A Complex Landscape: Understanding The Geography Of Israel And Gaza
A Complex Landscape: Understanding the Geography of Israel and Gaza
Related Articles: A Complex Landscape: Understanding the Geography of Israel and Gaza
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to A Complex Landscape: Understanding the Geography of Israel and Gaza. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
A Complex Landscape: Understanding the Geography of Israel and Gaza

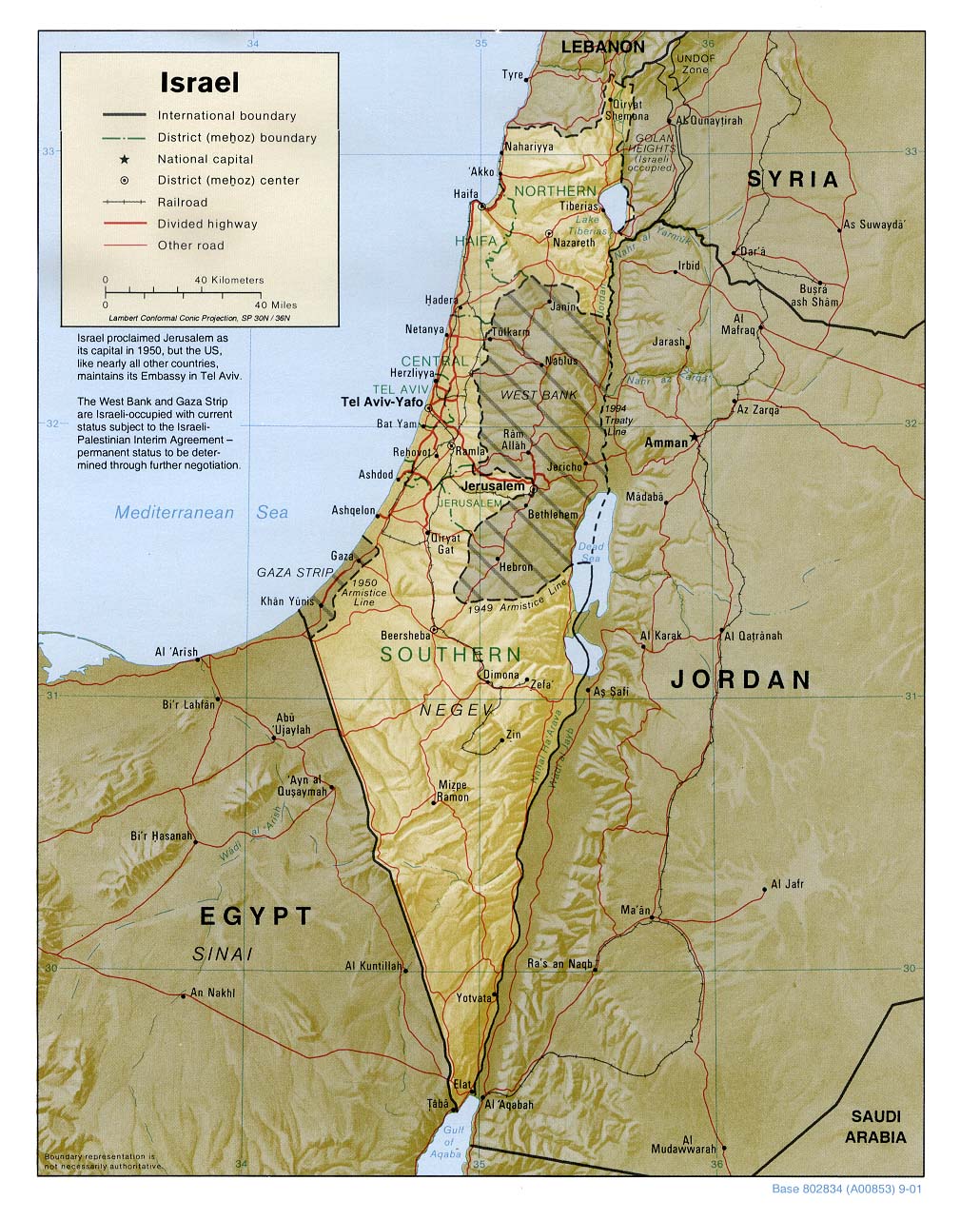
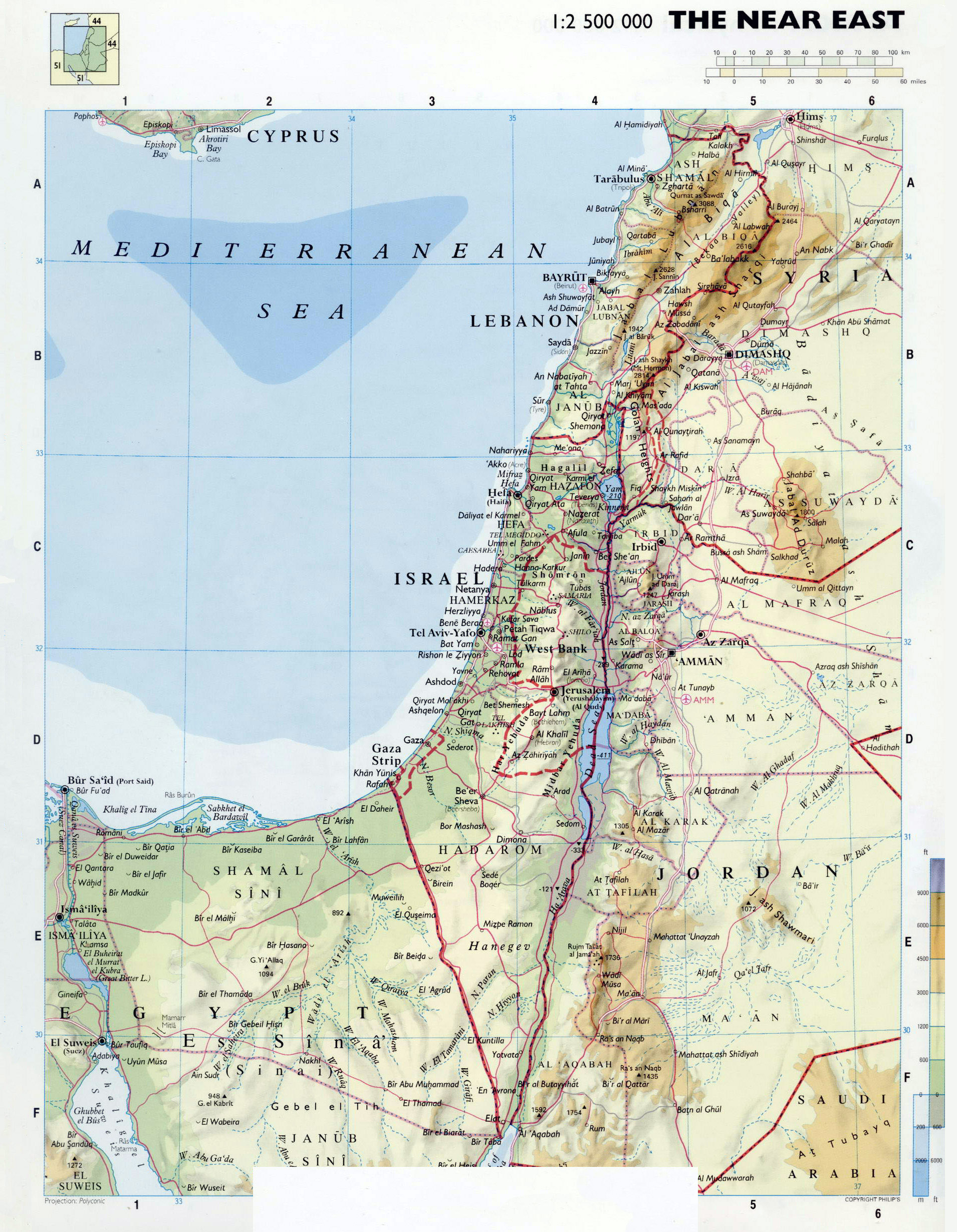
The region encompassing Israel and Gaza is a complex tapestry of history, politics, and geography. Understanding the geographical context is crucial for grasping the ongoing conflict and the challenges facing both sides. This article aims to provide a detailed overview of the map of Israel and Gaza, highlighting its key features, historical significance, and the implications of its current configuration.
A Land of Contrasts: The Geography of Israel
Israel, a country in the Middle East, occupies a strategically significant location at the crossroads of three continents: Africa, Asia, and Europe. The country’s diverse geography encompasses a variety of landscapes, from the fertile coastal plains to the arid Negev desert in the south.
1. The Coastal Plain: This fertile strip of land along the Mediterranean Sea is Israel’s economic heartland, home to major cities like Tel Aviv, Haifa, and Ashdod. It’s a densely populated area with a thriving agricultural sector.
2. The Central Highlands: Rising inland from the coastal plain, the Central Highlands are characterized by rolling hills and valleys. This region is home to Jerusalem, Israel’s capital, and the historic city of Hebron. It’s also a key agricultural area, producing olives, grapes, and citrus fruits.
3. The Jordan Rift Valley: Running along the eastern border of Israel, the Jordan Rift Valley is a geological depression that includes the Dead Sea, the lowest point on Earth. The valley is home to a unique ecosystem and is rich in mineral resources.
4. The Negev Desert: Covering roughly half of Israel’s landmass, the Negev Desert is a vast, arid region with sparse vegetation. Despite its harsh climate, the Negev is home to a growing number of settlements and industries, including solar energy projects.
The Enclave of Gaza: A Separate Entity
The Gaza Strip, located on the Mediterranean coast, is a small, densely populated Palestinian territory. It’s separated from Israel by a heavily fortified border and is under Israeli control. The Gaza Strip is a distinct geographical entity with its own unique characteristics.
