A Geographical Exploration Of Africa, Asia, And Europe: A Look At Three Continents
A Geographical Exploration of Africa, Asia, and Europe: A Look at Three Continents
Related Articles: A Geographical Exploration of Africa, Asia, and Europe: A Look at Three Continents
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to A Geographical Exploration of Africa, Asia, and Europe: A Look at Three Continents. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
A Geographical Exploration of Africa, Asia, and Europe: A Look at Three Continents
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/2168347_eadc315ad3_o-59cee288685fbe0011acd4c6.jpg)
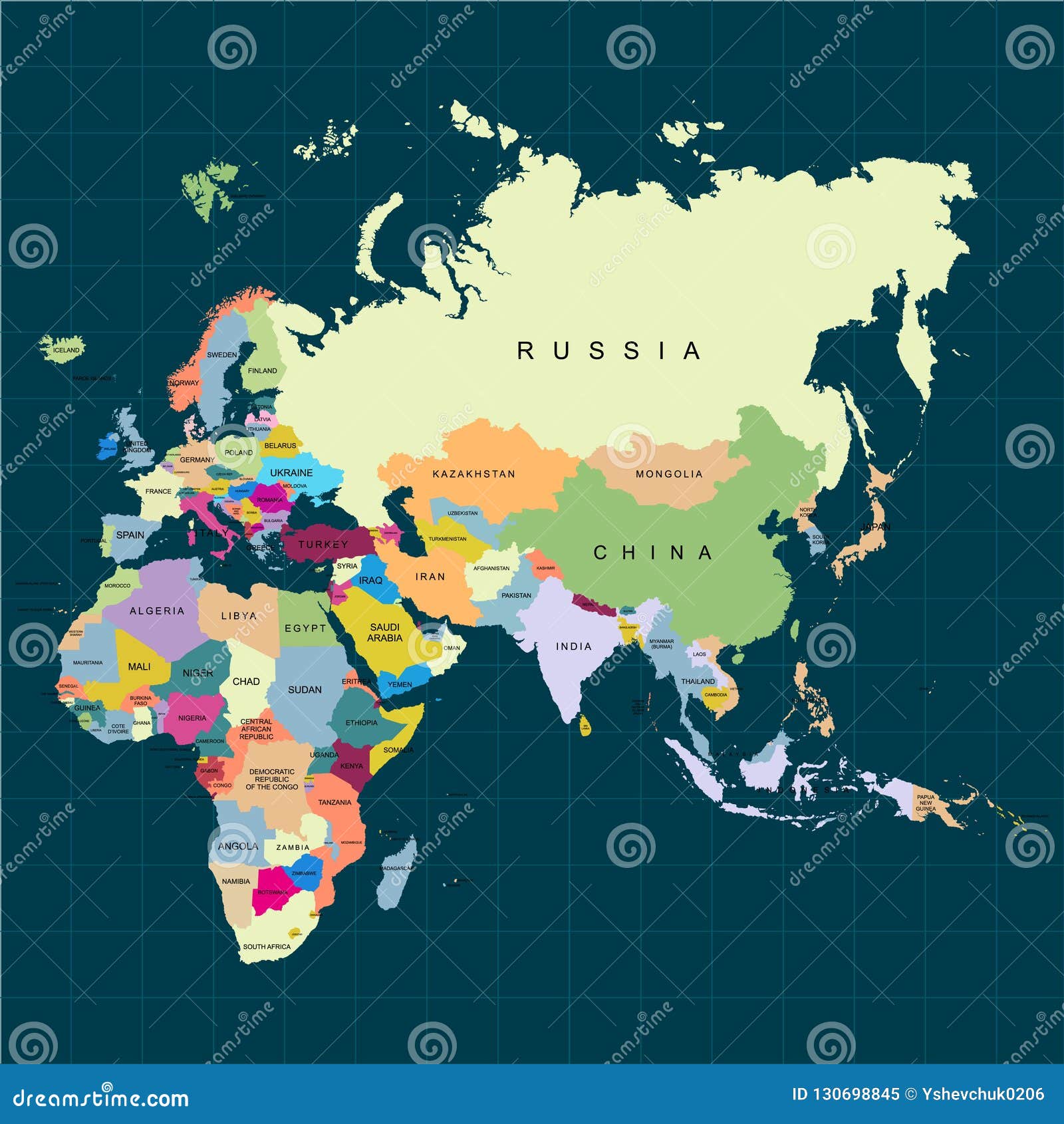
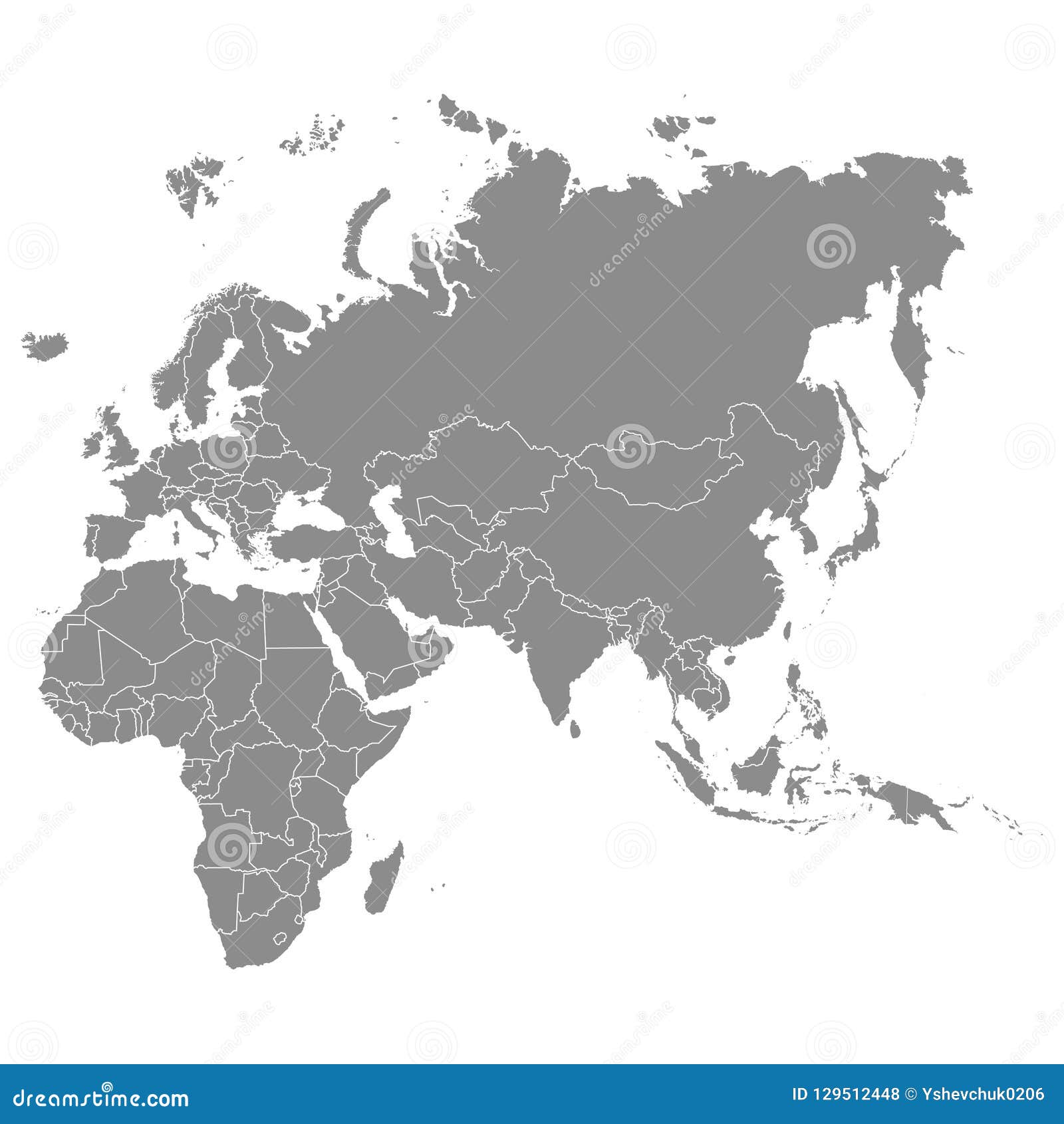
The vast landscapes of Africa, Asia, and Europe, collectively home to over 60% of the world’s population, represent a tapestry of diverse cultures, histories, and ecosystems. Understanding the geographical features and political boundaries of these continents is crucial for comprehending global dynamics, from economic interdependence to environmental challenges. This exploration delves into the intricate map of Africa, Asia, and Europe, highlighting key geographical features, political divisions, and the interconnectedness of these continents.
Africa: A Continent of Diversity
Africa, the second-largest continent by landmass, is characterized by its vast and diverse geography, ranging from the Sahara Desert, the world’s largest hot desert, to the lush rainforests of the Congo Basin. The continent is further distinguished by its dramatic topography, encompassing towering mountain ranges like the Atlas Mountains and the Drakensberg, as well as expansive savannas and fertile river valleys.
Political Landscape: The African continent is divided into 54 independent countries, each with its unique history, culture, and political system. From the vast expanse of Sudan and Algeria to the smaller island nations of Cape Verde and Comoros, the political map of Africa reflects a complex tapestry of colonial legacies, ethnicities, and evolving political landscapes.
Key Geographical Features:
- Sahara Desert: The largest hot desert in the world, covering over 3.3 million square miles, and stretching across northern Africa.
- Nile River: The longest river in the world, flowing through eleven countries and supporting a significant population.
- Great Rift Valley: A geological formation stretching over 4,000 miles, marking a zone of tectonic activity and volcanic activity.
- Congo Basin: Home to the second-largest rainforest in the world, characterized by rich biodiversity and significant carbon sequestration.
