A Comparative Analysis Of Indonesia And Singapore: Exploring Geographic And Economic Landscapes
A Comparative Analysis of Indonesia and Singapore: Exploring Geographic and Economic Landscapes
Related Articles: A Comparative Analysis of Indonesia and Singapore: Exploring Geographic and Economic Landscapes
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to A Comparative Analysis of Indonesia and Singapore: Exploring Geographic and Economic Landscapes. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
A Comparative Analysis of Indonesia and Singapore: Exploring Geographic and Economic Landscapes

Indonesia and Singapore, despite their geographical proximity, stand in stark contrast in terms of their size, resources, and economic development. Understanding the distinct geographical and economic landscapes of these two Southeast Asian nations offers valuable insights into their unique challenges and opportunities. This analysis delves into their contrasting geographies, economic profiles, and the implications of these differences on their respective development trajectories.
I. Geographical Contrasts: A Tale of Two Islands
Indonesia: The Archipelago Giant
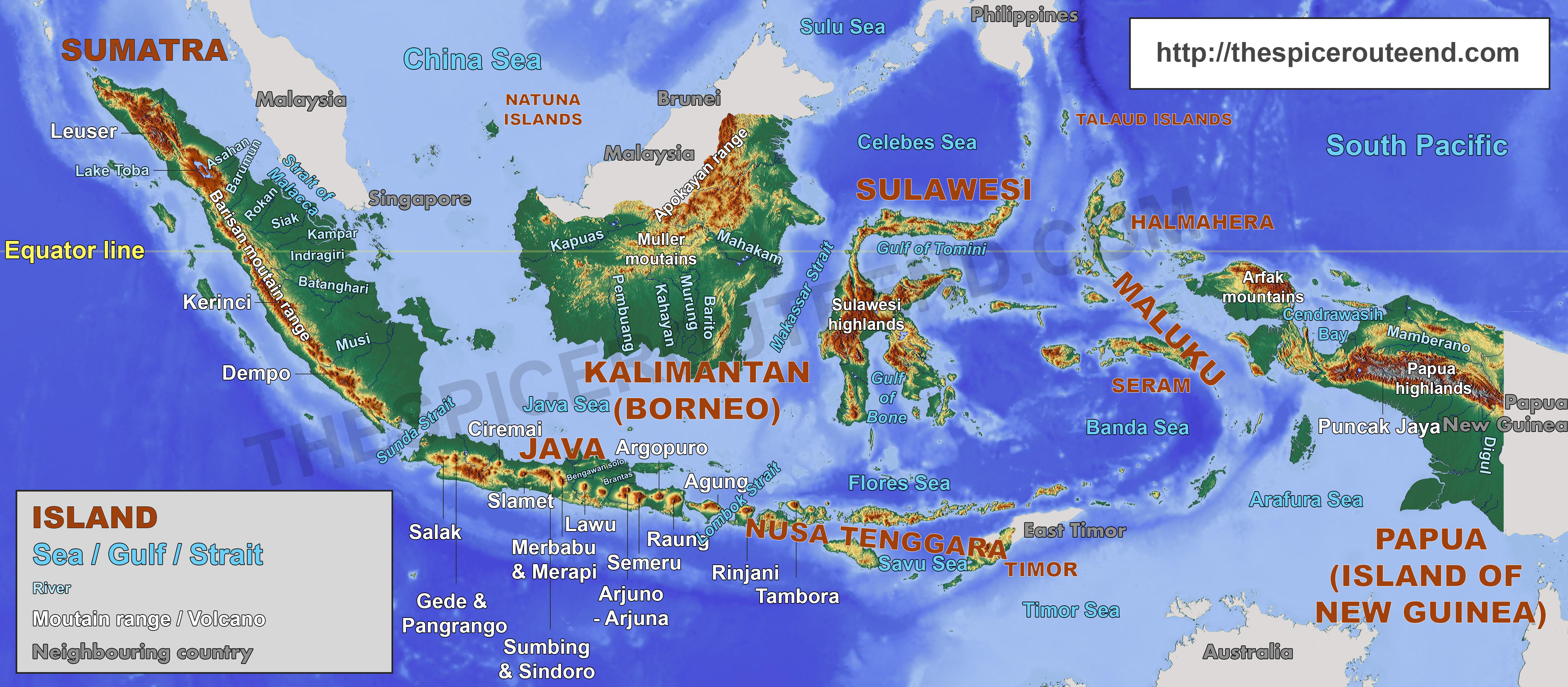
Indonesia, the world’s largest archipelago nation, sprawls across a vast expanse of 1,904,569 square kilometers, encompassing over 17,000 islands. This vast geography presents both advantages and challenges. Its diverse landscape, encompassing volcanic mountains, fertile plains, and dense rainforests, offers a wealth of natural resources, including oil, gas, minerals, and timber. However, this geographic complexity also poses logistical hurdles, making transportation and infrastructure development a significant challenge.
Singapore: The City-State
In contrast, Singapore, a city-state with a land area of just 719.1 square kilometers, is a compact and densely populated nation. Its small size necessitates a focus on efficient land use, leading to a highly urbanized environment with limited natural resources. This geographic constraint has fostered a unique approach to development, emphasizing trade, finance, and technological innovation.
