A Comparative Study Of Africa And Europe: Mapping The Continents’ Intertwined Histories And Futures
A Comparative Study of Africa and Europe: Mapping the Continents’ Intertwined Histories and Futures
Related Articles: A Comparative Study of Africa and Europe: Mapping the Continents’ Intertwined Histories and Futures
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to A Comparative Study of Africa and Europe: Mapping the Continents’ Intertwined Histories and Futures. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
A Comparative Study of Africa and Europe: Mapping the Continents’ Intertwined Histories and Futures
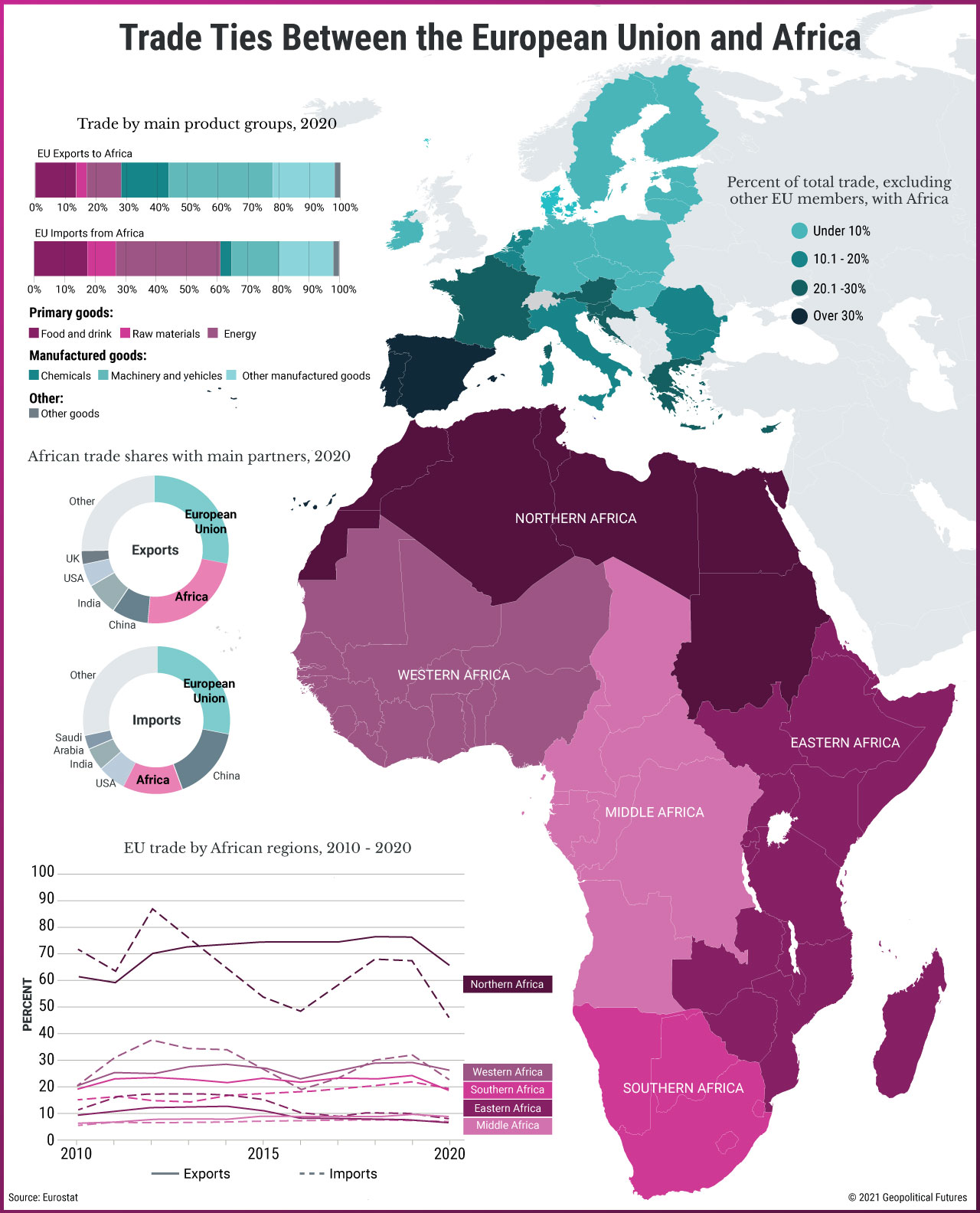
Africa and Europe, two continents separated by the Mediterranean Sea, are inextricably linked by history, culture, and geography. This article examines the multifaceted relationship between these two landmasses, exploring their shared past, present interactions, and potential future trajectories. By analyzing key aspects of their demographics, economies, politics, and environmental challenges, we aim to provide a comprehensive understanding of the intricate tapestry woven by these two continents.
