A Comparative Study Of Russia, Ukraine, And Israel: Examining Geography, History, And Contemporary Challenges
A Comparative Study of Russia, Ukraine, and Israel: Examining Geography, History, and Contemporary Challenges
Related Articles: A Comparative Study of Russia, Ukraine, and Israel: Examining Geography, History, and Contemporary Challenges
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to A Comparative Study of Russia, Ukraine, and Israel: Examining Geography, History, and Contemporary Challenges. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
A Comparative Study of Russia, Ukraine, and Israel: Examining Geography, History, and Contemporary Challenges
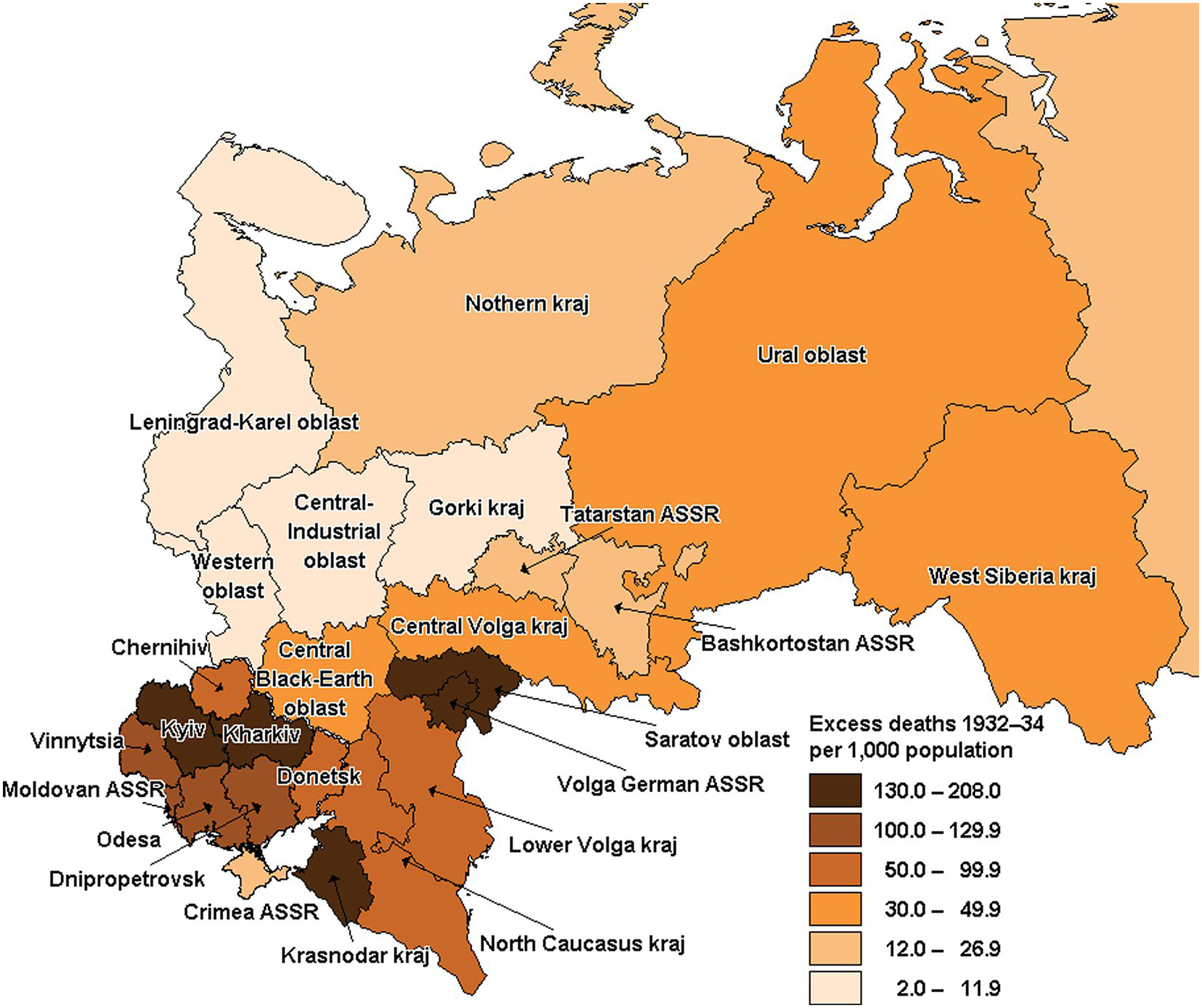
This article explores the geographical, historical, and contemporary contexts of Russia, Ukraine, and Israel, highlighting their unique characteristics and interconnectedness. While seemingly disparate in location and historical trajectory, these nations share a complex web of relationships, shaped by shared experiences, geopolitical dynamics, and enduring cultural influences.