II. Economic Divergence: From Resource-Rich to Innovation-Driven
Indonesia: Resource-Based Economy with Growing Manufacturing
Indonesia’s vast natural resources have historically formed the backbone of its economy. Oil and gas extraction, mining, and agriculture remain significant contributors to its GDP. In recent years, the country has witnessed a surge in manufacturing, particularly in the automotive, electronics, and textile sectors. However, Indonesia faces challenges in diversifying its economy beyond resource extraction and improving its manufacturing competitiveness.
Singapore: A Global Financial Hub and Innovation Leader
Singapore’s small size and limited natural resources have propelled it towards a highly developed, knowledge-based economy. It has strategically positioned itself as a global financial center, attracting international investment and fostering a thriving financial services sector. The country has also invested heavily in research and development, emerging as a leader in technology and innovation.
III. Geopolitical Implications: Regional Powerhouses with Distinct Approaches
Indonesia: A Regional Leader with Growing International Influence
Indonesia’s vast size and population make it a regional heavyweight with growing international influence. Its commitment to non-alignment and its role in regional organizations like ASEAN have solidified its position as a key player in Southeast Asian affairs. The country’s economic growth and its efforts to promote regional stability have further enhanced its global standing.
Singapore: A Strategic Partner with Global Reach
Singapore, while smaller in size, leverages its strategic location and its highly developed economy to play a significant role in global affairs. It is a key partner for major powers like the United States and China, serving as a vital hub for trade, finance, and investment. Singapore’s proactive foreign policy and its commitment to free trade have earned it global respect and influence.
IV. The Future Landscape: Challenges and Opportunities
Indonesia: Harnessing Potential for Sustainable Growth
Indonesia faces the challenge of sustainably managing its vast natural resources, promoting inclusive economic growth, and improving infrastructure to support its development ambitions. The country also needs to address issues related to poverty, inequality, and environmental degradation. However, its large domestic market, its growing middle class, and its strategic location offer significant opportunities for future growth.
Singapore: Maintaining Competitiveness and Innovation
Singapore’s success is predicated on its ability to maintain its competitiveness and remain at the forefront of innovation. The country faces challenges in attracting and retaining talent, managing its aging population, and adapting to rapid technological advancements. However, its strong institutions, its pro-business environment, and its commitment to continuous improvement provide a solid foundation for continued success.
V. Conclusion: A Comparative Perspective
The contrasting geographies and economic profiles of Indonesia and Singapore provide a compelling case study in development strategies. Indonesia’s vast resources and its growing manufacturing sector offer immense potential, while Singapore’s focus on innovation and its position as a global financial hub have propelled it to the forefront of economic development. While both nations face distinct challenges, their unique strengths and their commitment to regional and global cooperation offer promising prospects for continued growth and prosperity.
FAQs
Q1: What are the key geographical differences between Indonesia and Singapore?
A: Indonesia is the world’s largest archipelago nation, encompassing over 17,000 islands, while Singapore is a city-state with a land area of just 719.1 square kilometers. Indonesia’s vast size presents logistical challenges, while Singapore’s small size necessitates efficient land use and a focus on urban development.
Q2: How do the economic profiles of Indonesia and Singapore differ?
A: Indonesia’s economy is largely resource-based, relying on oil and gas extraction, mining, and agriculture. Singapore, on the other hand, has a highly developed, knowledge-based economy focused on trade, finance, and technology.
Q3: What are the main geopolitical implications of the contrasting geographies and economies of Indonesia and Singapore?
A: Indonesia’s size and population make it a regional leader with growing international influence, while Singapore’s strategic location and its highly developed economy have made it a key partner for major powers.
Q4: What are the key challenges and opportunities facing Indonesia and Singapore in the future?
A: Indonesia faces challenges in sustainably managing its resources, promoting inclusive growth, and improving infrastructure. Singapore needs to maintain its competitiveness, attract talent, and adapt to rapid technological advancements. Both nations have significant opportunities for continued growth and prosperity.
Tips
- Stay informed about the latest developments in both countries. Monitor economic indicators, political changes, and key policy initiatives.
- Explore business opportunities in both markets. Understand the strengths and weaknesses of each economy to identify potential investment and trade opportunities.
- Embrace cultural diversity and foster cross-cultural understanding. Appreciate the unique cultures and traditions of Indonesia and Singapore to enhance collaboration and communication.
Conclusion
Indonesia and Singapore, despite their geographical proximity, present contrasting examples of development strategies. Indonesia’s vast resources and its emerging manufacturing sector hold immense potential for growth, while Singapore’s focus on innovation and its global financial prowess have propelled it to the forefront of economic development. Understanding the distinct geographies and economic profiles of these two nations offers valuable insights into the complexities and opportunities of Southeast Asian development. By embracing their unique strengths and fostering collaboration, Indonesia and Singapore can continue to contribute significantly to the region’s prosperity and stability.



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into A Comparative Analysis of Indonesia and Singapore: Exploring Geographic and Economic Landscapes. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!