A Comparative Look At The Maps Of Malaysia And Indonesia: Unveiling Geographic Diversity And Shared Histories
A Comparative Look at the Maps of Malaysia and Indonesia: Unveiling Geographic Diversity and Shared Histories
Related Articles: A Comparative Look at the Maps of Malaysia and Indonesia: Unveiling Geographic Diversity and Shared Histories
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to A Comparative Look at the Maps of Malaysia and Indonesia: Unveiling Geographic Diversity and Shared Histories. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
A Comparative Look at the Maps of Malaysia and Indonesia: Unveiling Geographic Diversity and Shared Histories
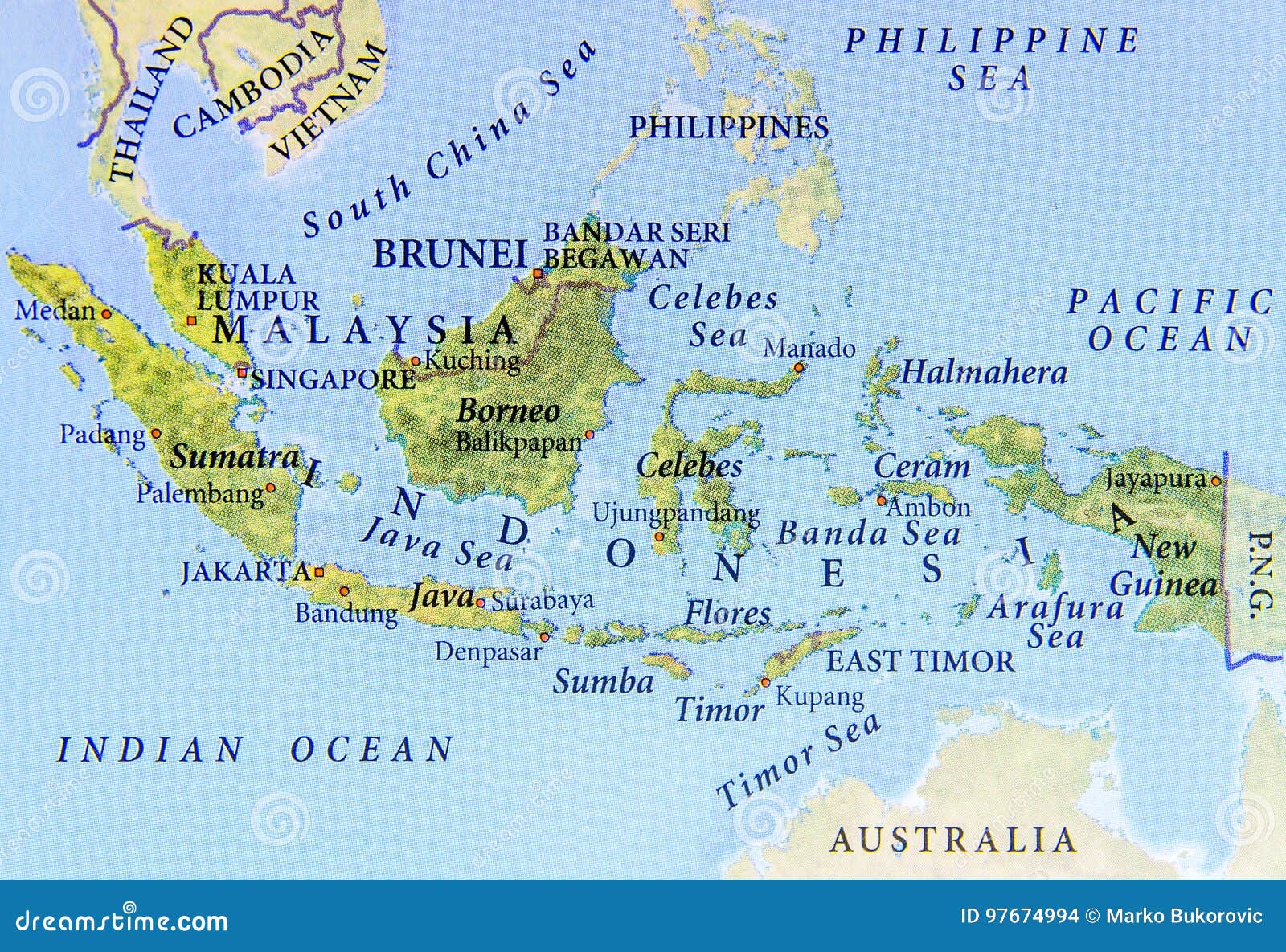
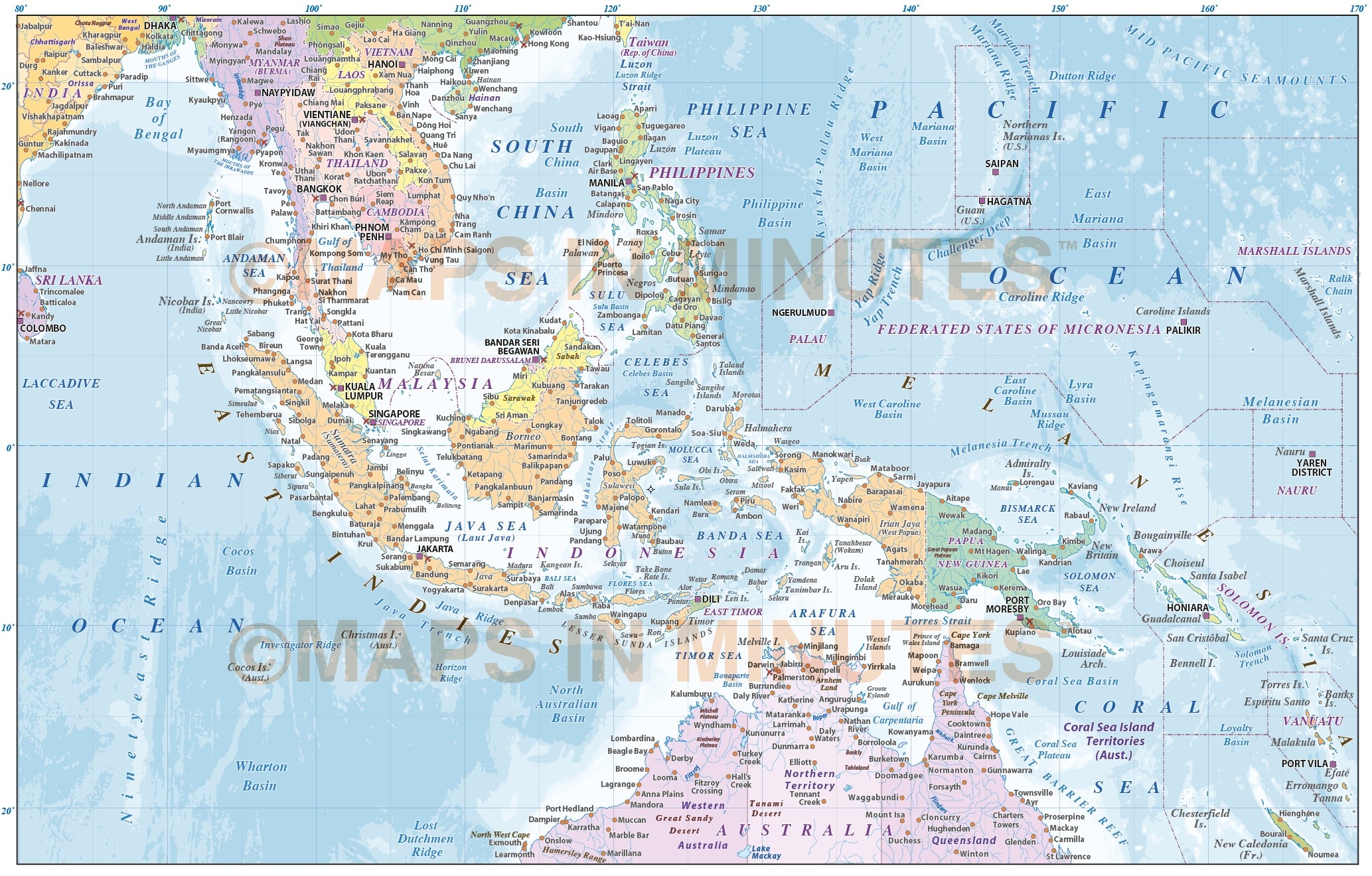
The Southeast Asian archipelago, a tapestry woven from countless islands, harbors two nations of remarkable geographic and cultural richness: Malaysia and Indonesia. While geographically distinct, their maps reveal intricate connections, shaped by shared historical experiences, environmental influences, and cultural exchanges. This exploration delves into the geographical nuances of each country, highlighting their unique features while revealing the intricate web of shared characteristics that bind them.
