A Geographic Portrait Of Israel: A Nation Shaped By History And Conflict
A Geographic Portrait of Israel: A Nation Shaped by History and Conflict
Related Articles: A Geographic Portrait of Israel: A Nation Shaped by History and Conflict
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to A Geographic Portrait of Israel: A Nation Shaped by History and Conflict. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
A Geographic Portrait of Israel: A Nation Shaped by History and Conflict
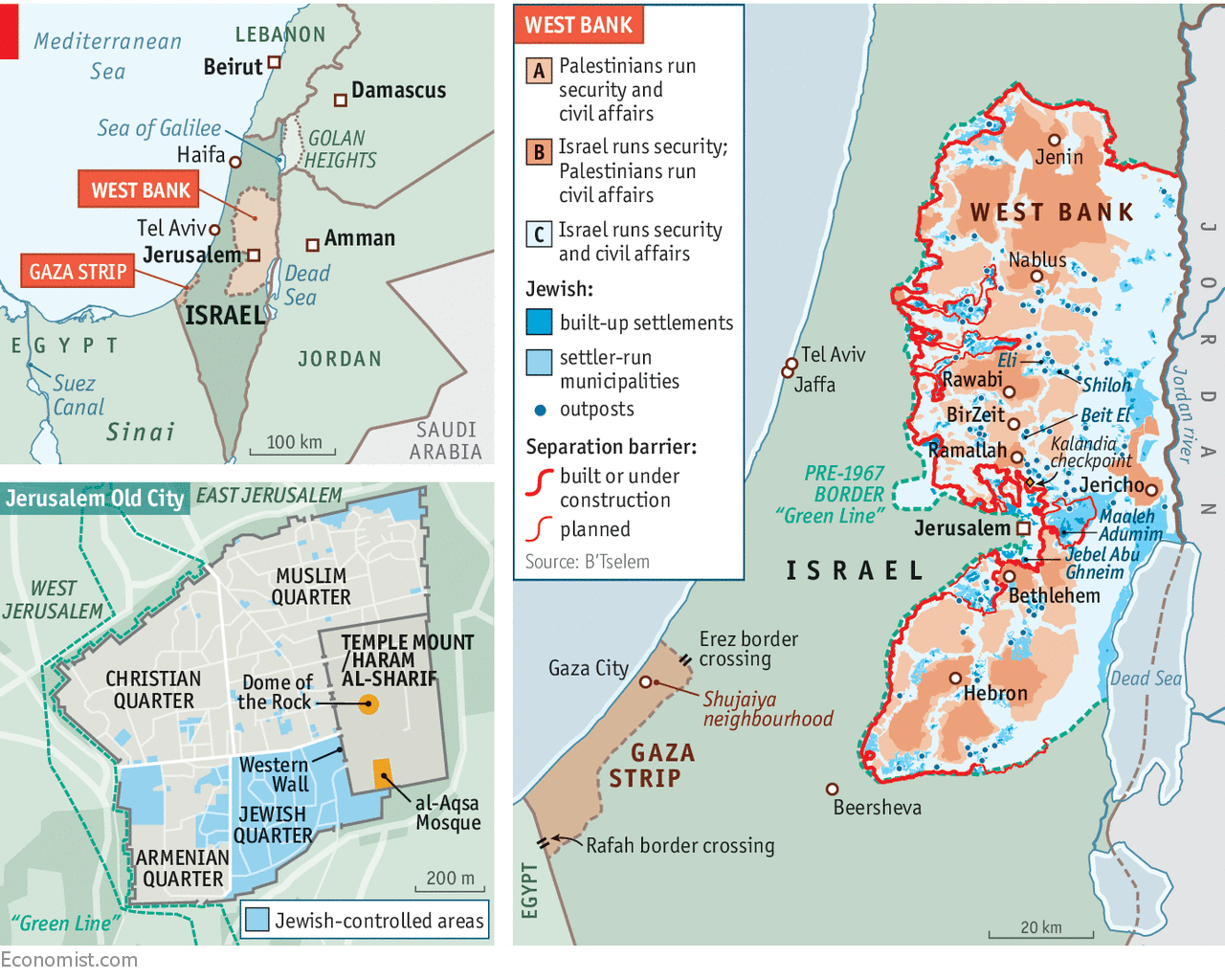
Israel, a nation nestled in the Middle East, occupies a geographically unique and historically significant region. Its location at the crossroads of continents, its diverse landscape, and its complex political history all contribute to its distinctive appearance on the map.
A Land of Contrasts:
Israel’s physical geography is characterized by a remarkable diversity, compressed into a relatively small area. The country stretches approximately 470 kilometers (292 miles) from north to south and 150 kilometers (93 miles) at its widest point. This narrow strip of land is home to a range of geographical features, from the snow-capped peaks of Mount Hermon in the north to the arid Negev Desert in the south.