1. A Small and Densely Populated Area: The Gaza Strip is only 41 kilometers long and 6 to 12 kilometers wide, with a population exceeding 2 million. This high population density contributes to the challenges faced by the Palestinian population, including limited resources and infrastructure.
2. A Coastal Strip with Limited Resources: The Gaza Strip’s proximity to the Mediterranean Sea provides access to fishing, a key source of income for many Gazans. However, the limited land area and the presence of a blockade imposed by Israel severely restrict economic opportunities.
3. A History of Conflict and Displacement: The Gaza Strip has been a focal point of the Israeli-Palestinian conflict, experiencing multiple wars and periods of occupation. This history has left a lasting impact on the physical and social landscape of the territory.
The Importance of the Map: A Complex Historical Context
The map of Israel and Gaza reflects a complex history of conflict, displacement, and political maneuvering. Understanding the historical context is essential for grasping the current situation:
1. The British Mandate and the 1948 War: Following World War I, Britain was granted a mandate to govern Palestine. This period saw increasing tensions between Jewish and Arab populations, culminating in the 1948 Arab-Israeli War. The war resulted in the establishment of Israel and the displacement of hundreds of thousands of Palestinians.
2. The 1967 Six-Day War: The 1967 war saw Israel capture the West Bank, East Jerusalem, and the Gaza Strip from Jordan and Egypt. This expansion of Israeli control led to a prolonged occupation and the continuation of the conflict.
3. The Oslo Accords and the Second Intifada: In the 1990s, the Oslo Accords aimed to establish a two-state solution, with the creation of an independent Palestinian state alongside Israel. However, these efforts were derailed by the Second Intifada, a Palestinian uprising that began in 2000.
4. The Hamas Takeover and the Blockade: In 2007, the Islamist group Hamas seized control of the Gaza Strip. This event led to a tightening of the Israeli blockade, which has significantly restricted the flow of goods, people, and information into and out of Gaza.
The Implications of the Current Configuration: A Search for Peace
The current configuration of Israel and Gaza presents significant challenges to achieving a lasting peace. The ongoing conflict has had a devastating impact on both sides, leading to loss of life, displacement, and economic hardship.
1. The Two-State Solution: A Contested Vision: The two-state solution, with the creation of an independent Palestinian state alongside Israel, remains the most widely supported framework for peace. However, significant obstacles remain, including disagreements over borders, settlements, and the status of Jerusalem.
2. The Importance of International Pressure: The international community plays a crucial role in promoting peace and resolving the conflict. International pressure, sanctions, and initiatives are essential for creating an environment conducive to dialogue and negotiation.
3. The Role of Civil Society: Civil society organizations, both Israeli and Palestinian, play a vital role in fostering dialogue, promoting understanding, and advocating for peaceful solutions. These organizations work to build bridges between communities and challenge the narratives of conflict.
FAQs: Understanding the Complexities of the Map
1. What is the status of Jerusalem?
Jerusalem is a city claimed by both Israelis and Palestinians. It holds significant religious importance for both Jews and Muslims and is a focal point of the conflict. The city’s status remains a major obstacle to a peace agreement.
2. What are the settlements?
Settlements are Israeli civilian communities built on land claimed by Palestinians in the West Bank and East Jerusalem. The expansion of settlements is widely considered an obstacle to a two-state solution and a source of tension between Israelis and Palestinians.
3. What is the role of the international community?
The international community plays a crucial role in the Israeli-Palestinian conflict. The United Nations, the European Union, and other organizations provide humanitarian aid, monitor the situation, and attempt to facilitate peace negotiations.
4. What are the key challenges to achieving peace?
The key challenges to achieving peace include the lack of trust between the two sides, the issue of settlements, the status of Jerusalem, and the ongoing violence.
Tips for Understanding the Map
1. Utilize Geographic Resources: Explore online maps, atlases, and satellite imagery to visualize the physical features, political boundaries, and key locations of the region.
2. Engage with Historical Context: Read books, articles, and documentaries that provide a comprehensive understanding of the historical events that have shaped the current situation.
3. Follow the News and Current Events: Stay informed about the latest developments in the region by reading news articles, watching documentaries, and following reputable news sources.
4. Engage in Dialogue and Discussion: Engage in conversations with others about the issues, listen to different perspectives, and challenge your own assumptions.
Conclusion: A Path Towards Peace
The map of Israel and Gaza is a powerful visual representation of a complex and multifaceted conflict. Understanding the geography, history, and current dynamics of the region is essential for fostering informed dialogue, promoting peace, and working towards a just and lasting solution. While the path to peace remains challenging, engaging with the issues, fostering understanding, and promoting dialogue are crucial steps towards a brighter future for both Israelis and Palestinians.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into A Complex Landscape: Understanding the Geography of Israel and Gaza. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!