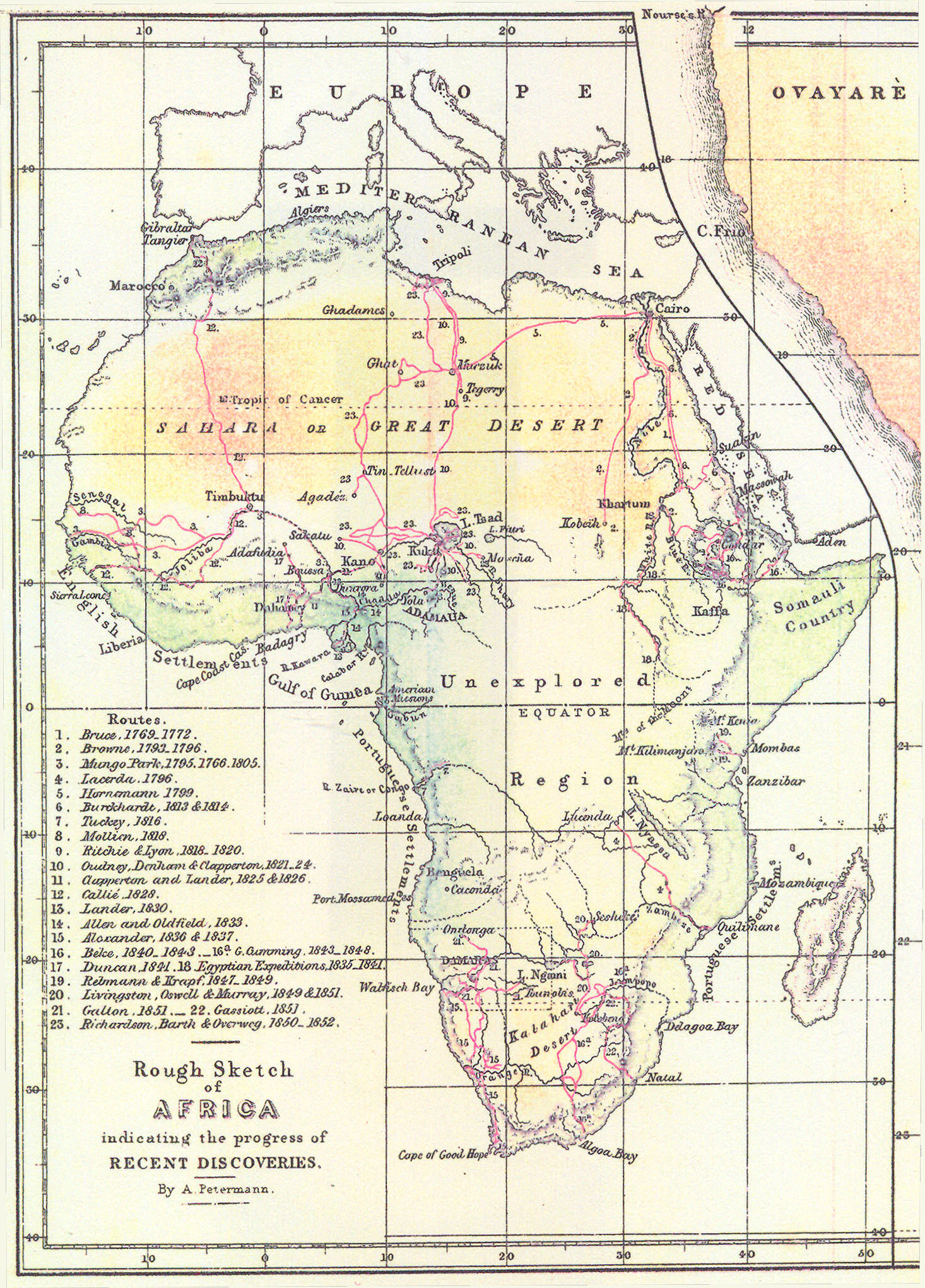
The Importance of Understanding the Map of Africa
Understanding the geographical distribution of African countries is crucial for a variety of reasons:
- Political Context: The map provides a visual representation of the continent’s political landscape, highlighting the boundaries and relationships between nations. This understanding is essential for comprehending regional conflicts, alliances, and political movements.
- Economic Development: The map can be used to analyze the distribution of natural resources, infrastructure, and economic activity across the continent. This information is crucial for developing sustainable economic strategies and promoting regional trade.
- Social and Cultural Dynamics: The map provides a framework for understanding the distribution of different ethnic groups, languages, and cultural practices across the continent. This knowledge is essential for promoting cultural understanding and fostering inter-community dialogue.
- Environmental Concerns: The map helps visualize the distribution of different ecosystems, such as rainforests, deserts, and savannas, and the challenges they face, such as deforestation, desertification, and climate change. This understanding is crucial for developing effective environmental conservation strategies.
FAQs about the Map of Africa
Q: How many countries are in Africa?
A: There are 54 sovereign nations in Africa.
Q: What is the largest country in Africa?
A: Algeria is the largest country in Africa by land area.
Q: What is the most populous country in Africa?
A: Nigeria is the most populous country in Africa.
Q: What are some of the major geographical features of Africa?
A: Africa is home to a variety of geographical features, including the Sahara Desert, the Nile River, the Great Rift Valley, and the Atlas Mountains.
Q: What are some of the challenges facing Africa?
A: Africa faces a number of challenges, including poverty, hunger, disease, conflict, and climate change.
Tips for Understanding the Map of Africa
- Start with a basic map: Use a simple map of Africa to familiarize yourself with the continent’s shape and the locations of major countries.
- Focus on regions: Divide Africa into regions, such as North Africa, West Africa, Central Africa, East Africa, and Southern Africa. This will help you organize your understanding of the continent’s diversity.
- Learn about key geographical features: Identify important geographical features, such as rivers, mountains, deserts, and lakes. This will help you understand the continent’s natural environment.
- Explore individual countries: Once you have a basic understanding of the continent, delve deeper into individual countries. Research their history, culture, economy, and challenges.
Conclusion
The map of Africa is a powerful tool for understanding the continent’s rich diversity and complex challenges. By studying the geographical distribution of African nations, we can gain a deeper appreciation for the continent’s history, culture, and potential. This understanding is essential for promoting sustainable development, fostering inter-community dialogue, and building a more peaceful and prosperous future for Africa.
:no_upscale()/cdn.vox-cdn.com/uploads/chorus_asset/file/4247569/Africa_comp.jpg)




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into A Geographical Exploration of Africa: Understanding the Continent’s Diverse Nations. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!