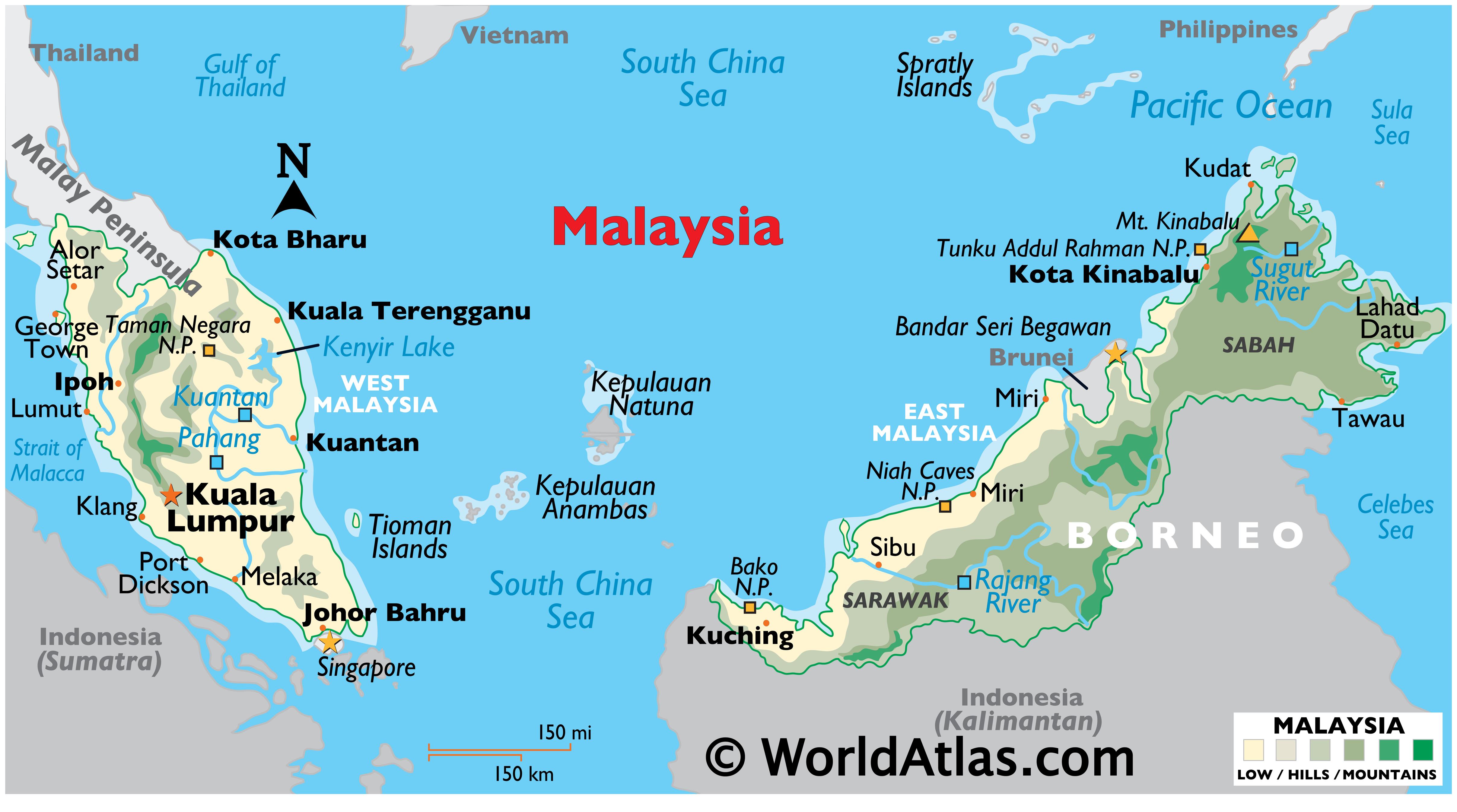
I. Malaysia: A Peninsula and Islands Intertwined
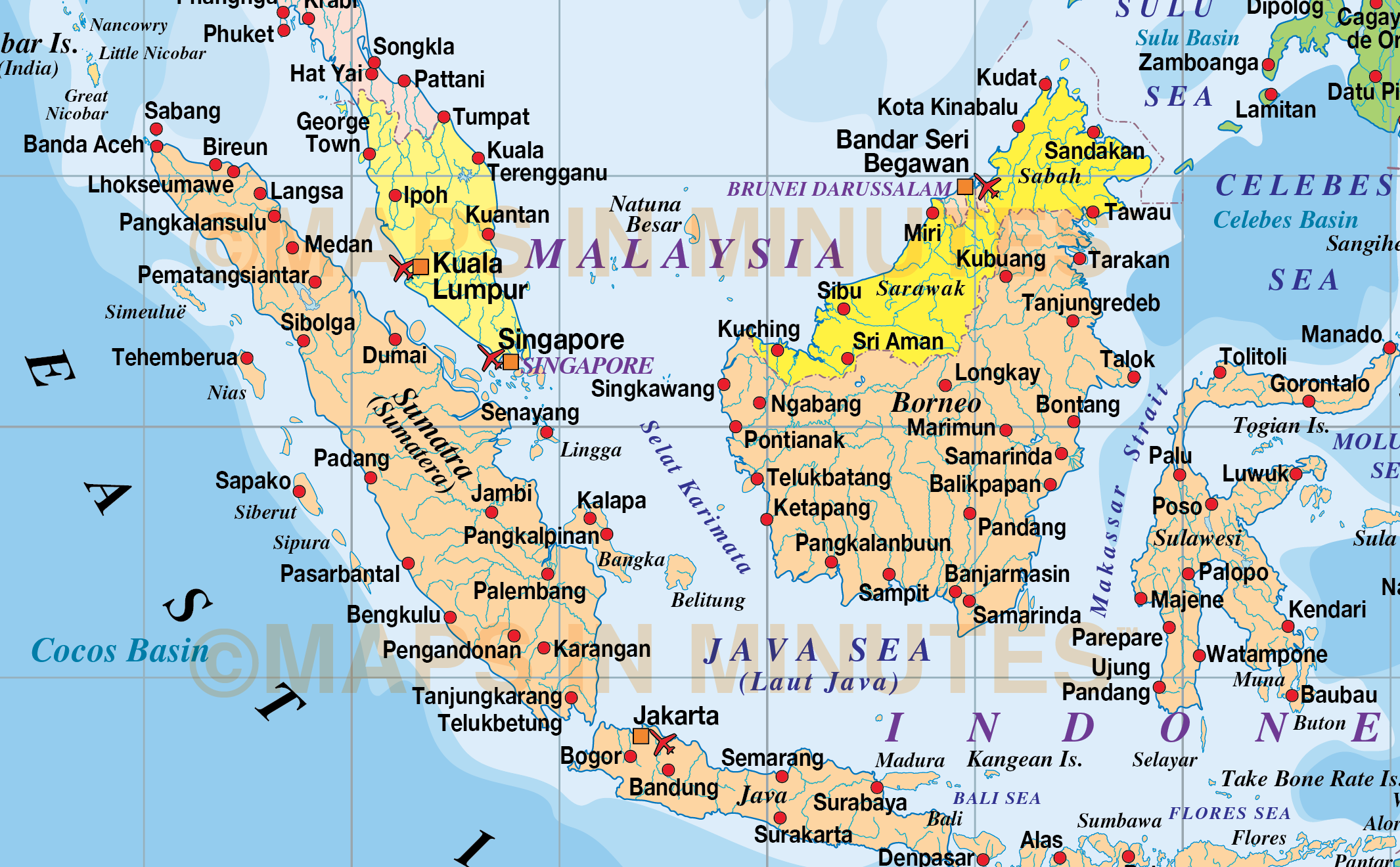
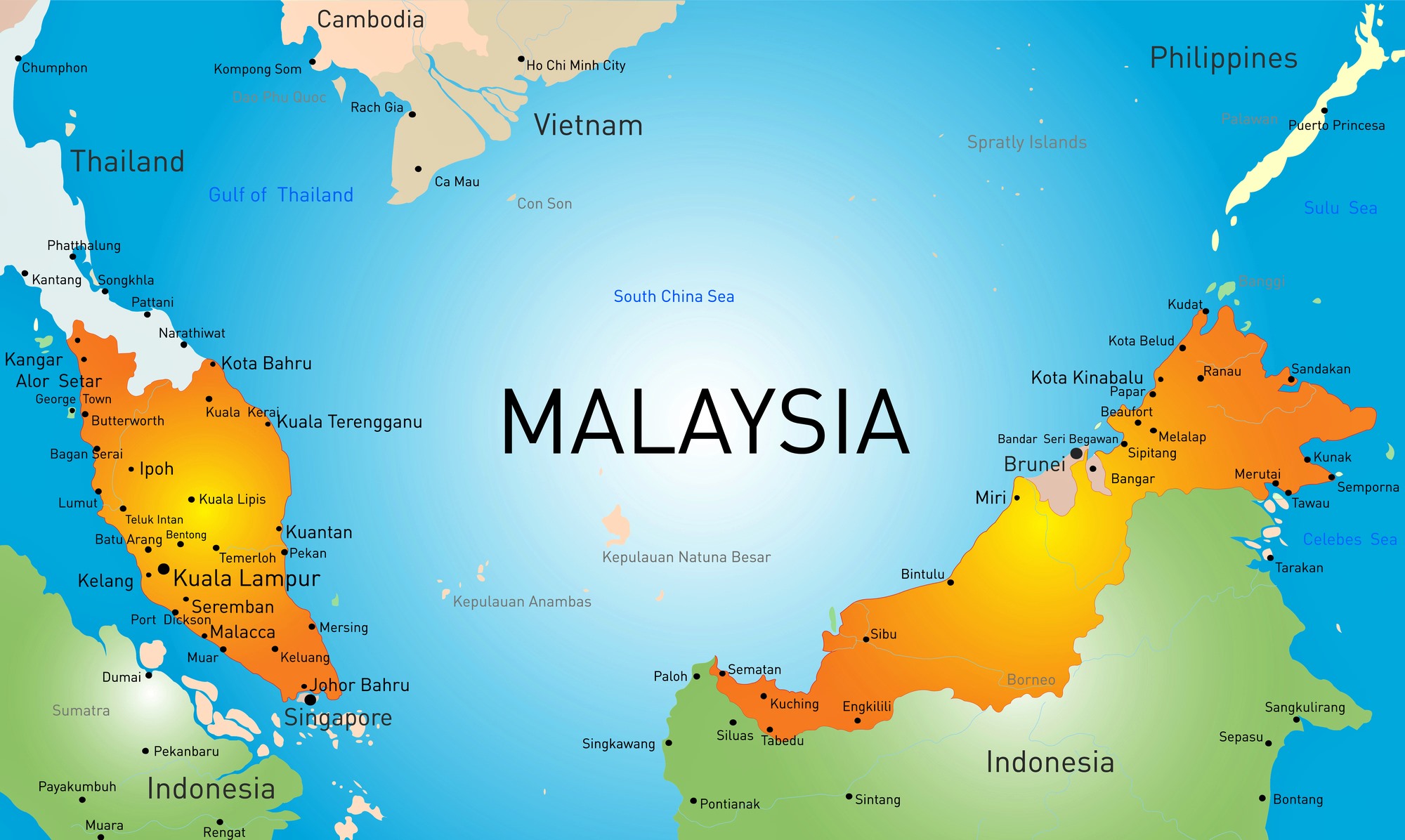
Malaysia’s map is a testament to its dualistic nature, encompassing both a peninsular region and a series of islands in the South China Sea. The peninsular portion, known as Peninsular Malaysia, is a long, narrow strip of land bordered by Thailand to the north and Singapore to the south. This region is characterized by a diverse landscape, featuring coastal plains, rolling hills, and the rugged Titiwangsa Mountains, which form the backbone of the peninsula.