A Shared Past: From Ancient Trade to Colonialism and Beyond
The connection between Africa and Europe dates back millennia. Ancient civilizations in both regions engaged in trade, cultural exchange, and even conflict. The Phoenicians, Greeks, and Romans established trading posts along the African coast, bringing goods from the continent to Europe and vice versa. This early interaction laid the foundation for a complex relationship that would evolve over centuries.
The European Renaissance, fueled by exploration and expansion, saw the rise of colonialism in Africa. From the 15th century onward, European powers established colonies across the continent, exploiting its resources and shaping its political and social structures. The legacy of colonialism continues to influence both continents, leaving behind deep scars of exploitation, inequality, and social divisions.
Despite the negative aspects of colonialism, it also led to the introduction of new technologies, ideas, and institutions in Africa. This, combined with the burgeoning trade networks, contributed to the continent’s economic and social development, albeit unevenly distributed.
Mapping the Present: Interconnected Economies and Political Landscapes
Today, Africa and Europe are deeply intertwined economically and politically. The European Union (EU) is Africa’s largest trading partner, with significant investments in infrastructure, energy, and agriculture across the continent. This economic interdependence creates opportunities for growth and development but also highlights the challenges of unequal power dynamics and potential exploitation.
The relationship between Africa and Europe is further complicated by the issue of migration. Millions of Africans have migrated to Europe in search of better opportunities and escape conflict or poverty. This has led to complex debates about immigration, asylum, and integration, raising questions about human rights, security, and social cohesion in both regions.
Moreover, the political landscape of Africa and Europe is interconnected. The EU plays a significant role in promoting democracy, good governance, and human rights in Africa. However, the relationship is often fraught with tension, as European powers grapple with the complexities of engaging with diverse African governments and societies.
Environmental Challenges: A Shared Responsibility
Climate change presents a significant challenge for both Africa and Europe. The continent of Africa is particularly vulnerable to the impacts of climate change, facing increased droughts, desertification, and extreme weather events. These challenges have profound implications for food security, water resources, and human displacement.
Europe, as a major contributor to global greenhouse gas emissions, has a responsibility to address climate change and support Africa’s efforts to adapt and mitigate its impacts. This requires collaborative efforts to promote sustainable development, invest in renewable energy, and implement policies that reduce carbon footprints.
Looking Ahead: Towards a More Equitable Future
The relationship between Africa and Europe is multifaceted and constantly evolving. Moving forward, it is crucial to foster a more equitable and mutually beneficial partnership based on shared values and common goals. This necessitates a shift from traditional power dynamics towards a more collaborative approach that prioritizes:
- Sustainable Development: Fostering economic growth in Africa that is inclusive, sustainable, and environmentally responsible.
- Human Rights and Democracy: Promoting human rights, good governance, and democratic principles across the continent.
- Climate Action: Working together to address climate change and its impacts on both continents.
- Migration and Mobility: Implementing fair and humane policies that address migration flows and promote integration.
FAQs
Q: What are the key historical events that shaped the relationship between Africa and Europe?
A: Key historical events include the ancient trade networks, the European Renaissance and the rise of colonialism, the decolonization movement, and the establishment of the European Union.
Q: What are the major economic ties between Africa and Europe?
A: The EU is Africa’s largest trading partner, with significant investments in various sectors. Trade, investment, and aid flows constitute the major economic ties.
Q: What are the challenges related to migration between Africa and Europe?
A: Challenges include managing migration flows, addressing asylum seekers, promoting integration, and combating xenophobia.
Q: How can the relationship between Africa and Europe be strengthened in the future?
A: Strengthening the relationship requires a shift towards a more equitable and collaborative partnership based on shared values and common goals.
Tips
- Engage with diverse perspectives: Seek out different viewpoints on the relationship between Africa and Europe to gain a comprehensive understanding.
- Explore historical sources: Study historical documents, narratives, and artifacts to gain insights into the complex past.
- Follow current events: Stay informed about the latest developments in the relationship between the two continents.
- Support organizations working on Africa-Europe cooperation: Contribute to organizations promoting sustainable development, human rights, and collaboration.
Conclusion
The relationship between Africa and Europe is a complex tapestry woven from history, economics, politics, and shared challenges. Understanding this intricate relationship is essential for building a more equitable and sustainable future for both continents. By fostering collaboration, promoting shared values, and addressing common challenges, Africa and Europe can create a partnership that benefits all. This requires a commitment to dialogue, understanding, and a shared vision for a more prosperous and just world.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into A Comparative Study of Africa and Europe: Mapping the Continents’ Intertwined Histories and Futures. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!