The central region of Israel is dominated by the coastal plain, a fertile strip of land bordering the Mediterranean Sea. This area is home to major cities like Tel Aviv and Haifa, and it is a significant agricultural hub. Inland, the landscape rises to the rolling hills of the Judean Mountains, where Jerusalem, the country’s capital, is situated.
To the east, the Jordan River Valley, a deep rift valley, separates Israel from Jordan. This valley is home to the Dead Sea, the lowest point on Earth, and the Sea of Galilee, a freshwater lake with significant religious and cultural importance.
Political Boundaries and Territorial Disputes:
The borders of Israel have been a subject of continuous debate and conflict since the nation’s establishment in 1948. The current political map of Israel is a result of several wars, treaties, and agreements, each shaping the country’s territorial configuration.
The Israeli-Palestinian conflict is a major factor influencing the country’s borders. The West Bank, a territory occupied by Israel since 1967, is claimed by Palestinians as part of a future independent state. The status of Jerusalem, a city sacred to Jews, Christians, and Muslims, is also a major point of contention.
The Golan Heights, a strategically important plateau overlooking the Sea of Galilee, was captured by Israel from Syria in 1967 and annexed in 1981, a move not recognized internationally. The Gaza Strip, a coastal territory bordering Egypt, is governed by Hamas, an Islamist group that has been engaged in conflicts with Israel since 2007.
The Significance of Location:
Israel’s strategic location at the crossroads of three continents – Africa, Asia, and Europe – has shaped its history and its role in the global political landscape. This location has made Israel a center of trade and cultural exchange throughout history.
The country’s proximity to major oil and gas reserves in the Eastern Mediterranean has also made it a significant player in the global energy market. Israel’s strong military and technological capabilities have further enhanced its regional influence.
Understanding the Map:
A map of Israel reveals a complex tapestry of history, culture, and conflict. It showcases the country’s diverse landscape, its political boundaries, and its strategic location. Studying the map provides a valuable insight into the nation’s past, present, and potential future.
FAQs:
Q: What are the major cities in Israel?
A: The major cities in Israel include Jerusalem, Tel Aviv, Haifa, Beersheba, and Netanya. Jerusalem, the country’s capital, is a major religious and cultural center. Tel Aviv is a vibrant coastal city known for its beaches, nightlife, and cultural scene. Haifa is a major port city with a significant industrial sector. Beersheba is a growing city in the Negev Desert. Netanya is a popular tourist destination on the Mediterranean coast.
Q: What are the major geographical features of Israel?
A: Major geographical features of Israel include the Mediterranean Sea, the Judean Mountains, the Jordan River Valley, the Dead Sea, the Sea of Galilee, and the Negev Desert.
Q: What is the status of the West Bank and Gaza Strip?
A: The West Bank is a territory occupied by Israel since 1967, claimed by Palestinians as part of a future independent state. The Gaza Strip is a coastal territory bordering Egypt, governed by Hamas, an Islamist group that has been engaged in conflicts with Israel since 2007.
Q: What are the major religions practiced in Israel?
A: The major religions practiced in Israel are Judaism, Islam, and Christianity. Jerusalem is a sacred city for all three religions.
Tips:
- Use a detailed map: A detailed map of Israel will provide a more comprehensive understanding of the country’s geography and political boundaries.
- Study the historical context: Understanding the historical context of the region will help to interpret the current political situation and the ongoing conflicts.
- Explore different perspectives: Consider different perspectives on the Israeli-Palestinian conflict and the country’s territorial disputes.
- Engage with online resources: There are numerous online resources available that provide detailed information about Israel’s geography, history, and culture.
Conclusion:
Israel’s appearance on the map is a reflection of its complex and multifaceted history. The country’s diverse landscape, its strategic location, and its ongoing political conflicts have shaped its unique identity and its role in the global arena. Understanding the geography of Israel is crucial to grasping the complexities of the region and its place in the world.