Russia: A Eurasian Giant
Russia, spanning eleven time zones and encompassing a vast expanse of land, is the largest country in the world by land area. Its geographical position, straddling Europe and Asia, has profoundly influenced its history and culture. The vastness of its territory, encompassing diverse landscapes from the frozen Arctic tundra to the fertile steppes, has presented challenges and opportunities alike.
Key Geographical Features:
- The Ural Mountains: A natural border separating Europe from Asia, the Ural Mountains play a significant role in Russia’s historical and cultural identity.
- The Siberian Plain: Home to vast forests, mineral resources, and indigenous populations, Siberia is a crucial component of Russia’s economic and strategic landscape.
- The Caucasus Mountains: The Caucasus region, bordering the Black Sea and the Caspian Sea, is a zone of cultural and ethnic diversity, marked by historical conflicts and geopolitical tensions.
- The Black Sea: A vital waterway connecting Russia to the Mediterranean Sea and the Middle East, the Black Sea has played a crucial role in Russian naval history and trade.
Ukraine: A Bridge Between East and West
Ukraine, situated in Eastern Europe, shares a long and complex history with Russia. Its location, bridging the East European Plain and the Black Sea, has made it a strategic crossroads throughout history. Ukraine has been a battleground for empires, a conduit for cultural exchange, and a source of conflict and cooperation.
Key Geographical Features:
- The Dnieper River: Flowing through the heart of Ukraine, the Dnieper River has served as a vital waterway for trade and transportation, shaping the country’s economic and cultural development.
- The Crimean Peninsula: A strategically important peninsula, Crimea has been a subject of historical disputes and territorial claims, culminating in the 2014 annexation by Russia.
- The Black Sea Coast: The Black Sea coast, with its fertile plains and access to international trade, has played a pivotal role in Ukraine’s agricultural production and economic prosperity.
Israel: A Land of Ancient History and Modern Challenges
Israel, located in the Middle East, is a small but strategically significant nation with a rich history and complex contemporary challenges. Its geographic location at the crossroads of three continents, its historical significance, and its ongoing conflict with neighboring states have made it a focal point of global attention.
Key Geographical Features:
- The Mediterranean Sea: The Mediterranean Sea provides Israel with access to international trade and maritime routes, playing a key role in its economic development and strategic positioning.
- The Negev Desert: Covering a significant portion of Israel’s territory, the Negev Desert presents both challenges and opportunities for resource management and agricultural development.
- The Jordan River: A vital source of water for both Israel and its neighbors, the Jordan River is a crucial resource and a potential source of conflict.
Historical Intertwining: Shared Experiences and Divergent Paths
The histories of Russia, Ukraine, and Israel are intertwined, marked by periods of cooperation and conflict, shared cultural influences, and divergent paths of development.
- The Soviet Era: Ukraine was a constituent republic of the Soviet Union, experiencing significant social and economic changes under Soviet rule. Russia, as the dominant power within the Soviet system, played a major role in shaping Ukraine’s political and cultural landscape.
- The Cold War: Israel, aligned with the Western bloc during the Cold War, navigated a complex geopolitical landscape, facing challenges from both the Soviet Union and its Arab neighbors.
- Post-Soviet Transition: Following the collapse of the Soviet Union, Ukraine embarked on a path toward independence, seeking to establish its own national identity and forge closer ties with the West. Russia, facing a period of economic and political instability, sought to maintain influence over its former republics, leading to tensions with Ukraine.
Contemporary Challenges: Geopolitical Tensions and Regional Conflicts
The contemporary relationships between Russia, Ukraine, and Israel are characterized by ongoing geopolitical tensions, regional conflicts, and competing interests.
- The Russia-Ukraine Conflict: The 2014 annexation of Crimea by Russia and the ongoing conflict in eastern Ukraine have created a deep divide between the two countries, raising concerns about Russian expansionism and the future of European security.
- The Israeli-Palestinian Conflict: The Israeli-Palestinian conflict, a long-standing source of regional instability, continues to pose significant challenges for both Israel and its neighbors. The conflict has international repercussions, impacting global diplomacy and security.
- The Middle East Geopolitical Landscape: Israel’s strategic location in the Middle East makes it a key player in regional power dynamics. The country’s relationship with its Arab neighbors, its security cooperation with the United States, and its role in regional conflicts all contribute to a complex and dynamic geopolitical environment.
FAQs:
Q: What are the major geopolitical challenges facing Russia, Ukraine, and Israel?
A: The major geopolitical challenges facing these nations include:
- Russia: Maintaining its influence in the former Soviet republics, managing relations with the West, and addressing internal economic and social challenges.
- Ukraine: Rebuilding its economy, strengthening its national identity, and navigating its relationship with Russia.
- Israel: Resolving the Israeli-Palestinian conflict, managing regional tensions, and ensuring its national security.
Q: How do the geographical features of these countries shape their history and contemporary challenges?
A: Geography plays a crucial role in shaping the history and challenges of these nations.