The eastern portion of Malaysia, known as East Malaysia, comprises two large islands, Sarawak and Sabah, located on the island of Borneo. These islands boast a rich biodiversity, showcasing lush rainforests, towering peaks, and extensive coastal areas.
A. Peninsular Malaysia: A Tapestry of Diversity
Peninsular Malaysia’s map reveals a landscape sculpted by its location at the crossroads of major trade routes. The coastal plains, particularly in the west, have long been centers of commerce and urban development, with major cities like Kuala Lumpur, Malacca, and Penang thriving along the coast. The central highlands, dominated by the Titiwangsa Mountains, provide a stark contrast, featuring lush rainforests and indigenous communities who have lived in harmony with the environment for centuries.
B. East Malaysia: A Realm of Untamed Beauty
The map of East Malaysia paints a picture of untamed wilderness. Sarawak and Sabah, on the island of Borneo, are home to some of the most biodiverse rainforests in the world, teeming with rare flora and fauna. The islands also boast breathtaking mountain ranges, including Mount Kinabalu, the highest peak in Southeast Asia, and a vast coastline dotted with pristine beaches and coral reefs.
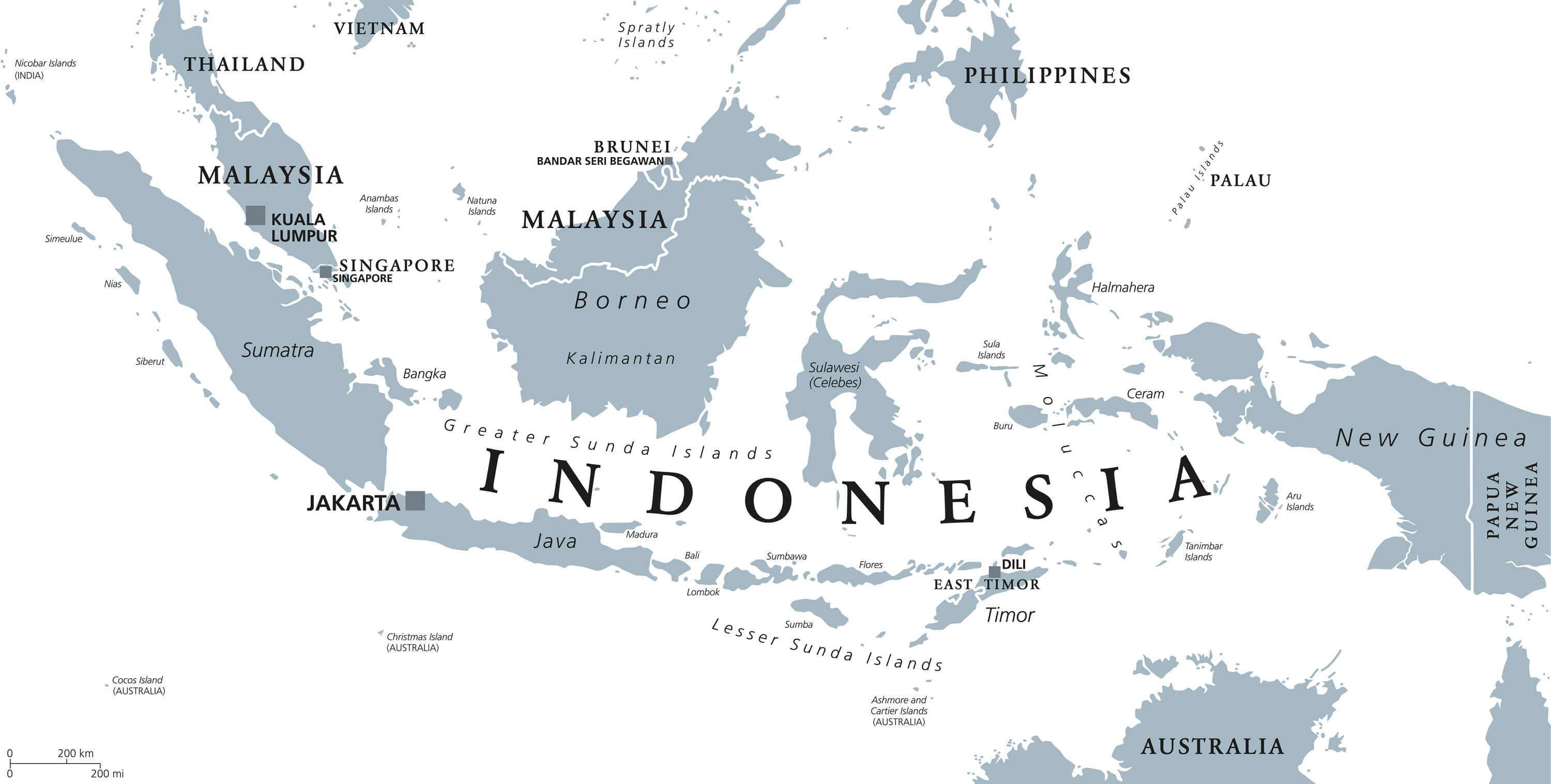
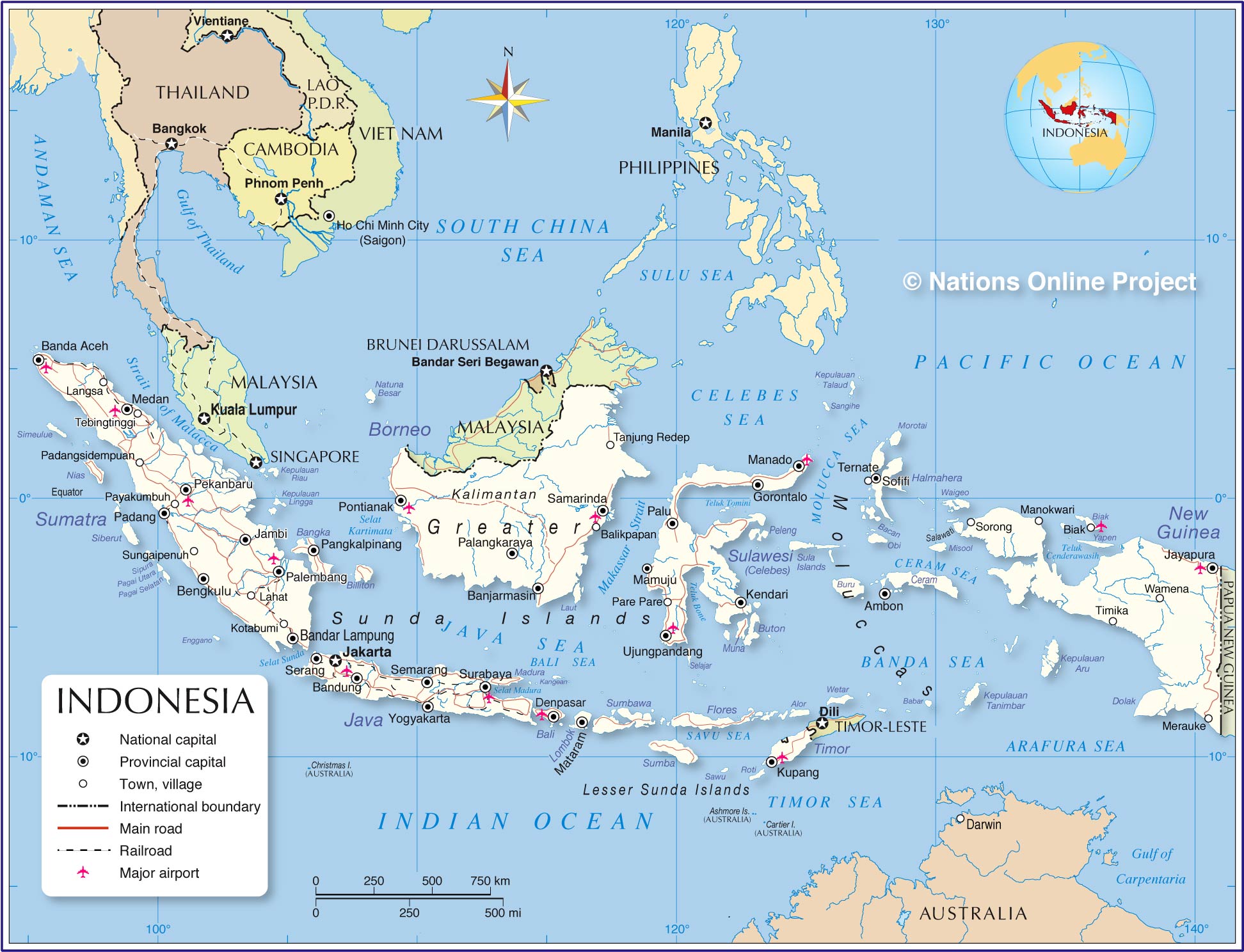
II. Indonesia: A Mosaic of Islands
Indonesia’s map is a masterpiece of geographical complexity, boasting over 17,000 islands, only around 6,000 of which are inhabited. This vast archipelago stretches across the equator, encompassing a diverse range of landscapes, from volcanic mountains to lush rainforests, from vast plains to idyllic beaches.
