A Geographic Overview Of Poland: Understanding The Land And Its People
A Geographic Overview of Poland: Understanding the Land and its People
Related Articles: A Geographic Overview of Poland: Understanding the Land and its People
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to A Geographic Overview of Poland: Understanding the Land and its People. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
A Geographic Overview of Poland: Understanding the Land and its People

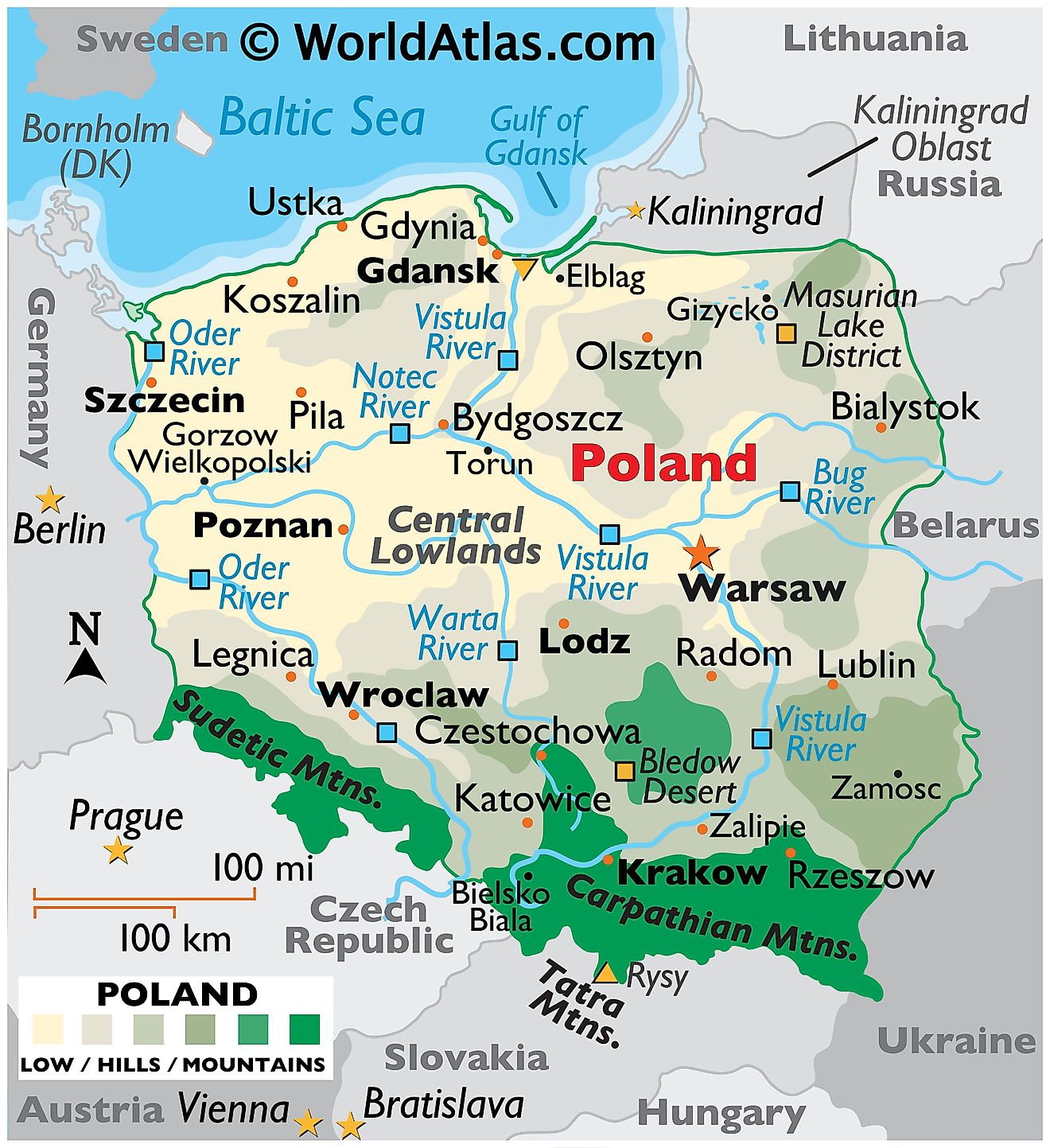
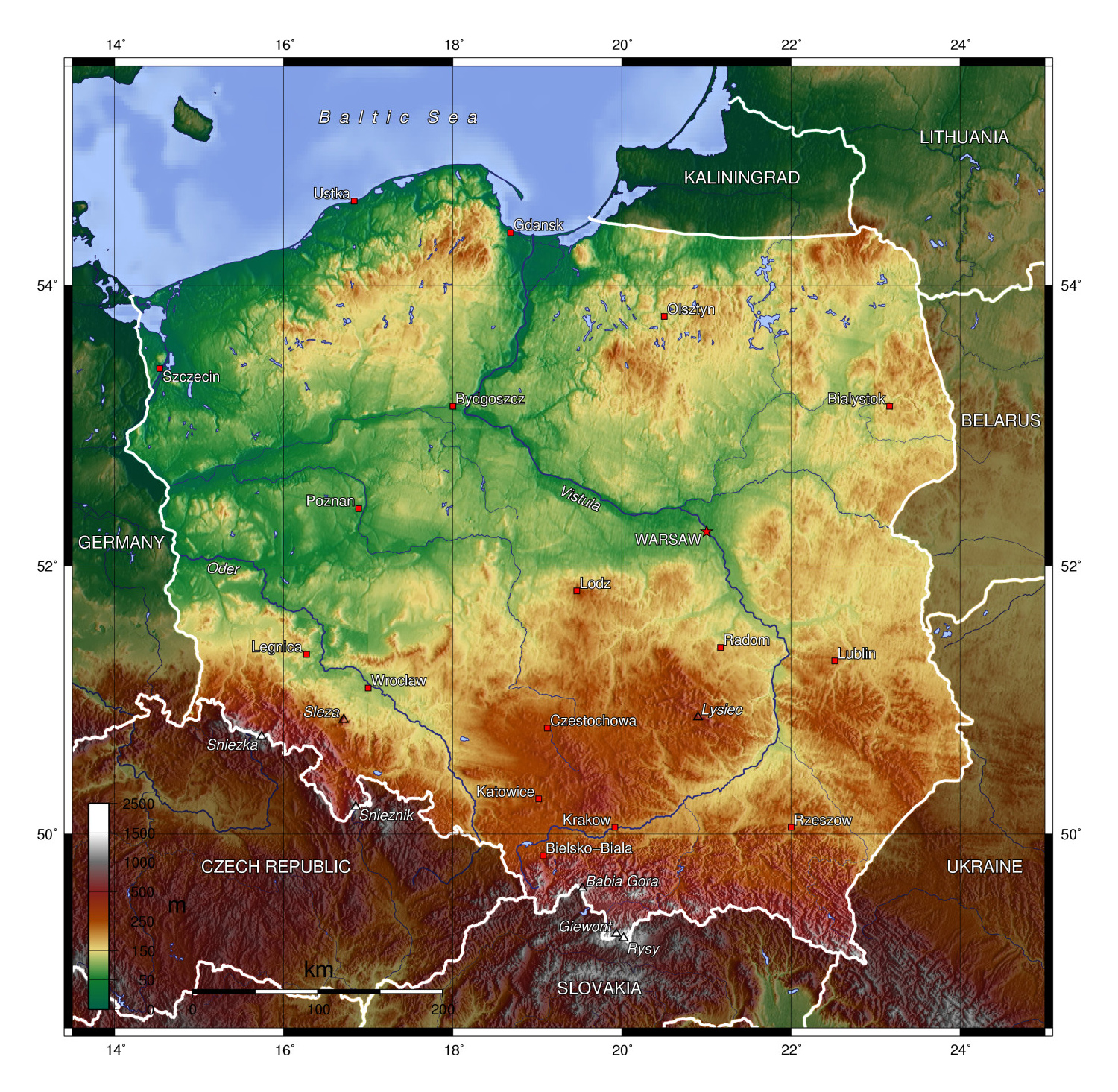
Poland, nestled in the heart of Central Europe, is a country steeped in history, culture, and natural beauty. Its diverse landscape, stretching from the Baltic Sea coast to the Carpathian Mountains, has shaped its identity and played a crucial role in its development. This article delves into the geographic features of Poland, exploring its diverse regions, natural resources, and the impact of its location on its history and culture.