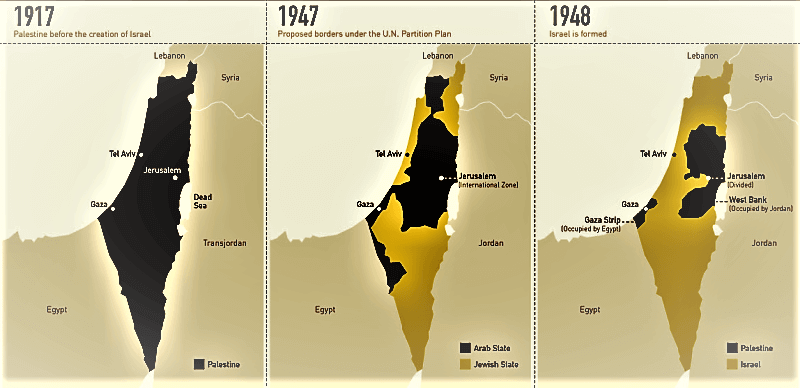
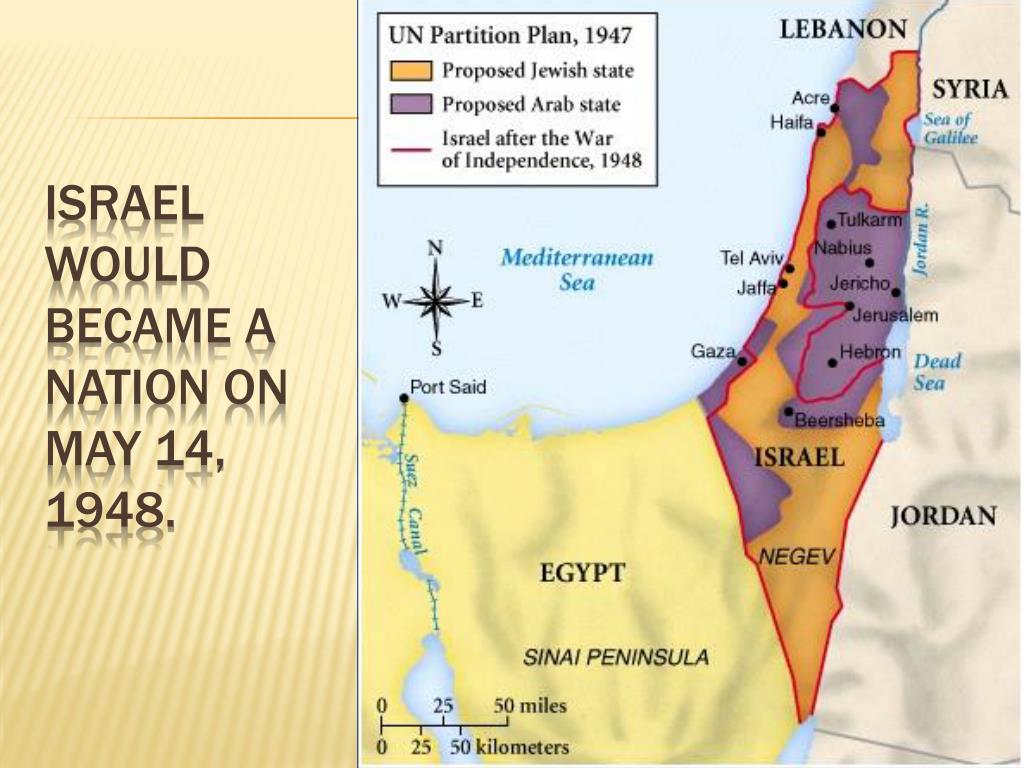


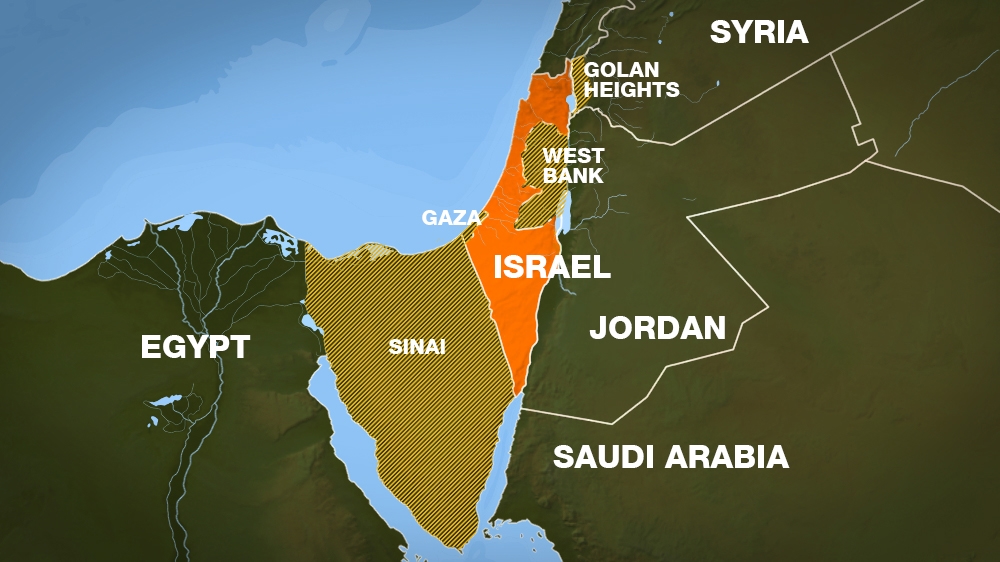
![Israel Palestine Conflict History, Israel Palestine Conflict Summary [UPSC Notes]](https://cdn1.byjus.com/wp-content/uploads/2021/05/israel-palestine.png)
/cloudfront-ap-southeast-2.images.arcpublishing.com/nzme/OPROIYFQTOAN4FCQMY5YTOZRBY.jpg)

Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into A Geographic Portrait of Israel: A Nation Shaped by History and Conflict. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!