- Russia: Its vast size and diverse landscapes have presented challenges in terms of governance, infrastructure development, and resource management. Its location has also made it a natural bridge between Europe and Asia, influencing its historical development and its role in global affairs.
- Ukraine: Its location at the crossroads of East and West has made it a battleground for empires and a conduit for cultural exchange. Its fertile plains and access to the Black Sea have contributed to its agricultural wealth, while also making it vulnerable to geopolitical pressures.
- Israel: Its location at the crossroads of three continents has made it a strategic crossroads throughout history. Its limited land area and scarce water resources present significant challenges, while its proximity to neighboring states has fueled ongoing conflicts.
Q: What are the key historical events that have shaped the relationships between these countries?
A: Key historical events include:
- The Soviet Era: The Soviet Union’s rule over Ukraine had a profound impact on the country’s political and cultural landscape.
- The Cold War: The Cold War era witnessed the formation of alliances and rivalries between Russia, Ukraine, and Israel, shaping their geopolitical alignments and relationships with other nations.
- The collapse of the Soviet Union: The collapse of the Soviet Union led to Ukraine’s independence and a period of political and economic instability in Russia, creating new challenges and opportunities for both countries.
Tips for Understanding the Dynamics of Russia, Ukraine, and Israel:
- Focus on geography: Understanding the geographical features of these countries is crucial for understanding their history, culture, and contemporary challenges.
- Consider historical context: Understanding the historical events that have shaped these nations is essential for interpreting their current relationships and geopolitical dynamics.
- Examine contemporary challenges: Analyze the contemporary challenges facing these countries, including geopolitical tensions, regional conflicts, and economic disparities.
- Engage with multiple perspectives: Consider diverse viewpoints and perspectives from different stakeholders involved in the relationships between these countries.
Conclusion:
The relationships between Russia, Ukraine, and Israel are multifaceted and complex, shaped by shared experiences, geopolitical dynamics, and enduring cultural influences. Understanding their geographical, historical, and contemporary contexts is crucial for navigating the complexities of international relations and promoting peaceful resolutions to ongoing conflicts. The future of these nations, intertwined by history and geography, will be shaped by the choices made by their leaders and the actions of their people.


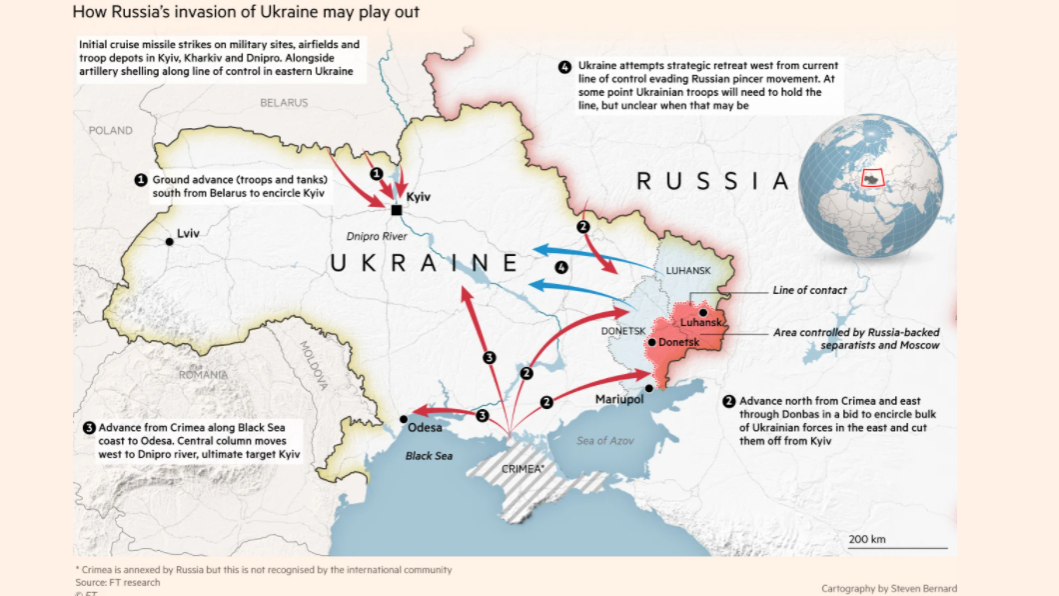


Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into A Comparative Study of Russia, Ukraine, and Israel: Examining Geography, History, and Contemporary Challenges. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!
![Ukraine-Russia war: The latest maps and key developments [Video]](https://s.yimg.com/ny/api/res/1.2/E7AJk2yH_wXpb3J5kUhueg--/YXBwaWQ9aGlnaGxhbmRlcjt3PTEyMDA7aD02NzU-/https://media.zenfs.com/en/aol_uk_yahoo_news_us_903/e9cead3fbcaf59e8b567461b79214018)