A Mosaic of Landscapes:
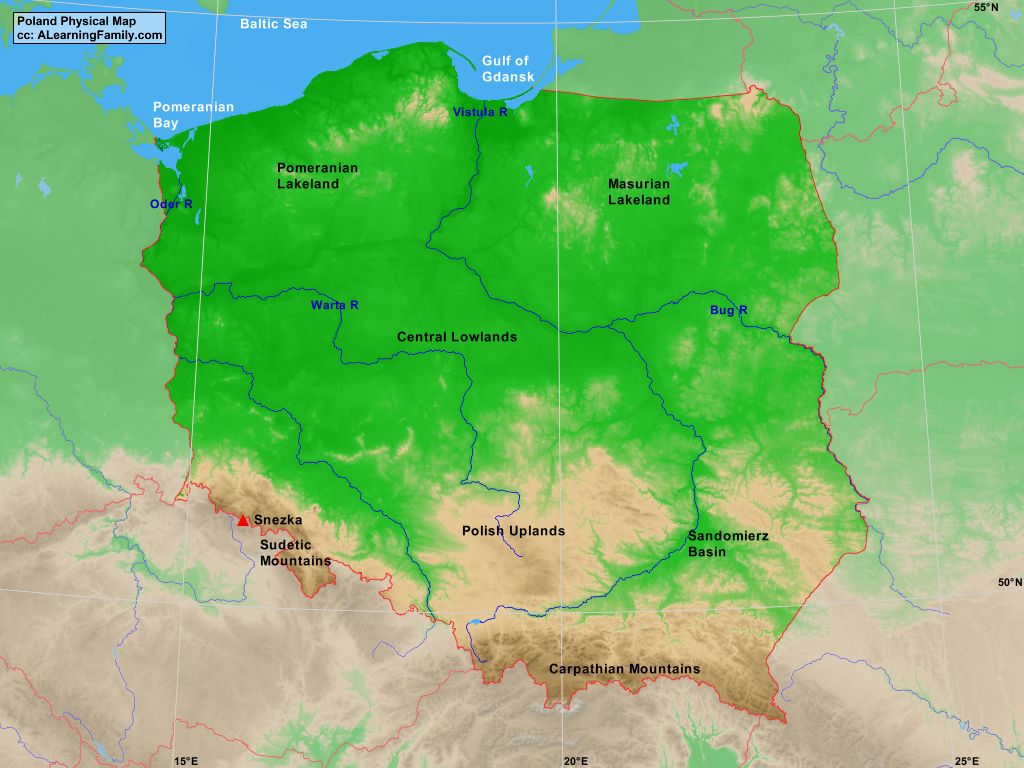
Poland’s geographic diversity is a testament to its position at the crossroads of Europe. The country can be broadly divided into five distinct regions:
-
The Baltic Coast: This region, characterized by sandy beaches, coastal lagoons, and the iconic port city of Gdańsk, offers a unique blend of maritime influences and traditional Polish charm. The Baltic Sea plays a vital role in the region’s economy, providing access to international trade routes and supporting fishing industries.
-
The Northern Lowlands: This vast plain, encompassing the majority of Poland’s territory, is a land of fertile farmland, dense forests, and rolling hills. Its flat topography makes it ideal for agriculture, and its rich soil contributes to Poland’s reputation as a major food producer.
-
The Masurian Lake District: This region, dotted with over 2,000 lakes, offers breathtaking scenery and opportunities for outdoor recreation. The lakes, interconnected by canals, provide a network of waterways for boating, fishing, and exploring the region’s natural beauty.
-
The Carpathian Mountains: These majestic mountains, forming a natural border between Poland and Slovakia, offer a stark contrast to the flatlands. Their rugged peaks and dense forests provide opportunities for hiking, skiing, and enjoying the pristine wilderness.