Asia: The Largest and Most Populous Continent
Asia, the largest and most populous continent, encompasses an astonishing diversity of landscapes, cultures, and economies. From the towering Himalayas, home to the world’s highest peak, Mount Everest, to the vast Siberian plains, Asia’s geography is characterized by its extremes. The continent is also home to major river systems like the Yangtze and Ganges, supporting dense populations and extensive agricultural production.
Political Landscape: Asia is home to 49 independent countries, ranging from the global superpowers of China and India to smaller nations like Bhutan and Timor-Leste. The political map of Asia reflects a complex history of empires, colonial influences, and evolving political systems.
Key Geographical Features:
- Himalayas: The world’s highest mountain range, home to Mount Everest and other towering peaks.
- Ganges River: A sacred river for Hindus, flowing through India and Bangladesh, supporting a large population and agriculture.
- Siberian Plain: The largest plain in the world, spanning across Russia and characterized by its harsh climate and vast forests.
- Arabian Peninsula: The largest peninsula in the world, known for its arid climate, oil reserves, and diverse cultures.
Europe: A Continent of History and Innovation
Europe, the second-smallest continent by landmass, is a continent of rich history, cultural diversity, and innovation. The continent is characterized by its varied landscapes, including the Alps, the Pyrenees, and the Carpathians, as well as extensive plains and coastal regions. Europe’s history is marked by its role in global trade, exploration, and technological advancements.
Political Landscape: Europe is home to 44 independent countries, with the European Union (EU) representing a significant political and economic bloc. From the historical powerhouse of Germany to the small island nation of Malta, the political map of Europe reflects a complex interplay of historical alliances, cultural identities, and evolving political agendas.
Key Geographical Features:
- Alps: The highest mountain range in Europe, stretching across several countries and home to glaciers and alpine meadows.
- Rhine River: A major waterway flowing through several countries, connecting industrial centers and facilitating trade.
- Mediterranean Sea: A large sea surrounded by Europe, Africa, and Asia, playing a crucial role in trade and cultural exchange.
- Baltic Sea: A shallow sea located in Northern Europe, connecting several countries and supporting important fishing industries.
Interconnectedness: A Global Perspective
The maps of Africa, Asia, and Europe reveal a complex web of interconnectedness, both geographically and politically. These continents share borders, trade routes, and cultural influences, creating a dynamic global landscape.
- Trade Routes: The Silk Road, a historic trade route connecting Asia and Europe, exemplifies the long-standing economic ties between these continents. Modern trade routes further emphasize the interconnectedness of these regions, with global supply chains spanning across continents.
- Migration Patterns: Historical and contemporary migration patterns highlight the movement of people across continents, driven by economic opportunities, political conflicts, and cultural exchange.
- Environmental Challenges: Climate change, deforestation, and pollution are global challenges that impact all three continents, highlighting the need for international cooperation and sustainable practices.
Conclusion: A Global Perspective
The maps of Africa, Asia, and Europe offer a glimpse into the diverse and interconnected world we inhabit. Understanding the geographical features, political boundaries, and historical interactions of these continents is essential for comprehending global trends, from economic development and political alliances to environmental challenges and cultural exchange. As we continue to navigate a rapidly evolving world, a deeper understanding of these continents will be crucial for fostering cooperation, promoting sustainable development, and building a more interconnected and peaceful global community.
FAQs:
-
What are the major geographical features of Africa?
- The Sahara Desert, the Nile River, the Great Rift Valley, and the Congo Basin are some of the most prominent geographical features of Africa.
-
What are the major religions practiced in Asia?
- Asia is home to a wide range of religions, including Hinduism, Buddhism, Islam, Christianity, and Confucianism.
-
What are the major languages spoken in Europe?
- Europe is a linguistic mosaic, with a variety of languages spoken, including English, French, German, Spanish, Italian, and Russian.
-
What are the major economic challenges facing Africa?
- Africa faces challenges such as poverty, inequality, and limited access to education and healthcare.
-
What are the major environmental challenges facing Asia?
- Asia faces challenges such as air pollution, deforestation, and water scarcity.
-
What are the major political challenges facing Europe?
- Europe faces challenges such as migration, terrorism, and the rise of nationalism.
Tips for Studying the Maps of Africa, Asia, and Europe:
- Use a variety of resources: Explore maps, atlases, documentaries, and online resources to gain a comprehensive understanding of these continents.
- Focus on key geographical features: Identify the major mountain ranges, rivers, deserts, and other geographical features that define each continent.
- Understand political boundaries: Learn the names and locations of the countries within each continent, paying attention to their political systems and historical context.
- Connect the dots: Explore the interconnectedness of these continents through trade routes, migration patterns, and shared environmental challenges.
- Engage with diverse perspectives: Seek out different perspectives on the history, culture, and challenges facing these continents.
Conclusion:
The maps of Africa, Asia, and Europe are more than just geographical representations; they are windows into a complex and interconnected world. By studying these maps and understanding the diversity and interconnectedness of these continents, we can gain a deeper appreciation for the global landscape and foster a more informed and engaged approach to international relations and global challenges.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into A Geographical Exploration of Africa, Asia, and Europe: A Look at Three Continents. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!