A. The Greater Sunda Islands: The Heart of Indonesia
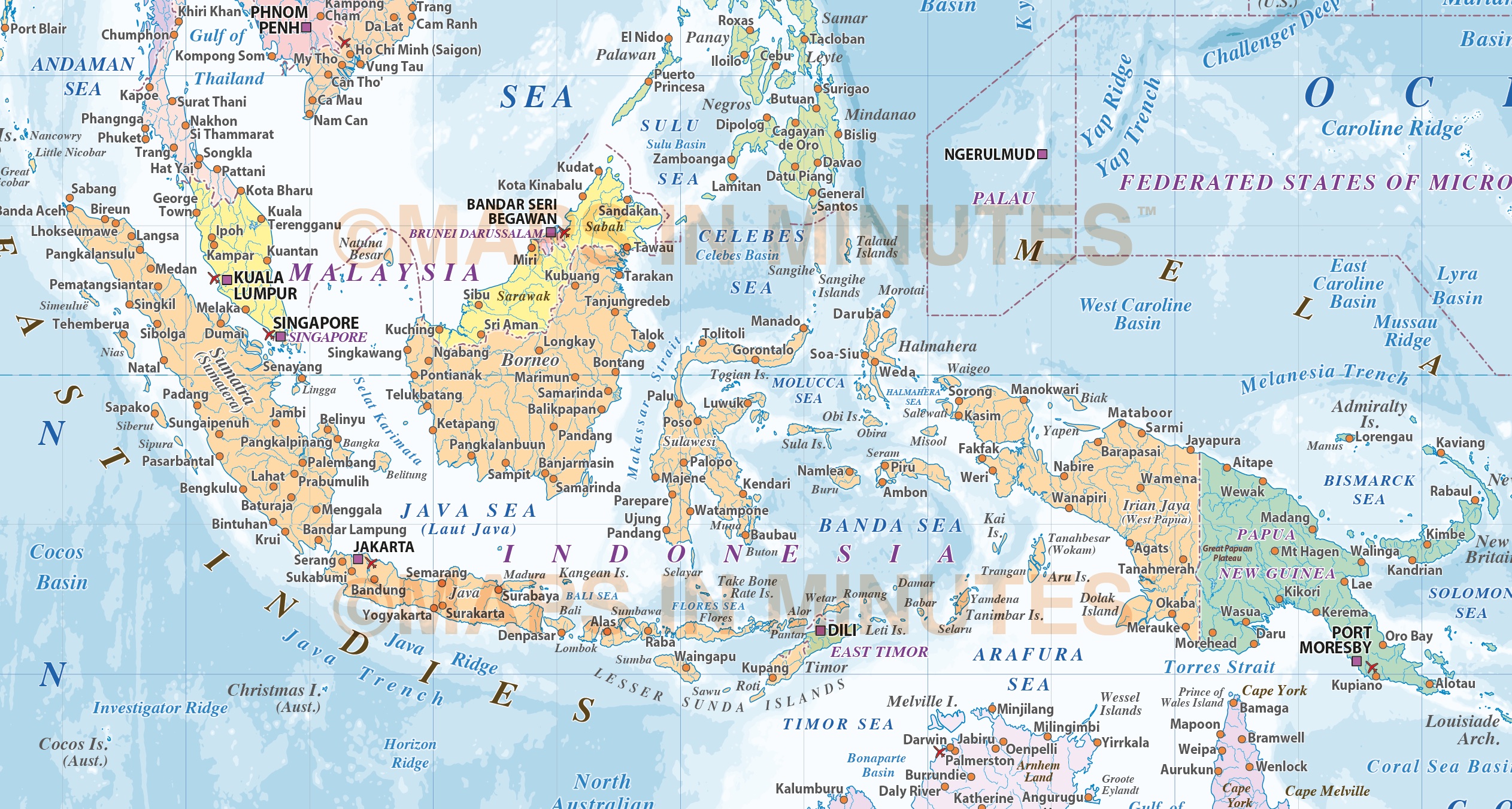
The map of Indonesia’s Greater Sunda Islands, including Sumatra, Java, Borneo (shared with Malaysia), and Sulawesi, reveals the core of the nation’s cultural and economic heartland. Java, the most populous island, is home to Jakarta, the capital city, and is a center of agriculture and industry. Sumatra, known for its rich biodiversity and oil reserves, is also home to the ancient city of Medan. Borneo, shared with Malaysia and Brunei, is a vast island dominated by rainforests and indigenous communities. Sulawesi, shaped like a human hand, is a land of rugged mountains and diverse cultures.