-
The Silesian Upland: This region, characterized by rolling hills and fertile valleys, is home to Poland’s industrial heartland. Its rich deposits of coal and other minerals have fueled its economic growth, making it a significant center for manufacturing and heavy industry.
Natural Resources and Economic Significance:
Poland’s diverse landscape has endowed it with a wealth of natural resources, shaping its economy and influencing its history.
-
Agriculture: The fertile Northern Lowlands have made Poland a major agricultural producer, with wheat, barley, rye, and potatoes being key crops. Poland’s agricultural sector plays a vital role in its economy, providing food security and contributing to its export markets.
-
Forestry: Poland’s extensive forests, covering nearly 30% of its land area, provide a valuable resource for timber, paper, and other wood-based products. The forests also play a crucial role in maintaining biodiversity and mitigating climate change.
-
Mineral Resources: Poland is rich in mineral resources, with coal being the most significant. The Silesian Upland, with its abundant coal deposits, has historically been the heart of Poland’s energy sector. Other important minerals include copper, zinc, lead, and sulfur.
-
Water Resources: Poland has access to the Baltic Sea and numerous rivers, providing important transportation routes and sources of freshwater. The country’s vast network of rivers and canals has facilitated trade and connected its regions, contributing to its economic development.
The Influence of Location:
Poland’s strategic location at the crossroads of Europe has profoundly shaped its history and culture. Its position between Germany and Russia has made it a battleground for centuries, leading to periods of both prosperity and hardship.
-
Historical Crossroads: Poland’s location has made it a bridge between Eastern and Western Europe, influencing its cultural development and fostering a unique identity. It has been a melting pot of different cultures, with elements of Slavic, Germanic, and even Asian influences.
-
Trade and Connectivity: Poland’s location has facilitated trade and communication with its neighbors. Its access to the Baltic Sea and its extensive network of roads and railways have made it a hub for international trade and transportation.
-
Geopolitical Significance: Poland’s position has also made it a key player in regional and international politics. Its strategic location, bordering several NATO members, has made it a significant factor in maintaining security and stability in Central Europe.
FAQs about Poland’s Geography:
1. What is the highest point in Poland?
The highest point in Poland is Rysy, located in the Tatra Mountains, with an elevation of 2,499 meters (8,199 feet).
2. What is the largest lake in Poland?
The largest lake in Poland is Lake Śniardwy, located in the Masurian Lake District, with an area of 113.8 square kilometers (44 square miles).
3. What is the most important river in Poland?
The most important river in Poland is the Vistula River, which flows through the country from south to north and empties into the Baltic Sea.
4. What is the climate like in Poland?
Poland has a temperate continental climate, with warm summers and cold winters. The country experiences significant seasonal variations in temperature and precipitation.
5. What are the main environmental challenges facing Poland?
Poland faces various environmental challenges, including air pollution, water pollution, and deforestation. The country has been working to address these issues through environmental policies and initiatives.
Tips for Visiting Poland:
-
Explore the diverse landscapes: From the Baltic Sea coast to the Carpathian Mountains, Poland offers a wide range of landscapes to explore.
-
Visit the historical cities: Poland is home to many historic cities, including Warsaw, Kraków, Gdańsk, and Wrocław.
-
Experience the Polish culture: Immerse yourself in Polish culture by attending concerts, theater performances, and traditional festivals.
-
Sample the delicious cuisine: Polish cuisine is known for its hearty and flavorful dishes, such as pierogi, bigos, and kielbasa.
-
Learn a few Polish phrases: While English is widely spoken in tourist areas, learning a few basic Polish phrases can enhance your travel experience.
Conclusion:
Poland’s geography is a defining feature of its identity, shaping its history, culture, and economy. Its diverse landscapes, rich natural resources, and strategic location have played a crucial role in its development. From its fertile farmlands to its majestic mountains, from its bustling cities to its pristine forests, Poland offers a tapestry of experiences for visitors and residents alike. Understanding its geographic features provides a deeper appreciation for the country’s unique character and its place in the heart of Europe.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into A Geographic Overview of Poland: Understanding the Land and its People. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!