B. The Lesser Sunda Islands: A String of Jewels
The Lesser Sunda Islands, stretching from Bali in the west to Timor in the east, are a chain of volcanic islands renowned for their natural beauty and cultural heritage. Bali, known as the "Land of the Gods," is a popular tourist destination, famed for its temples, rice paddies, and vibrant arts scene. Lombok, located east of Bali, is known for its pristine beaches, volcanic landscapes, and traditional Sasak culture.
III. Shared Histories and Cultural Exchanges
The maps of Malaysia and Indonesia, despite their geographical differences, reveal a shared history and cultural tapestry woven from centuries of interaction. Both nations were once part of the ancient maritime trading network, known as the "Spice Route," which connected Southeast Asia with India, China, and the Middle East. This historical connection has left a lasting legacy on the cultural landscapes of both countries, reflected in their languages, religions, and culinary traditions.
A. The Influence of Trade and Migration
The maps of both countries show how trade routes, particularly those traversing the Strait of Malacca, facilitated the exchange of goods, ideas, and people. This led to the blending of cultures, with Malay, Chinese, Indian, and Arab influences shaping the identity of both nations. The presence of Chinese communities, particularly in major cities like Kuala Lumpur and Jakarta, is a testament to the long-standing trade ties between Southeast Asia and China.
B. A Shared Religious Heritage
The maps of Malaysia and Indonesia reveal a predominantly Muslim landscape, with Islam being the dominant religion in both countries. The spread of Islam through trade and missionary efforts in the 14th and 15th centuries left a profound impact on the cultural and social fabric of both nations. The presence of mosques, Islamic schools, and religious festivals are a testament to the enduring legacy of Islam in the region.
IV. Navigating the Maps: Importance and Benefits
Understanding the maps of Malaysia and Indonesia offers numerous benefits, enriching our understanding of the region’s complex history, diverse cultures, and unique environment.
A. Historical Perspective: The maps provide a visual representation of the historical forces that shaped the region, from the rise and fall of empires to the impact of colonialism. They reveal the interconnectedness of Southeast Asian nations, highlighting the shared experiences of trade, migration, and cultural exchange.
B. Cultural Appreciation: The maps offer a window into the diverse cultures of Malaysia and Indonesia, showcasing the unique traditions, languages, and arts of different communities. They demonstrate the rich tapestry of cultural influences that have shaped the region, from ancient indigenous practices to the impact of Islam and other religions.
C. Environmental Understanding: The maps highlight the remarkable biodiversity of both countries, showcasing the diverse ecosystems, from lush rainforests to coral reefs. They serve as a reminder of the importance of protecting these fragile environments for future generations.
D. Economic Insights: The maps reveal the key economic centers of both countries, highlighting the importance of trade, agriculture, and tourism. They provide insights into the economic potential of the region, drawing attention to its strategic location and abundant resources.
V. FAQs
1. What is the largest island in Malaysia?
The largest island in Malaysia is Borneo, which it shares with Indonesia and Brunei.
2. What is the capital city of Indonesia?
The capital city of Indonesia is Jakarta, located on the island of Java.
3. What is the most populated island in Indonesia?
The most populated island in Indonesia is Java, home to the capital city of Jakarta and a large portion of the country’s population.
4. What is the highest mountain in Malaysia?
The highest mountain in Malaysia is Mount Kinabalu, located in Sabah, East Malaysia.
5. What is the main religion in Malaysia and Indonesia?
The main religion in both Malaysia and Indonesia is Islam.
VI. Tips for Exploring the Maps
1. Focus on Key Geographic Features: Pay attention to the major islands, mountain ranges, rivers, and coastal areas. These features provide a framework for understanding the physical landscape and its impact on human settlements and cultures.
2. Explore Historical Maps: Examine historical maps to trace the evolution of boundaries, trade routes, and cultural influences over time. This provides a deeper understanding of the region’s historical context.
3. Utilize Online Resources: Access online maps and interactive atlases to explore the region in detail. These resources often provide additional information on demographics, climate, and economic activities.
4. Combine Maps with Other Information: Integrate maps with other sources of information, such as historical accounts, travelogues, and cultural studies. This creates a more comprehensive understanding of the region’s complexities.
5. Engage in Discussion: Share your observations and insights with others to foster a deeper appreciation of the maps’ significance and the region’s rich history and culture.
VII. Conclusion
The maps of Malaysia and Indonesia serve as powerful tools for understanding the geographical, historical, and cultural nuances of these Southeast Asian nations. They reveal a region brimming with natural beauty, cultural diversity, and a shared history that continues to shape the present and future. By exploring these maps, we gain a deeper appreciation for the intricate connections that bind these nations, fostering a sense of respect and understanding for the people and landscapes of Southeast Asia.

Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into A Comparative Look at the Maps of Malaysia and Indonesia: Unveiling Geographic Diversity and Shared Histories. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!